|
Khom Script (Ong Kommadam)
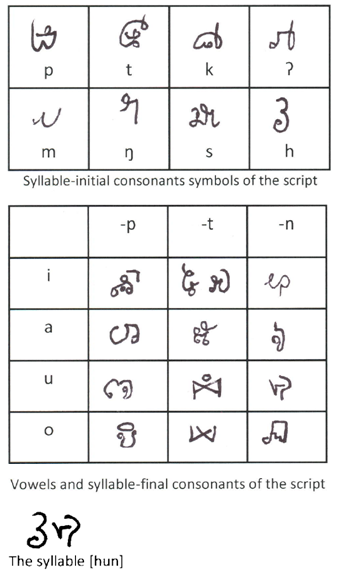
The Khom script is a writing system formerly used in Laos. The term "Khom" is also used to refer to the Ancient Khmer lettering used in Thailand's Buddhist temples to inscribe sacred Buddhist mantras and prayers, but that is an entirely different script. History The script was invented by Ong Kommadam, a leader in the rebellion against the French colonizers. He began using the script as early as 1924, but its use did not continue after his death in 1936. Ong Kommadam claimed supernatural titles, including “King of the Khom”, “God of the Khom”, “Sky God of the Khom” (Sidwell 2008:17). The script was linked to his divine claims, messages written in this script carried mystical power as well as meaning. The script was invented by Ong Kommandam for conveying secret messages that could not be deciphered by the French or Siamese forces that had divided Laos. He had taken over as leader after the death of Ong Kèo during the Holy Man's Rebellion. As Ong Kommandam and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khom Script , a script developed in Laos by the rebel leader Ong Kommadam in the 1920s
{{disambiguation ...
Khom script may refer to either of the following writing systems derived from the Khmer script: * Khom Thai script, a script based on Khmer script and historically used in Thailand *Khom script (Ong Kommadam) The Khom script is a writing system formerly used in Laos. The term "Khom" is also used to refer to the Ancient Khmer lettering used in Thailand's Buddhist temples to inscribe sacred Buddhist mantras and prayers, but that is an entirely different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lao Theung
The Lao Theung or Lao Thoeng (Lao: ລາວເທິງ ) is one of the traditional divisions of ethnic groups living in Laos (the others being the Lao Loum and the Lao Soung). It literally indicates the "midland Lao", and comprises a variety of different ethnic groups of mostly Austro-Asiatic origin. In 1993, the Lao Theung formed 24% of the country's population. History Lao Theung are largely of Mon-Khmer stock, and are believed to be the autochthonous population of mainland Southeast Asia, having migrated south in pre-historical time.Martin Stuart-Fox: ''Historical Dictionary of Laos.'' 3. Auflage, Scarecrow Press, Lanham (MD)/Plymouth 2008, S. 191, Eintrag ''Lao Theung''.Jan Ovesen: ''All Lao? Minorities in the Lao People’s Democratic Republic.'' In: Christopher R. Duncan: ''Civilizing the Margins. Southeast Asian Government Policies for the Development of Minorities.'' NUS Press, Singapur 2008, S. 216. Their legendary origin is related in the "Pumpkin Story" in James ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Writing Systems Introduced In 1924
Writing is the act of creating a persistent representation of language. A writing system includes a particular set of symbols called a ''script'', as well as the rules by which they encode a particular spoken language. Every written language arises from a corresponding spoken language; while the use of language is universal across human societies, most spoken languages are not written. Writing is a cognitive and social activity involving neuropsychological and physical processes. The outcome of this activity, also called ''writing'' (or a ''text'') is a series of physically inscribed, mechanically transferred, or digitally represented symbols. Reading is the corresponding process of interpreting a written text, with the interpreter referred to as a ''reader''. In general, writing systems do not constitute languages in and of themselves, but rather a means of encoding language such that it can be read by others across time and space. While not all languages use a writing s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obsolete Writing Systems
Obsolescence is the process of becoming antiquated, out of date, old-fashioned, no longer in general use, or no longer useful, or the condition of being in such a state. When used in a biological sense, it means imperfect or rudimentary when compared with the corresponding part of other organisms. The international standard IEC 62402:2019 Obsolescence Management defines obsolescence as the "transition from available to unavailable from the manufacturer in accordance with the original specification". Obsolescence frequently occurs because a replacement has become available that has, in sum, more advantages compared to the disadvantages incurred by maintaining or repairing the original. Obsolete also refers to something that is already disused or discarded, or antiquated. Typically, obsolescence is preceded by a gradual decline in popularity. Consequences Driven by rapid technological changes, new components are developed and launched on the market with increasing speed. The resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Journal Of The Sociology Of Language
The ''International Journal of the Sociology of Language'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal covering the field of sociology of language. It was established in 1974 by the eminent sociologist of language Joshua Fishman, who has served many years as editor-in-chief,. Today, the editor is Ofelia Garcia Otheguy. Each issue focuses on a single topic within the scope of the journal's field, for example "Sociolinguistic Issues in Azerbaijan", "The Official Language Minorities in Canada" and "Jewish Language Contact". Each issue also publishes a book review and many issues also include a study relating to the sociology of endangered languages or small language communities. The journal is published by Walter de Gruyter. The European Reference Index for the Humanities categorizes it in the "INT2" sub-category ("international publications with significant visibility and influence in the various research domains in different countries"). The journal is abstracted and indexed by International ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Sidwell
Paul James Sidwell is an Australian linguist based in Canberra, Australia, who has held research and lecturing positions at the Australian National University. Sidwell, who is also an expert and consultant in forensic linguistics, is most notable for his work on the historical linguistics of the Austroasiatic language family, and has published reconstructions of the Austroasiatic, Bahnaric, Katuic, Palaungic, Khasic, and Nicobaric proto-languages. Sidwell is currently the president of the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society (SEALS) and also regularly organises the International Conference on Austroasiatic Linguistics (ICAAL). Career In 2001, Sidwell was appointed as a collaborating scientist at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, Leipzig. From 2001 to 2004, he was an Australian Research Council Postdoctoral Research Fellow at the Australian National University, remaining there from 2005 to 2007 as a visiting research fellow, funded by the Max Planck ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laven Language
Laven is a Mon–Khmer dialect cluster of southern Laos. Laven is the exonym given by the Laotian government, while the autonym of many of those speakers is Jru' . Varieties are: * Jru' (also spelled ''Jruq)'' *Juk Juk or JUK may refer to: * JuK, software * Juk (food), Korean rice porridge * Juk language, a Mon–Khmer language spoken in Laos * Ukkusissat Heliport (IATA: JUK), in Greenland * Wapan language (ISO 639-3: juk), a Jukunoid language of Nigeria {{ ... * Su' (also spelled ''Suq)'' Laven varieties are described in detail by Therapan L-Thongkum and Paul Sidwell (2003). Further reading *Sidwell, Paul. 2019. Reconstructing language contact and social change on Boloven Plateau, Laos'. Presented at ALMSEA (The Anthropology of Language in Mainland Southeast Asia), University of Sydney, Aug. 19-20.Slides. References *Sidwell, Paul (2003). A Handbook of comparative Bahnaric, Vol. 1: West Bahnaric'. Pacific Linguistics, 551. Canberra: Research School of Pacific and Asian S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bopomofo
Bopomofo, also called Zhuyin Fuhao ( ; ), or simply Zhuyin, is a Chinese transliteration, transliteration system for Standard Chinese and other Sinitic languages. It is the principal method of teaching Chinese Mandarin pronunciation in Taiwan. It consists of 37 characters and five tone (linguistics), tone marks, which together can transcribe all possible sounds in Mandarin Chinese. Bopomofo was first introduced in China during the 1910s by the Beiyang government, where it was used alongside Wade–Giles, a romanization system which used a modified Latin alphabet. Today, Bopomofo is more common in Taiwan than on the mainland, and is used as the primary Chinese input method, electronic input method for Taiwanese Mandarin, as well as in dictionaries and other non-official documents. Terminology ''Bopomofo'' is the name used for the system by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and Unicode. Analogous to how the word ''alphabet'' is derived from the names of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syllabary
In the Linguistics, linguistic study of Written language, written languages, a syllabary is a set of grapheme, written symbols that represent the syllables or (more frequently) mora (linguistics), morae which make up words. A symbol in a syllabary, called a syllabogram, typically represents an (optional) consonant sound (simple onset (linguistics), onset) followed by a vowel sound (nucleus (syllable), nucleus)—that is, a CV (consonant+vowel) or V syllable—but other phonogram (linguistics), phonographic mappings, such as CVC, CV- tone, and C (normally nasals at the end of syllables), are also found in syllabaries. Types A writing system using a syllabary is ''complete'' when it covers all syllables in the corresponding spoken language without requiring complex orthography, orthographic / graphemic rules, like implicit codas ( ⇒ /C1VC2/), silent vowels ( ⇒ /C1V1C2/) or echo vowels ( ⇒ /C1V1C2/). This loosely corresponds to ''shallow'' orthographies in alphabetic writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khom
KHOM (100.9 FM) is an American radio station licensed to serve Salem, the county seat of Fulton County, Arkansas. As of July 31, 2013, the station is owned by E-Communications, LLC. Programming KHOM broadcasts a classic hits format to the greater West Plains, Missouri, area. Until the 2011 sale, this station had aired a country music format of some sort since its establishment in 1977, most recently the " Real Country" format from Cumulus Media Networks branded as "K-Home 100.9". From the 2011 sale until July 31, 2013, the station aired a sports radio format provided by ESPN. History The station, then known by the call sign "KSAR", began regular broadcast operations in September 1977. Owned and operated by the Salem Broadcasting Company (with Ronald E. Plumee as company owner and president), KSAR originally broadcast a contemporary country music format with 2,500 watts of effective radiated power on a frequency of 95.9 MHz. In May 1983, Salem Broadcasting reached an agreem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and southwest. The country has a population of approximately eight million. Its Capital city, capital and most populous city is Vientiane. The country is characterized by mountainous terrain, Buddhist temples, including the UNESCO's World Heritage Site of Luang Prabang, and French colonial architecture. The country traces its historic and cultural identity to Lan Xang, a kingdom which existed from the 13th to 18th centuries. Through its location, the kingdom was a hub for overland trade. In 1707, Lan Xang split into three kingdoms: Kingdom of Luang Phrabang, Luang Prabang, Kingdom of Vientiane, Vientiane, and Kingdom of Champasak, Champasak. In 1893, these kingdoms were unified under French protection as part of French Indochina. Laos was und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |