|
Jordanian Levantine
Jordanian Arabic is a dialect continuum of mutually intelligible varieties of Arabic spoken by the population of the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan. Jordanian Arabic can be divided into sedentary and Bedouin varieties. Sedentary varieties belong to the Levantine Arabic dialect continuum. Bedouin varieties are further divided into two groups, Northwest Arabian Arabic varieties of the south, and Najdi Arabic and Shawi Arabic varieties of the north. Jordanian Arabic varieties are Semitic. They are spoken by more than 6 million people, and understood throughout the Levant and, to various extents, in other Arabic-speaking regions. As in all Arab countries, language use in Jordan is characterized by diglossia; Modern Standard Arabic is the official language used in most written documents and the media, while daily conversation is conducted in the local colloquial varieties. Together with Palestinian Arabic, it has the ISO 639-3 language code "ajp", known as South Levantine Arabic. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan River. Jordan is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the south and east, Iraq to the northeast, Syria to the north, and the Palestinian West Bank, Israel, and the Dead Sea to the west. It has a coastline in its southwest on the Gulf of Aqaba's Red Sea, which separates Jordan from Egypt. Amman is Jordan's capital and largest city, as well as its economic, political, and cultural centre. Modern-day Jordan has been inhabited by humans since the Paleolithic period. Three stable kingdoms emerged there at the end of the Bronze Age: Ammon, Moab and Edom. In the third century BC, the Arab Nabataeans established their Kingdom with Petra as the capital. Later rulers of the Transjordan region include the Assyrian, Babylonian, Roman, Byzantine, Rashidun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amman
Amman (; ar, عَمَّان, ' ; Ammonite language, Ammonite: 𐤓𐤁𐤕 𐤏𐤌𐤍 ''Rabat ʻAmān'') is the capital and largest city of Jordan, and the country's economic, political, and cultural center. With a population of 4,061,150 as of 2021, Amman is Jordan's primate city and is the List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city in the Levant region, the list of largest cities in the Arab world, fifth-largest city in the Arab world, and the list of largest metropolitan areas of the Middle East, ninth largest metropolitan area in the Middle East. The earliest evidence of settlement in Amman dates to the 8th millennium BC, in a Neolithic site known as ʿAin Ghazal, 'Ain Ghazal, where the world's ʿAin Ghazal statues, oldest statues of the human form have been unearthed. During the Iron Age, the city was known as Rabat Aman and served as the capital of the Ammon, Ammonite Kingdom. In the 3rd century BC, Ptolemy II Philadelphus, Pharaoh of Ptole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negev
The Negev or Negeb (; he, הַנֶּגֶב, hanNegév; ar, ٱلنَّقَب, an-Naqab) is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southern end is the Gulf of Aqaba and the resort city and port of Eilat. It contains several development towns, including Dimona, Arad and Mitzpe Ramon, as well as a number of small Bedouin towns, including Rahat and Tel Sheva and Lakiya. There are also several kibbutzim, including Revivim and Sde Boker; the latter became the home of Israel's first Prime Minister, David Ben-Gurion, after his retirement from politics. Although historically part of a separate region (known during the Roman period as Arabia Petraea), the Negev was added to the proposed area of Mandatory Palestine, of which large parts later became Israel, on 10 July 1922, having been conceded by British representative St John Philby "in Trans-Jordan's name". Despite this, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howeitat
The Howeitat or Huwaitat ( ar, الحويطات ''al-Ḥuwayṭāt'', Northwest Arabian Arabic, Northwest Arabian dialect: ''ál-Ḥwēṭāt'') are a large Banu Judham, Judhami tribe, that inhabits areas of present-day southern Jordan, the Sinai Peninsula and Sharqia Governorate, Sharqia governate in Egypt, the Negev, and northwestern Saudi Arabia. The Howeitat have several branches, notably the Ibn Jazi, the Abu Tayi, the Anjaddat, and the Sulaymanniyin, in addition to a number of associated tribes. History Formation Howeitat nomads were recorded as the only tribesmen living in the southern, inland area of the al-Karak-Shawbak ''sanjak'' (district) of the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century.Bakhit, Muhammad Adnan. (1982) ''The Ottoman Province of Damascus in the Sixteenth Century''. Beirut: Libraire du Liban. p. 194. According to the Ottoman historian Qutb al-Din al-Nahrawali (d. 1582), the tribe was a branch of the Banu Uqba, the dominant tribe of the al-Karak-Shawbak region du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
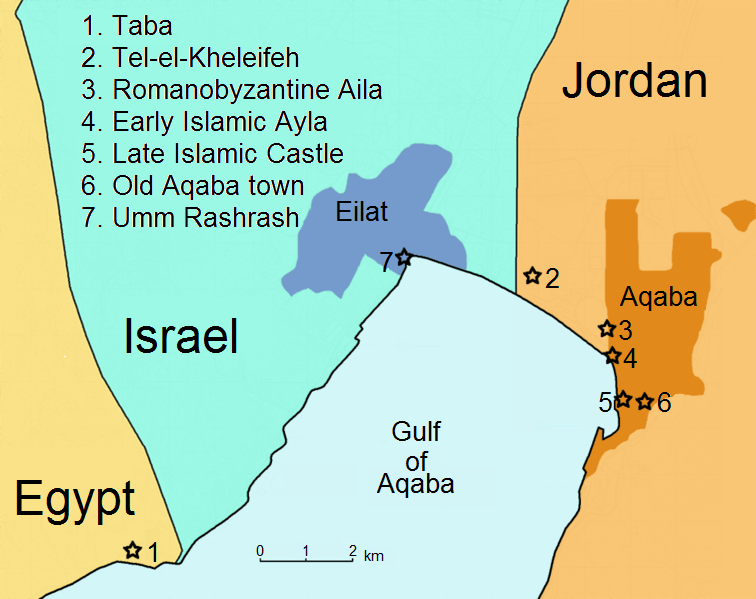
Aqaba
Aqaba (, also ; ar, العقبة, al-ʿAqaba, al-ʿAgaba, ) is the only coastal city in Jordan and the largest and most populous city on the Gulf of Aqaba. Situated in southernmost Jordan, Aqaba is the administrative centre of the Aqaba Governorate. The city had a population of 148,398 in 2015 and a land area of . Today, Aqaba plays a major role in the development of the Jordanian economy, through the vibrant trade and tourism sectors. The Port of Aqaba also serves other countries in the region. Aqaba's strategic location at the northeastern tip of the Red Sea between the continents of Asia and Africa has made its port important over the course of thousands of years. The ancient city was called ''Elath'', adopted in Latin as ''Aela'' and in Arabic as ''Ayla''. Its strategic location and proximity to copper mines made it a regional hub for copper production and trade in the Chalcolithic period. Aela became a bishopric under Byzantine rule and later became a Latin Catholic titu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoubak
Shoubak ( ar, الشوبك) is a municipality that lies at the northwestern edge of the Ma'an Governorate in Jordan. It had a population of 19,297. At one of the highest elevations above sea level in Jordan, this municipality is famous for apple and fruit farms. The Crusader castle Montreal is located in Shoubak. History Shoubak was first settled by the Edomites who had their capital in Busaira in neighboring Tafilah Governorate, in the second millennium BC. It was then settled by the Nabataeans in the first millennium BC. Shoubak is known for its Crusader castle Montreal. Along with Petra and Aqaba, Shoubak forms the third head of this triangle that lies on the cross road between Syria, Saudi Arabia and Egypt. Its unique high elevation (1330 m above sea level) gave it a strategic importance. The importance of Shoubak reached its peak after Baldwin I of Jerusalem took control of it, cutting the roots between Egypt and Syria, the Montreal castle was built on top of a hill t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ma'an
Ma'an ( ar, مَعان, Maʿān) is a city in southern Jordan, southwest of the capital Amman. It serves as the capital of the Ma'an Governorate. Its population was approximately 41,055 in 2015. Civilizations with the name of Ma'an have existed at least since the Nabatean period—the modern city is just northwest of the ancient town. The city is an important transport hub situated on the ancient King's Highway and also on the modern Desert Highway. History Ma'an was founded by the Minaeans (known as "Ma'in" in Arabic), an ancient Arab people based in Yemen, between the 2nd and 4th century BCE.Museum With No Frontiers, p. 203. The site was located on a major trade route and was settled by Minaean traders and merchants. Local tradition has it that the city was named after "Ma'an", the son of Lot.Gibb, p. 897. During the Byzantine era in Syria, Ma'an was part of the territory of the Arab Christian tribe of Banu Judham who served as vassals for the Byzantines in Transjordan. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tafilah
Tafilah ( ar, الطفيلة, 'aṭ-Ṭafīlah, ), also spelled Tafila, is a town with a population of 27,559 people in southern Jordan, located southwest of Amman. It is the capital of Tafilah Governorate. It is well known for having green gardens which contain olive and ficus, fig trees, and grape-vines. Tafilah was first built by the Edomites and was called Tophel. There are more than 360 natural springs in the at-Tafilah area, including the natural reservoir of Dana (Jordan), Dana and hot natural springs at Afra and Burbeita. There are two phosphate and cement mines in at-Tafilah, which are one of the country's main income sources. History Iron Age to Crusader period The oldest state formation established in the region on Tafilah was the kingdom of Edom, and Tafilah lies on the ruins of the Edomite city of Tophel. The capital of Edom was at Bozrah, Busairah 23 km to the south of Tafilah. Tafilah was later annexed by the Nabatean kingdom who, had its capital at Petra. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al Karak
Al-Karak ( ar, الكرك), is a city in Jordan known for its medieval castle, the Kerak Castle. The castle is one of the three largest castles in the region, the other two being in Syria. Al-Karak is the capital city of the Karak Governorate. Al-Karak lies to the south of Amman on the ancient King's Highway. It is situated on a hilltop about above sea level and is surrounded on three sides by a valley. Al-Karak has a view of the Dead Sea. A city of about 32,216 people (2005) has been built up around the castle and it has buildings from the 19th-century Ottoman period. The town is built on a triangular plateau, with the castle at its narrow southern tip. History Iron Age to Assyrian period Al-Karak has been inhabited since at least the Iron Age, and was an important city for the Moabites. In the Bible it is called ''Qer Harreseth'' or Kir of Moab, and is identified as having been subject to the Neo-Assyrian Empire; in the Books of Kings () and Book of Amos (), it is ment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moab
Moab ''Mōáb''; Assyrian: 𒈬𒀪𒁀𒀀𒀀 ''Mu'abâ'', 𒈠𒀪𒁀𒀀𒀀 ''Ma'bâ'', 𒈠𒀪𒀊 ''Ma'ab''; Egyptian: 𓈗𓇋𓃀𓅱𓈉 ''Mū'ībū'', name=, group= () is the name of an ancient Levantine kingdom whose territory is today located in the modern state of Jordan. The land is mountainous and lies alongside much of the eastern shore of the Dead Sea. The existence of the Kingdom of Moab is attested to by numerous archaeological findings, most notably the Mesha Stele, which describes the Moabite victory over an unnamed son of King Omri of Israel, an episode also noted in 2 Kings . The Moabite capital was Dibon. According to the Hebrew Bible, Moab was often in conflict with its Israelite neighbours to the west. Etymology The etymology of the word Moab is uncertain. The earliest gloss is found in the Koine Greek Septuagint () which explains the name, in obvious allusion to the account of Moab's parentage, as ἐκ τοῦ πατρός μου ("from my ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irbid
Irbid ( ar, إِربِد), known in ancient times as Arabella or Arbela (Άρβηλα in Ancient Greek language, Ancient Greek), is the capital and largest city of the Irbid Governorate. It also has the second largest metropolitan population in Jordan after Amman, with a population of around 2,003,800. Irbid is located about north of Amman on the northern ridge of the Gilead, equidistant from Pella, Jordan, Pella, Beit Ras (Capitolias), and Um Qais, and approximately south of the Syrian border. Irbid was built on successive Early Bronze Age settlements and was possibly the Hebrew Bible, biblical Beth Arbel and the Arbila of the Decapolis, a Hellenistic league of the 1st century BCE through the 2nd century CE. The population of Irbid swelled in the late 19th century, and prior to 1948 it served as a significant centre of transit trade. Irbid is the second largest metropolitan in Jordan by population after Amman. But as a city Irbid is the third largest one after Amman and Zarqa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hauran
The Hauran ( ar, حَوْرَان, ''Ḥawrān''; also spelled ''Hawran'' or ''Houran'') is a region that spans parts of southern Syria and northern Jordan. It is bound in the north by the Ghouta oasis, eastwards by the al-Safa (Syria), al-Safa field, to the south by Jordan's desert steppe and to the west by the Golan Heights. Traditionally, the Hauran consists of three subregions: the Nuqrah and Jaydur plains, the Jabal al-Druze massif, and the Lajat volcanic field. The population of the Hauran is largely Arab, but religiously heterogeneous; most inhabitants of the plains are Sunni Muslims belonging to large agrarian clans, while Druze form the majority in the eponymous Jabal al-Druze and a significant Greek Orthodox Church, Greek Orthodox and Melkite Greek Catholic Church, Greek Catholic minority inhabit the western foothills of Jabal al-Druze. The region's largest towns are Daraa, Ar Ramtha, al-Ramtha and al-Suwayda. From the mid-1st century BCE, the region was governed by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |