|
Juk Language
Juk (also known as Suai, Souei, Xuay) is a Mon–Khmer language of the Bahnaric The Bahnaric languages are a group of about thirty Austroasiatic languages spoken by about 700,000 people in Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos. Paul Sidwell notes that Austroasiatic/Mon–Khmer languages are lexically more similar to Bahnaric and Katui ... branch spoken in Sekong Province, Laos. According to Sidwell (2003), it was probably a northern dialect of Jru' that had differentiated through separation by migration. The Juk language was discovered by Thai linguist Therapan L-Thongkum. Juk speakers live in the village Ban Nyôkthông (Gnôkthông), located about 12 km north of Ban Kafe. It is located halfway between the towns of Tateng and Sekong. References *Sidwell, Paul (2003). A Handbook of comparative Bahnaric, Vol. 1: West Bahnaric'. Pacific Linguistics, 551. Canberra: Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies, Australian National University. Bahnaric languages Languages of Laos [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laos
Laos (, ''Lāo'' )), officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic ( Lao: ສາທາລະນະລັດ ປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ, French: République démocratique populaire lao), is a socialist state and the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. At the heart of the Indochinese Peninsula, Laos is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and southwest. Its capital and largest city is Vientiane. Present-day Laos traces its historic and cultural identity to Lan Xang, which existed from the 14th century to the 18th century as one of the largest kingdoms in Southeast Asia. Because of its central geographical location in Southeast Asia, the kingdom became a hub for overland trade and became wealthy economically and culturally. After a period of internal conflict, Lan Xang broke into three separate kingdoms: Luang Phrabang, Vientiane and Champa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahnaric Languages
The Bahnaric languages are a group of about thirty Austroasiatic languages spoken by about 700,000 people in Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos. Paul Sidwell notes that Austroasiatic/ Mon–Khmer languages are lexically more similar to Bahnaric and Katuic languages the closer they are geographically, independently of which branch of the family they belong to, but that Bahnaric and Katuic do not have any shared innovations that would suggest that together they form a branch of the Austroasiatic family, rather forming separate branches. Internal controversy Internal diversity suggests that the family broke up about 3,000 years ago. North Bahnaric is characterized by a register contrast between breathy and modal voice, which in Sedang has tensed to become modal–creaky voice. Lamam is a clan name of the neighboring Tampuon and Kaco’. Sidwell (2009) tentatively classifies the Bahnaric languages into four branches, with Cua (Kor) classified independently as East Bahnaric. Unclassifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Bahnaric Languages
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth. Etymology The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some Romance languages (''ouest'' in French, ''oest'' in Catalan, ''ovest'' in Italian, ''oeste'' in Spanish and Portuguese). As in other languages, the word formation stems from the fact that west is the direction of the setting sun in the evening: 'west' derives from the Indo-European root ''*wes'' reduced from ''*wes-pero'' 'evening, night', cognate with Ancient Greek ἕσπερος hesperos 'evening; evening star; western' and Latin vesper 'evening; west'. Examples of the same formation in other languages include Latin occidens 'west' from occidō 'to go down, to set' and Hebrew מַעֲרָב maarav 'west' from עֶרֶב erev 'evening'. Navigation To go west using a compass for navigation (in a place where magnetic north is the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laven Language
Laven is a Mon–Khmer dialect cluster of southern Laos. Laven is the exonym given by the Laotian government, while the autonym of many of those speakers is Jru' . Varieties are: * Jru' (also spelled ''Jruq)'' *Juk Juk may refer to: * JuK, software * Juk (food), Korean rice porridge * Juk language, a Mon–Khmer language spoken in Laos * Ukkusissat Heliport, in Greenland * Wapan language Wapan (Jukun Wapan) or Kororofa, also known as Wukari after the lo ... * Su' (also spelled ''Suq)'' Laven varieties are described in detail by Therapan L-Thongkum and Paul Sidwell (2003). Further reading *Sidwell, Paul. 2019. Reconstructing language contact and social change on Boloven Plateau, Laos'. Presented at ALMSEA (The Anthropology of Language in Mainland Southeast Asia), University of Sydney, Aug. 19-20.Slides. References *Sidwell, Paul (2003). A Handbook of comparative Bahnaric, Vol. 1: West Bahnaric'. Pacific Linguistics, 551. Canberra: Research School of Pacific and Asian S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lao Script
Lao script or Akson Lao ( lo, ອັກສອນລາວ, links=no ) is the primary script used to write the Lao language and other minority languages in Laos. Its earlier form, the Tai Noi script, was also used to write the Isan language, but was replaced by the Thai script. It has 27 consonants ( ), 7 consonantal ligatures ( ), 33 vowels (/ ), and 4 tone marks ( ). The Lao alphabet was adapted from the Khmer script, which itself was derived from the Pallava script, a variant of the Grantha script descended from the Brāhmī script, which was used in southern India and South East Asia during the 5th and 6th centuries AD. Akson Lao is a sister system to the Thai script, with which it shares many similarities and roots. However, Lao has fewer characters and is formed in a more curvilinear fashion than Thai. Lao is written from left to right. Vowels can be written above, below, in front of, or behind consonants, with some vowel combinations written before, over, and after. Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
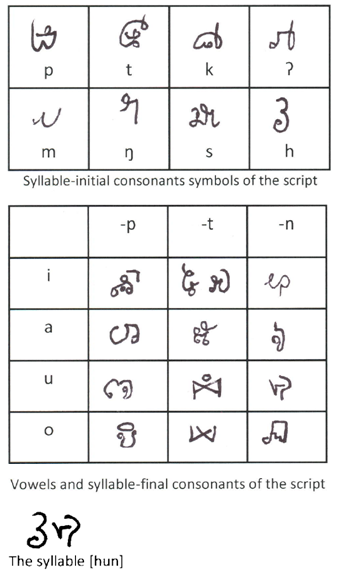
Khom Script (Ong Kommadam)
The Khom script is a writing system used in Laos. The term "Khom" is also used to refer to the Ancient Khmer lettering used in Thailand's Buddhist temples to inscribe sacred Buddhist mantras and prayers, but that is an entirely different script. History The script was invented by Ong Kommadam, a leader in the rebellion against the French colonizers. He began using the script as early as 1924, but its use did not continue after his death in 1936. Ong Kommadam claimed supernatural titles, including “King of the Khom”, “God of the Khom”, “Sky God of the Khom” (Sidwell 2008:17). The script was linked to his divine claims, messages written in this script carried mystical power as well as meaning. The script was invented for conveying secret messages that could not be deciphered by the French or Siamese forces that had divided Laos by Ong Kommandam, who had taken over as leader after the death of Ong Kèo during the Holy Man's Rebellion. As Ong Kommandam and many of his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mon–Khmer Languages
The Austroasiatic languages , , are a large language family in Mainland Southeast Asia and South Asia. These languages are scattered throughout parts of Thailand, Laos, India, Myanmar, Malaysia, Bangladesh, Nepal, and southern China and are the majority languages of Vietnam and Cambodia. There are around 117 million speakers of Austroasiatic languages. Of these languages, only Vietnamese, Khmer, and Mon have a long-established recorded history. Only two have official status as modern national languages: Vietnamese in Vietnam and Khmer in Cambodia. The Mon language is a recognized indigenous language in Myanmar and Thailand. In Myanmar, the Wa language is the de facto official language of Wa State. Santali is one of the 22 scheduled languages of India. The rest of the languages are spoken by minority groups and have no official status. '' Ethnologue'' identifies 168 Austroasiatic languages. These form thirteen established families (plus perhaps Shompen, which is poorly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |