|
Jose Ben Halafta
Jose ben Halafta or Yose ben Halafta (or Yose ben Halpetha) (Hebrew: רבי יוסי בן חלפתא; IPA: /ʁa'bi 'josi ben xa'lafta/) was a tanna of the fourth generation (2nd century CE). He is the fifth-most-frequently mentioned sage in the Mishnah. Of the many Rabbi Yose's in the Talmud, Yose Ben Halafta is the one who is simply referred to as Rabbi Yose. Biography He was born at Sepphoris; but his family was of Babylonian-Jewish origin. According to a genealogical chart found at Jerusalem, he was a descendant of Jonadab ben Rechab. He was one of Rabbi Akiva's five principal pupils, called "the restorers of the Law," who were afterward ordained by Judah ben Baba. He was also a student of Johanan ben Nuri, whose halakhot he transmitted and of Eutolemus. It is very likely that he studied much under his father, Halafta, whose authority he invokes in several instances. But his principal teacher was Akiva, whose system he followed in his interpretation of the Law. After havin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved throughout history as the main liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. Hebrew is the only Canaanite language still spoken today, and serves as the only truly successful example of a dead language that has been revived. It is also one of only two Northwest Semitic languages still in use, with the other being Aramaic. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as '' Lashon Hakodesh'' (, ) since an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keilim
''Keilim ''or ''Kelim'' ( he, כֵּלִים, literally "Vessels") is the first tractate in the Order of Tohorot in the Mishnah. It contains thirty chapters, making it the longest tractate in the entire Mishnah. The Tosefta on Keilim consists of twenty-five chapters,Jewish Encyclopedia bibliography: *Z. Frankel, Hodegetica in Mischnam', p. 263, Leipsic, 1859. divided into ''Bava Kama'' ("First Gate"), ''Bava Metzia'' ("Middle Gate"), and ''Bava Batra'' ("Final Gate") of ''Keilim''. The tractate discusses the laws of ritual purity and impurity pertaining to all types of vessels. * Chapter 1 clarifies the ranking of ritual impurities * Chapters 2–10 discuss earthenware vessels ( clay ovens, ranges, etc.) * Chapters 11–14 discuss metal vessels * Chapters 15–19 discuss vessels made of wood, leather, and bone * Chapters 20–25 discuss laws of purity and impurity pertaining to all vessels * Chapters 26–28 discuss laws pertaining to leather and clothing * Chapter 29 discusses t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shabbat (Talmud)
:''This is about part of the Talmud; for the Jewish day of rest, see Shabbat.'' Shabbat ( he, שַׁבָּת, lit. "Sabbath") is the first tractate of ''Seder Moed'' ("Order of Appointed Times") of the Mishnah and of the Talmud. The tractate deals with the laws and practices regarding observing the Jewish Sabbath (''Shabbat'' in Hebrew). The tractate focuses primarily on the categories and types of activities prohibited on the Sabbath according to interpretations of many verses in the Torah, notably and . The Mishnah and Talmud go to great lengths to carefully define and precisely determine the observance of the Sabbath. The tractate is thus one of the longest in terms of chapters in the Mishnah, and folio pages in the Talmud. It comprises 24 chapters and has a Gemara – rabbinical analysis of and commentary on the Mishnah – in both the Babylonian Talmud and all but the last four chapters of the Jerusalem Talmud. There is a Tosefta of 18 chapters on this tractate. As its nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simeon Bar Yohai
Shimon bar Yochai ( Zoharic Aramaic: שמעון בר יוחאי, ''Shim'on bar Yoḥai'') or Shimon ben Yochai (Mishnaic Hebrew: שמעון בן יוחאי, ''Shim'on ben Yoḥai''), also known by the acronym Rashbi, was a 2nd-century ''tannaitic'' sage in ancient Judea, said to be active after the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE. He was one of the most eminent disciples of Rabbi Akiva. The ''Zohar'', a 13th century foundational work of Kabbalah, is ascribed to him by Qabbalistic tradition, but this claim is universally rejected by scholars. In addition, the important legal works called Sifre and Mekhilta are attributed to him (not to be confused with the Mekhilta of Rabbi Ishmael, of which much of the text is the same). In the Mishnah, where he is the fourth-most mentioned sage, he is referred to as simply "Rabbi Shimon" (except Hagigah 1:7 and Avot 6:8). In the baraita, midrash and gemara his name occurs either as Shimon or as Shimon ben Yochai. According to modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
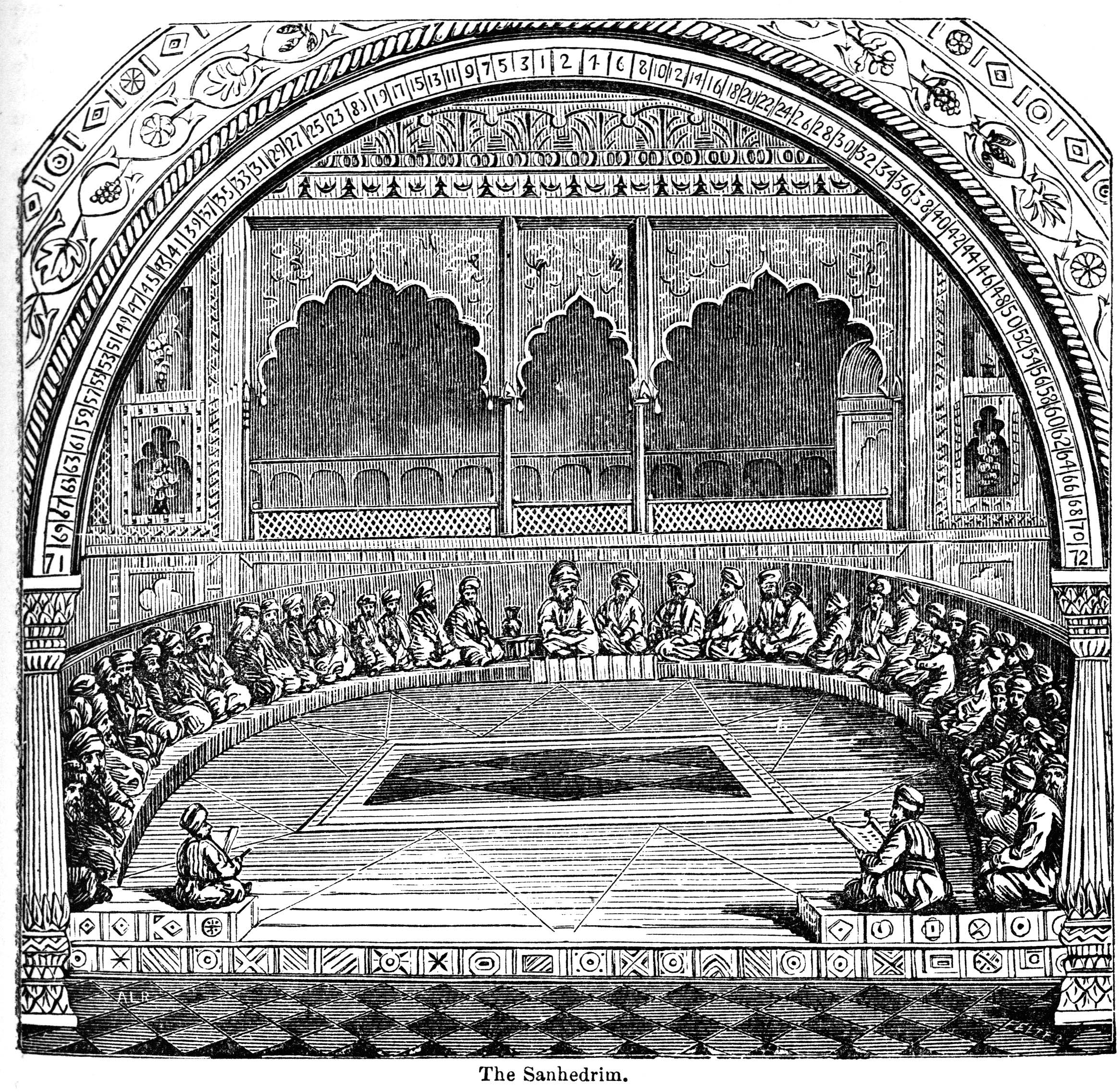
Sanhedrin
The Sanhedrin (Hebrew and Aramaic: סַנְהֶדְרִין; Greek: , ''synedrion'', 'sitting together,' hence 'assembly' or 'council') was an assembly of either 23 or 71 elders (known as "rabbis" after the destruction of the Second Temple), appointed to sit as a tribunal in every city in the ancient Land of Israel. There were two classes of Rabbinite Jewish courts which were called Sanhedrin, the Great Sanhedrin and the Lesser Sanhedrin. A lesser Sanhedrin of 23 judges was appointed to sit as a tribunal in each city, but there was only supposed to be one Great Sanhedrin of 71 judges, which among other roles acted as the Supreme Court, taking appeals from cases which were decided by lesser courts. In general usage, ''the Sanhedrin'' without qualifier normally refers to the Great Sanhedrin, which was presided over by the ''Nasi'', who functioned as its head or representing president, and was a member of the court; the ''Av Beit Din'' or the chief of the court, who was second to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usha (ancient)
Usha () was a city in the Western part of Galilee. The Arab village of Hawsha later occupied the ruins of the old site. The modern kibbutz of Usha, Israel is located nearby to the ruins. History The site came to renown in the 2nd century (c. 135), after the Hadrianic persecutions, when the Sanhedrin, or rabbinic court, was moved from Yavne in Judea to Usha, and then from Usha back to Yavne, and a second time from Yavne to Usha.Simon, Maurice, ed. (1990). ''Hebrew-English Edition of the Babylonian Talmud (Seder Moed), Rosh Hashanah, Beẓah, Sheḳalim''. The Soncino Press: London, s.v. ''Rosh Hashanah'' 31b (note 6, citing Horowitz, ''Palestine'', p.34) The Sanhedrin is thought to have continued there until it was dissolved during the reign of Verus, and re-established in Shefar'am under Marcus Aurelius. The final settlement in Usha indicates the ultimate spiritual supremacy of Galilee over Judea, the latter having become depopulated after the Second Jewish Revolt. Usha was al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bava Metzia
Bava Metzia (Talmudic Aramaic: בָּבָא מְצִיעָא, "The Middle Gate") is the second of the first three Talmudic tractates in the order of Nezikin ("Damages"), the other two being Bava Kamma and Bava Batra. Originally all three formed a single tractate called ''Nezikin'' (torts or injuries), each ''Bava'' being a Part or subdivision. Bava Metzia discusses civil matters such as property law and usury. It also examines one's obligations to guard lost property that have been found, or property explicitly entrusted to him. Mishnah The Mishnah of Bava Metzia contains ten chapters. Honorary trustee (''Shomer Hinam''), chapters 1-3 An honorary trustee is one who finds lost property. He has to keep it as '' shomer hinam'' (watching over another's property without receiving any remuneration) until he can restore it to the rightful owner (). The laws as to what constitutes finding, what to do with the things found, how to guard against false claimants, how to take care of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe. The eastern border of Anatolia has been held to be a line between the Gulf of Alexandretta and the Black Sea, bounded by the Armenian Highlands to the east and Mesopotamia to the southeast. By this definition Anatolia comprises approximately the western two-thirds of the Asian part of Turkey. Today, Anatolia is sometimes considered to be synonymous with Asia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pesahim
Pesachim ( he, פְּסָחִים, lit. "Paschal lambs" or "Passovers"), also spelled Pesahim, is the third tractate of ''Seder Moed'' ("Order of Festivals") of the Mishnah and of the Talmud. The tractate discusses the topics related to the Jewish holiday of Passover, and the Passover sacrifice, both called ''"Pesach"'' in Hebrew language, Hebrew. The tractate deals with the laws of ''matza'' (unleavened bread) and ''maror'' (bitter herbs), the prohibitions against owning or consuming '' chametz'' (leaven) on the festival, the details of the Paschal lamb that used to be offered at the Temple in Jerusalem, the order of the feast on the first evening of the holiday known as the Passover seder, and the laws of the supplemental " Second Pesach". Two reasons are given for the name of the tractate ''Pesachim'' being in the plural: either because the tractate originally comprised two parts, one dealing with the Passover sacrifice, and the second with the other aspects of the holiday, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megillah (Talmud)
Megillah ( he, מְגִילָּה, "scroll") is the tenth Tractate of Mishnah in the Order Moed. It and its Gemara deal with the laws of Purim and offers exegetical understandings to the Book of Esther. It also includes laws concerning the public reading of the Torah and other communal synagogue practices. There is also a segment in the first chapter which details certain miscellaneous laws. A megillah is a finely detailed account or book but the term by itself commonly refers to the Book of Esther. Sources * Schottenstein Edition of the Babylonian Talmud The ''Schottenstein Edition of the Babylonian Talmud'' is a 20th-century, 73-volume edition of the Babylonian Talmud (Talmud Bavli) featuring an elucidated translation and commentary, and published by ArtScroll, a division of Mesorah Publicati ...: ''Talmud Bavli: The Gemara, Schottenstein Edition - Tractate Megillah'', 1991, Artscroll External links Mishnah Megillah text in Hebrew [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bava Kamma
Bava Kamma ( tmr, בָּבָא קַמָּא, translit=Bāḇā Qammā, translation=The First Gate) is the first of a series of three Talmudic tractates in the order Nezikin ("Damages") that deal with civil matters such as damages and torts. The other two of these tractates are Bava Metzia ('The Middle Gate') and Bava Batra ('The Last Gate'): originally all three formed a single tractate called ''Nezikin'', each "Bava" meaning "part" or "subdivision." Bava Kamma discusses various forms of damage and the compensation owed for them. Biblical laws dealing with the cases discussed in Bava Kamma are contained in the following passages: , and . The principle that underlies the legislation in this respect is expressed by the sentence, "He that kindled the fire shall surely make restitution". Bava Kamma consists of ten chapters which may be grouped as follows: damage caused without criminality (chaps. 1-6); damage caused by a criminal act (chaps. 7-10). Mishna Damage caused without crim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halafta
Halafta or Rabbi Halafta (רבי חלפתא) was a rabbi who lived in Sepphoris in the Galilee during the late 1st and early 2nd centuries CE (second generation of tannaim). He was the father of Jose ben Halafta, and one of the latter's teachers of halakha. He is always cited without patronymic or cognomen. His descent is traced back to Jonadab the Rechabite. He was a senior contemporary of Gamaliel II and Johanan ben Nuri and conducted a rabbinic school at Sepphoris. Here he introduced some ritual reforms. Tradition relates that, together with Hananiah ben Teradion and Eleazar ben Mattai, he saw the monuments which Joshua had placed in the Jordan River. Ḥalafta seems to have attained an advanced age. He communicated to Gamaliel II an order given by his grandfather Gamaliel I, and which he had himself heard in the last years of Judea's independence; he subsequently participated in the Akavia controversy, and later he is met with in the company of Eleazar ben Azariah, Ḥuẓpi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |