|
Joshua B. Bederson
Joshua B. Bederson is an American neurosurgeon, Leonard I. Malis, MD/Corinne and Joseph Graber Professor of Neurosurgery, and System Chair of Neurosurgery at the Mount Sinai Health System in New York City. He is a Fellow of the American College of Surgeons, and an attending neurosurgeon at The Mount Sinai Hospital. Bederson has published more than 200 peer reviewed articles. Education and post-doctoral training In 1979, Bederson graduated Phi Beta Kappa from Cornell University, where he was the Ivy League Gymnastics All-Around Champion for three years. He earned his M.D. at the University of California, San Francisco in 1984, taking a year off to study sculpture in the master's degree program at New York University and hold a solo art show in New York City. Bederson completed both his internship and residency at the University of California, San Francisco. During his residency, he also studied neuropathology at the University of Torino in Italy and microvascular and skul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California, San Francisco
The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) is a public land-grant research university in San Francisco, California. It is part of the University of California system and is dedicated entirely to health science and life science. It conducts research and teaching in medical and biological sciences. UCSF was founded as Toland Medical College in 1864. in 1873, it became affiliated with the University of California as its Medical Department. In the same year, it incorporated the California College of Pharmacy and in 1881 it established a dentistry school. Its facilities were located in both Berkeley and San Francisco. In 1964, the school gained full administrative independence as a campus of the UC system, headed by its own chancellor, and in 1970 it gained its current name. Historically based at Parnassus Heights with satellite facilities throughout the city, UCSF developed a second major campus in the newly redeveloped Mission Bay district in the early 2000s. '' U.S. N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, and the Adriatic Sea to the southwest. Slovenia is mostly mountainous and forested, covers , and has a population of 2.1 million (2,108,708 people). Slovenes constitute over 80% of the country's population. Slovene, a South Slavic language, is the official language. Slovenia has a predominantly temperate continental climate, with the exception of the Slovene Littoral and the Julian Alps. A sub-mediterranean climate reaches to the northern extensions of the Dinaric Alps that traverse the country in a northwest–southeast direction. The Julian Alps in the northwest have an alpine climate. Toward the northeastern Pannonian Basin, a continental climate is more pronounced. Ljubljana, the capital and largest city of Slovenia, is geogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Carotid Artery
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) ( in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary '.) are that supply the head and neck with ; they divide in the neck to form the and |
Neuralgia
Neuralgia (Greek ''neuron'', "nerve" + ''algos'', "pain") is pain in the distribution of one or more nerves, as in intercostal neuralgia, trigeminal neuralgia, and glossopharyngeal neuralgia. Classification Under the general heading of neuralgia are trigeminal neuralgia (TN), atypical trigeminal neuralgia (ATN), occipital neuralgia, glossopharyngeal neuralgia and postherpetic neuralgia (caused by shingles or herpes). The term ''neuralgia'' is also used to refer to pain associated with sciatica and brachial plexopathy. Atypical (trigeminal) Atypical trigeminal neuralgia (ATN) is a rare form of neuralgia and may also be the most misdiagnosed form. The symptoms can be mistaken for migraines, dental problems such as temporomandibular joint disorder, musculoskeletal issues, and hypochondriasis. ATN can have a wide range of symptoms and the pain can fluctuate in intensity from mild aching to a crushing or burning sensation, and also to the extreme pain experienced with the more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arteriovenous Malformation
Arteriovenous malformation is an abnormal connection between arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary system. This vascular anomaly is widely known because of its occurrence in the central nervous system (usually cerebral AVM), but can appear in any location. Although many AVMs are asymptomatic, they can cause intense pain or bleeding or lead to other serious medical problems. AVMs are usually congenital and belong to the RASopathies. The genetic transmission patterns of AVMs are incomplete, but there are known genetic mutations (for instance in the epithelial line, tumor suppressor PTEN gene) which can lead to an increased occurrence throughout the body. Signs and symptoms Symptoms of AVM vary according to the location of the malformation. Roughly 88% of people with an AVM are asymptomatic; often the malformation is discovered as part of an autopsy or during treatment of an unrelated disorder (called in medicine an "incidental finding"); in rare cases, its expansion or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
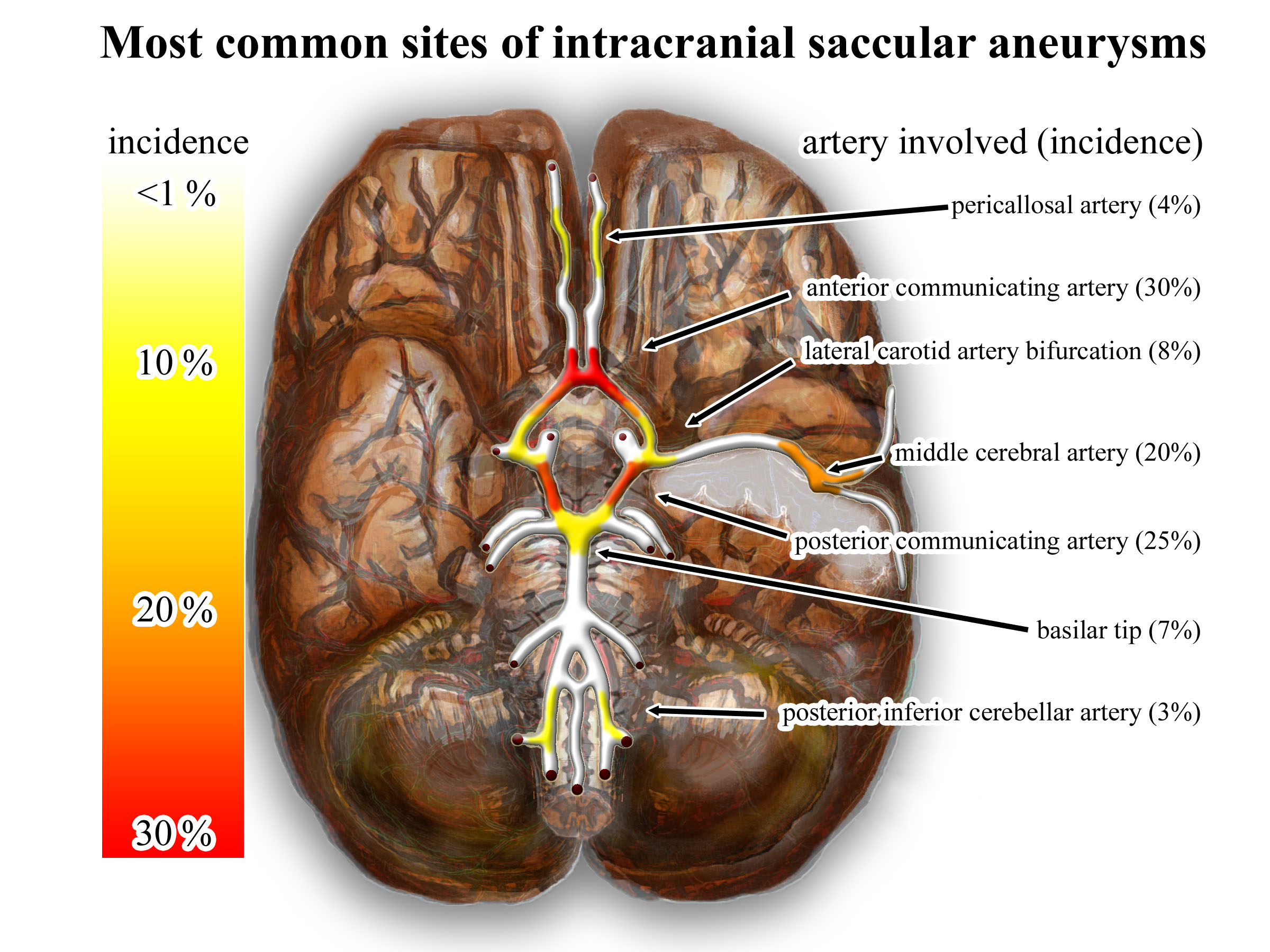
Cerebral Aneurysm
An intracranial aneurysm, also known as a brain aneurysm, is a cerebrovascular disorder in which weakness in the wall of a cerebral artery or vein causes a localized dilation or ballooning of the blood vessel. Aneurysms in the posterior circulation (basilar artery, vertebral arteries and posterior communicating artery) have a higher risk of rupture. Basilar artery aneurysms represent only 3–5% of all intracranial aneurysms but are the most common aneurysms in the posterior circulation. Classification Cerebral aneurysms are classified both by size and shape. Small aneurysms have a diameter of less than 15 mm. Larger aneurysms include those classified as large (15 to 25 mm), giant (25 to 50 mm), and super-giant (over 50 mm). Berry (saccular) aneurysms Saccular aneurysms, also known as berry aneurysms, appear as a round outpouching and are the most common form of cerebral aneurysm. Causes include connective tissue disorders, polycystic kidney disease, art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Tumor
A brain tumor occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain. There are two main types of tumors: malignant tumors and benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and secondary tumors, which most commonly have spread from tumors located outside the brain, known as brain metastasis tumors. All types of brain tumors may produce symptoms that vary depending on the size of the tumor and the part of the brain that is involved. Where symptoms exist, they may include headaches, seizures, problems with vision, vomiting and mental changes. Other symptoms may include difficulty walking, speaking, with sensations, or unconsciousness. The cause of most brain tumors is unknown. Uncommon risk factors include exposure to vinyl chloride, Epstein–Barr virus, ionizing radiation, and inherited syndromes such as neurofibromatosis, tuberous sclerosis, and von Hippel-Lindau Disease. Studies on mobile phone exposure hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Heart Association
The American Heart Association (AHA) is a nonprofit organization in the United States that funds cardiovascular medical research, educates consumers on healthy living and fosters appropriate cardiac care in an effort to reduce disability and deaths caused by cardiovascular disease and stroke. Originally formed in New York City in 1924, it is currently headquartered in Dallas, Texas. The American Heart Association is a national voluntary health agency. They are known for publishinguidelineson cardiovascular disease and prevention, standards on basic life support, advanced cardiac life support (ACLS), and pediatric advanced life support (PALS), and in 2014 issued its first guidelines for preventing strokes in women. They are known also for operating a number of highly visible public service campaigns starting in the 1970s, and also operate a number of fundraising events. In 1994, the ''Chronicle of Philanthropy'', an industry publication, released a study that showed the American H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institutes Of Health
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late 1880s and is now part of the United States Department of Health and Human Services. The majority of NIH facilities are located in Bethesda, Maryland, and other nearby suburbs of the Washington metropolitan area, with other primary facilities in the Research Triangle Park in North Carolina and smaller satellite facilities located around the United States. The NIH conducts its own scientific research through the NIH Intramural Research Program (IRP) and provides major biomedical research funding to non-NIH research facilities through its Extramural Research Program. , the IRP had 1,200 principal investigators and more than 4,000 postdoctoral fellows in basic, translational, and clinical research, being the largest biomedical research instit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is bleeding into the subarachnoid space—the area between the arachnoid membrane and the pia mater surrounding the brain. Symptoms may include a severe headache of rapid onset, vomiting, decreased level of consciousness, fever, and sometimes seizures. Neck stiffness or neck pain are also relatively common. In about a quarter of people a small bleed with resolving symptoms occurs within a month of a larger bleed. SAH may occur as a result of a head injury or spontaneously, usually from a ruptured cerebral aneurysm. Risk factors for spontaneous cases include high blood pressure, smoking, family history, alcoholism, and cocaine use. Generally, the diagnosis can be determined by a CT scan of the head if done within six hours of symptom onset. Occasionally, a lumbar puncture is also required. After confirmation further tests are usually performed to determine the underlying cause. Treatment is by prompt neurosurgery or endovascular coiling. Medicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebrovascular Disease
Cerebrovascular disease includes a variety of medical conditions that affect the blood vessels of the brain and the cerebral circulation. Arteries supplying oxygen and nutrients to the brain are often damaged or deformed in these disorders. The most common presentation of cerebrovascular disease is an ischemic stroke or mini-stroke and sometimes a hemorrhagic stroke. Hypertension (high blood pressure) is the most important contributing risk factor for stroke and cerebrovascular diseases as it can change the structure of blood vessels and result in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis narrows blood vessels in the brain, resulting in decreased cerebral perfusion. Other risk factors that contribute to stroke include smoking and diabetes. Narrowed cerebral arteries can lead to ischemic stroke, but continually elevated blood pressure can also cause tearing of vessels, leading to a hemorrhagic stroke. A stroke usually presents with an abrupt onset of a neurologic deficit – such as hemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |