|
Julius Rudolph Theodor Vogel
Julius Rudolph Theodor Vogel (30 July 1812 – 17 December 1841) was a German botanist.Biographical sketch by Gottfried Reinhold Treviranus, translated by Miles Joseph Berkeley. In Life He was born in Berlin, and studied at the Friedrich-Wilhelms-Gymnasium. He learned botany from Johann Friedrich Ruthe. In 1837 he graduated Ph.D. from the University of Berlin with a dissertation on the genus '' Cassia''. He was a ''privatdozent'' at Berlin and then from 1839 at the University of Bonn, where he took over duties after the death of Theodor Friedrich Ludwig Nees von Esenbeck. He worked particularly on Brazilian plants, and collaborated with Matthias Jakob Schleiden. In 1840 he worked on the collections of Franz Meyen who had just died. At the end of 1840 he travelled to England to meet the African Civilization Society, then planning the Niger expedition of 1841. Taking two years' leave from Bonn, he joined the expedition in May 1841, on the steamer ''Wilberforce''. He wrote letters f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botanist
Botany, also called plant science (or plant sciences), plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek word (') meaning " pasture", "herbs" " grass", or "fodder"; is in turn derived from (), "to feed" or "to graze". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists (in the strict sense) study approximately 410,000 species of land plants of which some 391,000 species are vascular plants (including approximately 369,000 species of flowering plants), and approximately 20,000 are bryophytes. Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
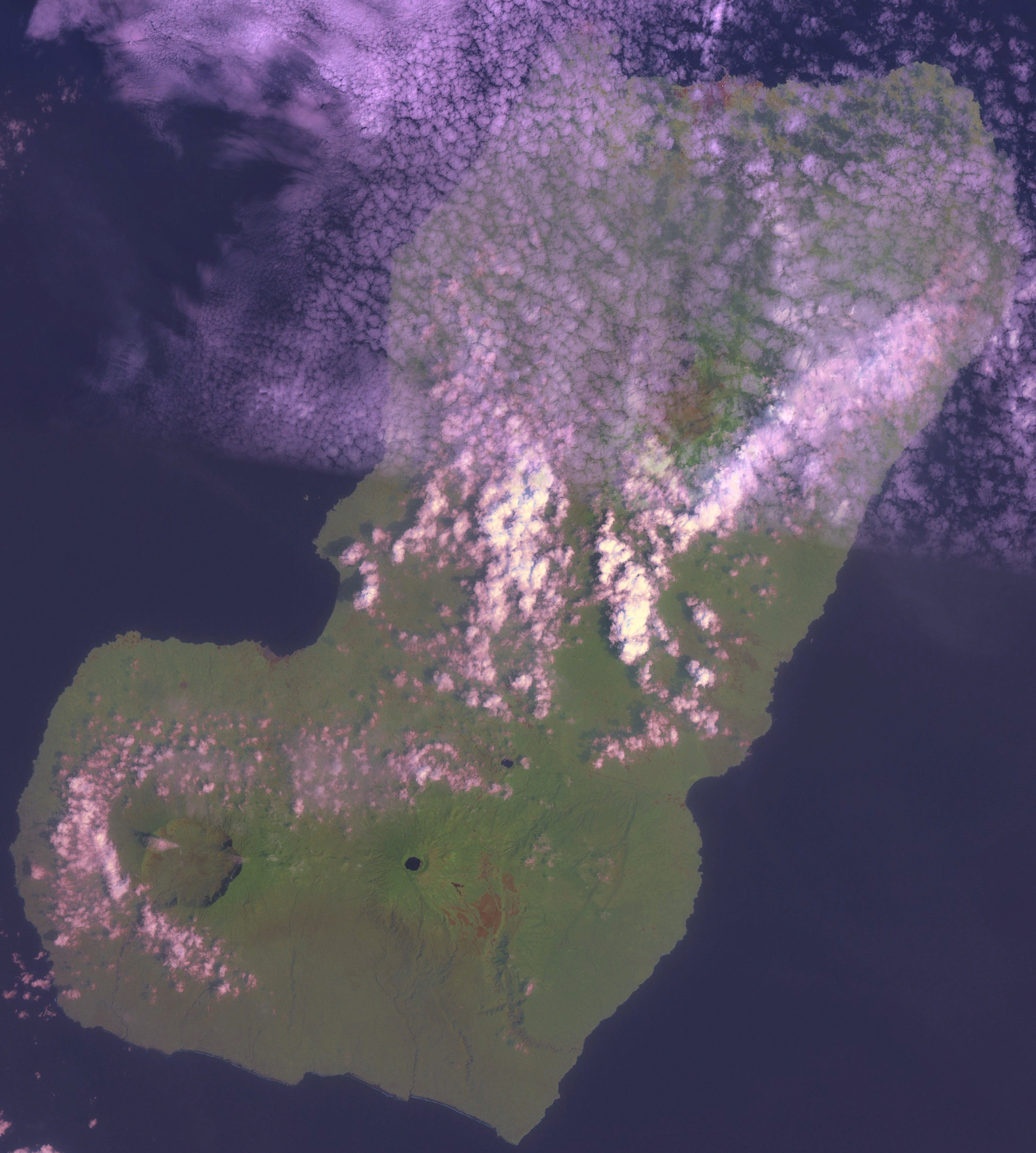
Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierra Leone has a tropical climate, with diverse environments ranging from savanna to rainforests. The country has a population of 7,092,113 as of the 2015 census. The capital and largest city is Freetown. The country is divided into five administrative regions, which are subdivided into 16 districts. Sierra Leone is a constitutional republic with a unicameral parliament and a directly elected president serving a five-year term with a maximum of two terms. The current president is Julius Maada Bio. Sierra Leone is a secular nation with the constitution providing for the separation of state and religion and freedom of conscience (which includes freedom of thoughts and religion). Muslims make up about three-quarters of the population, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1841 Deaths
Events January–March * January 20 – Charles Elliot of the United Kingdom, and Qishan of the Qing dynasty, agree to the Convention of Chuenpi. * January 26 – Britain occupies Hong Kong. Later in the year, the first census of the island records a population of about 7,500. * January 27 – The active volcano Mount Erebus in Antarctica is discovered, and named by James Clark Ross. * January 28 – Ross discovers the "Victoria Barrier", later known as the Ross Ice Shelf. On the same voyage, he discovers the Ross Sea, Victoria Land and Mount Terror. * January 30 – A fire ruins and destroys two-thirds of the villa (modern-day city) of Mayagüez, Puerto Rico. * February 4 – First known reference to Groundhog Day in North America, in the diary of a James Morris. * February 10 – The Act of Union (''British North America Act'', 1840) is proclaimed in Canada. * February 11 – The two colonies of the Canadas are merged, into the United Province of Canada. * Febru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1812 Births
Year 181 ( CLXXXI) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aurelius and Burrus (or, less frequently, year 934 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 181 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Imperator Lucius Aurelius Commodus and Lucius Antistius Burrus become Roman Consuls. * The Antonine Wall is overrun by the Picts in Britannia (approximate date). Oceania * The volcano associated with Lake Taupō in New Zealand erupts, one of the largest on Earth in the last 5,000 years. The effects of this eruption are seen as far away as Rome and China. Births * April 2 – Xian of Han, Chinese emperor (d. 234) * Zhuge Liang, Chinese chancellor and regent (d. 234) Deaths * Aelius Aristides, Greek orator and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century German Botanists
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium. The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanding beyond its British homeland for the first time during this century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Islamic gunpowder empires fell into decline and European imperialism brought much of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and almost all of Africa under colonial rule. It was also marked by the collapse of the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Author Citation (botany)
In botanical nomenclature, author citation is the way of citing the person or group of people who validly published a botanical name, i.e. who first published the name while fulfilling the formal requirements as specified by the ''International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants'' (''ICN''). In cases where a species is no longer in its original generic placement (i.e. a new combination of genus and specific epithet), both the authority for the original genus placement and that for the new combination are given (the former in parentheses). In botany, it is customary (though not obligatory) to abbreviate author names according to a recognised list of standard abbreviations. There are differences between the botanical code and the normal practice in zoology. In zoology, the publication year is given following the author names and the authorship of a new combination is normally omitted. A small number of more specialized practices also vary between the recommendation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kew Gardens
Kew Gardens is a botanical garden, botanic garden in southwest London that houses the "largest and most diverse botany, botanical and mycology, mycological collections in the world". Founded in 1840, from the exotic garden at Kew Park, its living collections include some of the 27,000 taxa curated by Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, while the herbarium, one of the largest in the world, has over preserved plant and fungal specimens. The library contains more than 750,000 volumes, and the illustrations collection contains more than 175,000 prints and drawings of plants. It is one of London's top tourist attractions and is a World Heritage Sites, World Heritage Site. Kew Gardens, together with the botanic gardens at Wakehurst Place, Wakehurst in Sussex, are managed by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, an internationally important botany, botanical research and education institution that employs over 1,100 staff and is a non-departmental public body sponsored by the Department for Envir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Mesurado
Cape Mesurado, also called Cape Montserrado, is a headland on the coast of Liberia near the capital Monrovia and the mouth of the Saint Paul River. It was named Cape Mesurado by Portuguese sailors in the 1560s. It is the promontory on which African American settlers established the city now called Monrovia on 25 April 1822. There is a lighthouse on Cape Mesurado, located in the Mamba Point neighborhood of Monrovia and in the cape's northwestern portion, that was established in 1855. It is currently inactive, although the Liberian government is seeking financial assistance to restore and reactivate the lighthouse. History Slave trading post Because Cape Mesurado was being used as a base for the illegal slave trade, in 1815 Governor William Maxwell of Sierra Leone sent an armed force there to interfere with it, seizing ships and merchandise and rescuing enslaved Africans who were working in the factories there. For their crimes, the factory owners, Robert Bostock and Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean to its south and southwest. It has a population of around 5 million and covers an area of . English is the official language, but over 20 indigenous languages are spoken, reflecting the country's ethnic and cultural diversity. The country's capital and largest city is Monrovia. Liberia began in the early 19th century as a project of the American Colonization Society (ACS), which believed black people would face better chances for freedom and prosperity in Africa than in the United States. Between 1822 and the outbreak of the American Civil War in 1861, more than 15,000 freed and free-born black people who faced social and legal oppression in the U.S., along with 3,198 Afro-Caribbeans, relocated to Liberia. Gradually developing an Americo-Liberian identity, the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Thomas Lowe
Richard Thomas Lowe (1802–1874) was an English scientist, a botanist, ichthyologist, malacologist, and a clergyman. In 1825 he graduated from Christ's College, Cambridge, and in the same year he took holy orders. In 1832 he became a clergyman in the Madeira Islands, where he was also a part-time naturalist, extensively studying the local flora and fauna. He wrote a book on the Madeiran flora. He died in 1874 when the ship he was on was wrecked off the Isles of Scilly. Taxa Lowe named and described numerous molluscan taxa, including: * ''Caseolus'', a land snail genus and eight species within it * ''Lemniscia ''Lemniscia'' is a genus of air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the family Geomitridae Geomitridae is a Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic Family (biology), family of small to medium-sized air-breathing land sna ...'', a land snail genus and two species within it See also * :Taxa named by Richard Thomas Lowe References * Notes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madeira
) , anthem = ( en, "Anthem of the Autonomous Region of Madeira") , song_type = Regional anthem , image_map=EU-Portugal_with_Madeira_circled.svg , map_alt=Location of Madeira , map_caption=Location of Madeira , subdivision_type=Sovereign state , subdivision_name=Portugal , established_title= Discovery , established_date=1418-1419 , established_title2=Settlement , established_date2=c. 1425 , established_title3=Autonomous status , established_date3=30 April 1976 , named_for = en, wood ( pt, madeira) , official_languages= Portuguese , demonym= en, Madeiran ( pt, Madeirense) , capital = Funchal , government_type= Autonomous Region , leader_title1=Representative of the Republic , leader_name1=Irineu Barreto , leader_title2= President of the Regional Government of Madeira , leader_name2= Miguel Albuquerque , leader_title3=President of the Legislative Assembly , leader_name3=José Manuel Rodrigues , legislature= Legislative Assembly , national_representation=Nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fernando Po (island)
Bioko (; historically Fernando Po; bvb, Ëtulá Ëria) is an island off the west coast of Africa and the northernmost part of Equatorial Guinea. Its population was 335,048 at the 2015 census and it covers an area of . The island is located off the Ambazonian segment of Cameroon, in the Bight of Biafra portion of the Gulf of Guinea. Its geology is volcanic; its highest peak is Pico Basile at . Malabo, on the north coast of the island, is the capital city of Equatorial Guinea. Etymology Bioko's native name is ''Ëtulá Ëria'' in the Bube language. For nearly 500 years, the island was known as ''Fernando Po'' ( pt, Fernando Pó, links=no; es, Fernando Poo, links=no), named for Portuguese navigator Fernão do Pó. Between 1973 and 1979 the island was named ''Macías Nguema Biyogo'' after the then president of Equatorial Guinea; the current name, Bioko, dates from 1979 and is in honour of politician Cristino Seriche Bioko. Geography Bioko has a total area of . It is lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |