|
Józef Bartosik
Józef Czeslaw Bartosik CB DSC (20 July 1917 – 14 January 2008) was a Polish Naval officer, born in Topola Wielka near Ostrów Wielkopolski, who served in Polish destroyers during World War II, under British naval command. Shortly after World War II, he joined the British Royal Navy and advanced to the rank of rear admiral, before his retirement in 1969. He died in England in January 2008. Wartime service in the Polish Navy In 1935, at the age of 18, he joined the Naval officer cadet school in Toruń. He graduated in 1938 and in 1939 he was the first watch officer in the cadet schooner ORP ''Iskra''. During the latter half of 1939, he led the wooden sailing ship on a voyage through the Mediterranean and into Southern Atlantic waters. On learning of the 1939 invasion of Poland by Nazi forces, ''Iskra'' returned from the Atlantic and left two crew members with the ship in Morocco. Along with the rest of ''Iskra''s crew, Bartosik boarded a French ship and departed for France, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topola Wielka
Topola Wielka is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Przygodzice, within Ostrów Wielkopolski County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, in west-central Poland. It lies approximately south-east of Ostrów Wielkopolski and southeast of the regional capital Poznań. Notable persons Flag rank Naval officer Józef Bartosik Józef Czeslaw Bartosik CB DSC (20 July 1917 – 14 January 2008) was a Polish Naval officer, born in Topola Wielka near Ostrów Wielkopolski, who served in Polish destroyers during World War II, under British naval command. Shortly after Worl ... was born in Topola Wielka, 1917. References Topola Wielka {{OstrówWielkopolski-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rear Admiral
Rear admiral is a senior naval flag officer rank, equivalent to a major general and air vice marshal and above that of a commodore and captain, but below that of a vice admiral. It is regarded as a two star "admiral" rank. It is often regarded as a two-star rank with a NATO code of OF-7. The term originated in the days of naval sailing squadrons and can trace its origins to the Royal Navy. Each naval squadron was assigned an admiral as its head, who commanded from the centre vessel and directed the squadron's activities. The admiral would in turn be assisted by a vice admiral, who commanded the lead ships that bore the brunt of a battle. In the rear of the squadron, a third admiral commanded the remaining ships and, as this section was considered to be in the least danger, the admiral in command of it was typically the most junior. This has continued into the modern age, with rear admiral the most junior admiralty of many navies. In most European navies, the equivalent rank i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spitsbergen
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norway. Constituting the westernmost bulk of the archipelago, it borders the Arctic Ocean, the Norwegian Sea, and the Greenland Sea. Spitsbergen covers an area of , making it the largest island in Norway and the 36th-largest in the world. The administrative centre is Longyearbyen. Other settlements, in addition to research outposts, are the Russian mining community of Barentsburg, the research community of Ny-Ålesund, and the mining outpost of Sveagruva. Spitsbergen was covered in of ice in 1999, which was approximately 58.5% of the island's total area. The island was first used as a whaling base in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which it was abandoned. Coal mining started at the end of the 19th century, and several permanent commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ORP Garland
HMS ''Garland'', also known by her Polish designation ORP ''Garland'', was a G-class destroyer built for the Royal Navy in the mid-1930s. During the Spanish Civil War of 1936–1939 the ship spent considerable time in Spanish waters, enforcing the arms blockade imposed by Britain and France on both sides of the conflict. Shortly after World War II began, she was badly damaged by the premature explosion of her own depth charges and required over six months of repairs. Before these were completed, ''Garland'' was loaned to the Polish Navy in May 1940. The ship was assigned to the Mediterranean Fleet afterwards and escorted convoys there before being assigned to the Western Approaches Command in September for escort duties. She escorted a convoy from Gibraltar to Malta during Operation Halberd in September 1941 and escorted Convoy PQ 16 from Iceland to Murmansk in May 1942. She was badly damaged by a near miss from a German bomber during that operation and required three months o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabteilung'' of the Imperial Navy, had been disbanded in May 1920 in accordance with the terms of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles which banned Germany from having any air force. During the interwar period, German pilots were trained secretly in violation of the treaty at Lipetsk Air Base in the Soviet Union. With the rise of the Nazi Party and the repudiation of the Versailles Treaty, the ''Luftwaffe''s existence was publicly acknowledged on 26 February 1935, just over two weeks before open defiance of the Versailles Treaty through German rearmament and conscription would be announced on 16 March. The Condor Legion, a ''Luftwaffe'' detachment sent to aid Nationalist forces in the Spanish Civil War, provided the force with a valuable testing grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ORP Błyskawica
ORP ''Błyskawica'' (Lightning) is a which served in the Polish Navy during World War II. It is the only Polish Navy ship to have been decorated with the ''Virtuti Militari'', Poland's highest military order for gallantry, and in 2012 was given the Pro Memoria Medal. ''Błyskawica'' is preserved as a museum ship in Gdynia and is the oldest preserved destroyer in the world. ''Błyskawica'' is moored next to the ''Dar Pomorza''. She was the second of two ''Grom'' (Thunderbolt)-class destroyers built for the Polish Navy by J. Samuel White, of Cowes, in 1935–37. The ''Grom'' class were two of the most heavily armed and fastest destroyers in World War II. Construction and design In 1934 the British shipbuilder J. Samuel White won a competition to design and build large destroyers for the Polish Navy, beating a proposal from fellow British shipbuilder Swan Hunter. (A design by the French shipyard Ateliers et Chantiers de la Loire had been rejected in 1933).Friedman 2009, p. 35. An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
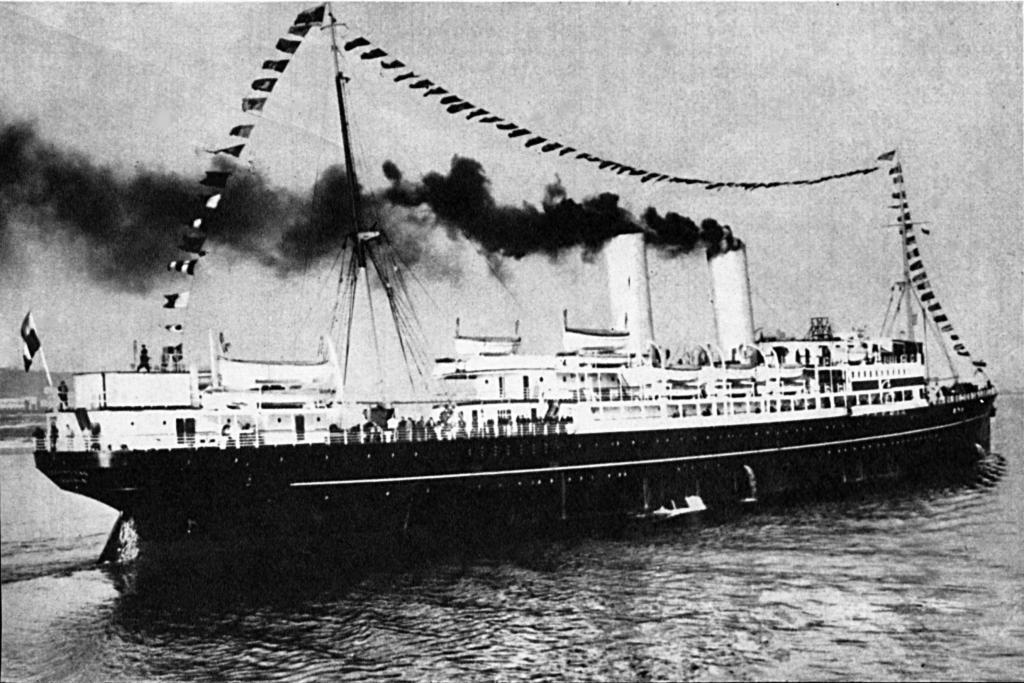
SS Kościuszko
''Kościuszko'' was a passenger steamship that was built in Scotland in 1915, sailed as a troopship in both World Wars, was an ocean liner between the wars, carried displaced persons after World War II and was scrapped in England in 1950. In her 35-year history the ship was registered in the merchant navies of the United Kingdom, Latvia and Poland. She was built as ''Czaritza'' and later bore the names ''Lituania'', ''Kościuszko'', ''Gdynia'' and ''Empire Helford''. The name ''Kościuszko'' refers to Tadeusz Kościuszko (1746 – 1817), a military leader, statesman and Polish national hero. Construction The Russian American Line ordered the ship before World War I to be an ocean liner to carry up to 1,000 passengers between New York and Arkhangelsk. Barclay, Curle & Co Ltd of Glasgow laid her keel in 1914, launched her as ''Czaritza'' on 14 February 1915 and completed her that May. Her yard number was 512. As built, ''Czaritza''s tonnages were and . She had twin four-cylind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Armed Forces In The West
The Polish Armed Forces in the West () refers to the Polish military formations formed to fight alongside the Western Allies against Nazi Germany and its allies during World War II. Polish forces were also raised within Soviet territories; these were the Polish Armed Forces in the East. The formations, loyal to the Polish government-in-exile, were first formed in France and its Middle East territories following the defeat and occupation of Poland by Germany and the Soviet Union in September 1939. After the fall of France in June 1940, the formations were recreated in the United Kingdom. Making a large contribution to the war effort, the Polish Armed Forces in the West was composed of army, air and naval forces. The Poles soon became shock troops in Allied service, most notably in the Battle of Monte Cassino during the Italian Campaign, where the Polish flag was raised on the ruined abbey on 18 May 1944, as well as in the Battle of Bologna and the Battle of Ancona (both also i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to the east, and the disputed territory of Western Sahara to the south. Mauritania lies to the south of Western Sahara. Morocco also claims the Spanish exclaves of Ceuta, Melilla and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, and several small Spanish-controlled islands off its coast. It spans an area of or , with a population of roughly 37 million. Its official and predominant religion is Islam, and the official languages are Arabic and Berber; the Moroccan dialect of Arabic and French are also widely spoken. Moroccan identity and culture is a mix of Arab, Berber, and European cultures. Its capital is Rabat, while its largest city is Casablanca. In a region inhabited since the Paleolithic Era over 300,000 years ago, the first Moroccan s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Nazi Germany. During Hitler's rise to power in 1930s Europe, it was frequently referred to as Hitlerism (german: Hitlerfaschismus). The later related term " neo-Nazism" is applied to other far-right groups with similar ideas which formed after the Second World War. Nazism is a form of fascism, with disdain for liberal democracy and the parliamentary system. It incorporates a dictatorship, fervent antisemitism, anti-communism, scientific racism, and the use of eugenics into its creed. Its extreme nationalism originated in pan-Germanism and the ethno-nationalist '' Völkisch'' movement which had been a prominent aspect of German nationalism since the late 19th century, and it was strongly influenced by the paramilitary groups that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1939 Invasion Of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week after the signing of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact between Germany and the Soviet Union, and one day after the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union had approved the pact. The Soviets invaded Poland on 17 September. The campaign ended on 6 October with Germany and the Soviet Union dividing and annexing the whole of Poland under the terms of the German–Soviet Frontier Treaty. The invasion is also known in Poland as the September campaign ( pl, kampania wrześniowa) or 1939 defensive war ( pl, wojna obronna 1939 roku, links=no) and known in Germany as the Poland campaign (german: Überfall auf Polen, Polenfeldzug). German forces invaded Poland from the north, south, and west the morning after the Gleiwitz incident. Slovak military forces adv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |