|
John Of Béthune (died 1238)
John of Béthune (; died 1238) was a French nobleman and military leader in the County of Artois.Jean-François Nieus, "Élisabeth Candavène, comtesse de Saint-Pol (†1240/47): une héritière face à la Couronne", in ''Femmes de pouvoir, femmes politiques durant les derniers siècles du Moyen Âge et au cours de la première Renaissance'' (De Boeck, 2012), pp. 185–211, esp. 196–200. John was the fifth son of William II, lord of Béthune, and Matilda, heiress of Dendermonde.André Duchesne, ''Histoire généalogique de la maison de Béthune'' (Paris, 1639), pp. 178–180. As such, he inherited little money and no land. His eldest brother, Daniel, lord of Béthune, was the first husband of Eustachie, daughter of Lord Gaucher III of Châtillon and the Countess Elisabeth of Saint-Pol. In 1228, between June and November, John married the widowed Elisabeth, who was almost forty. They had no children. John is first attested in 1220. In 1223, he subscribed his mother's act foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
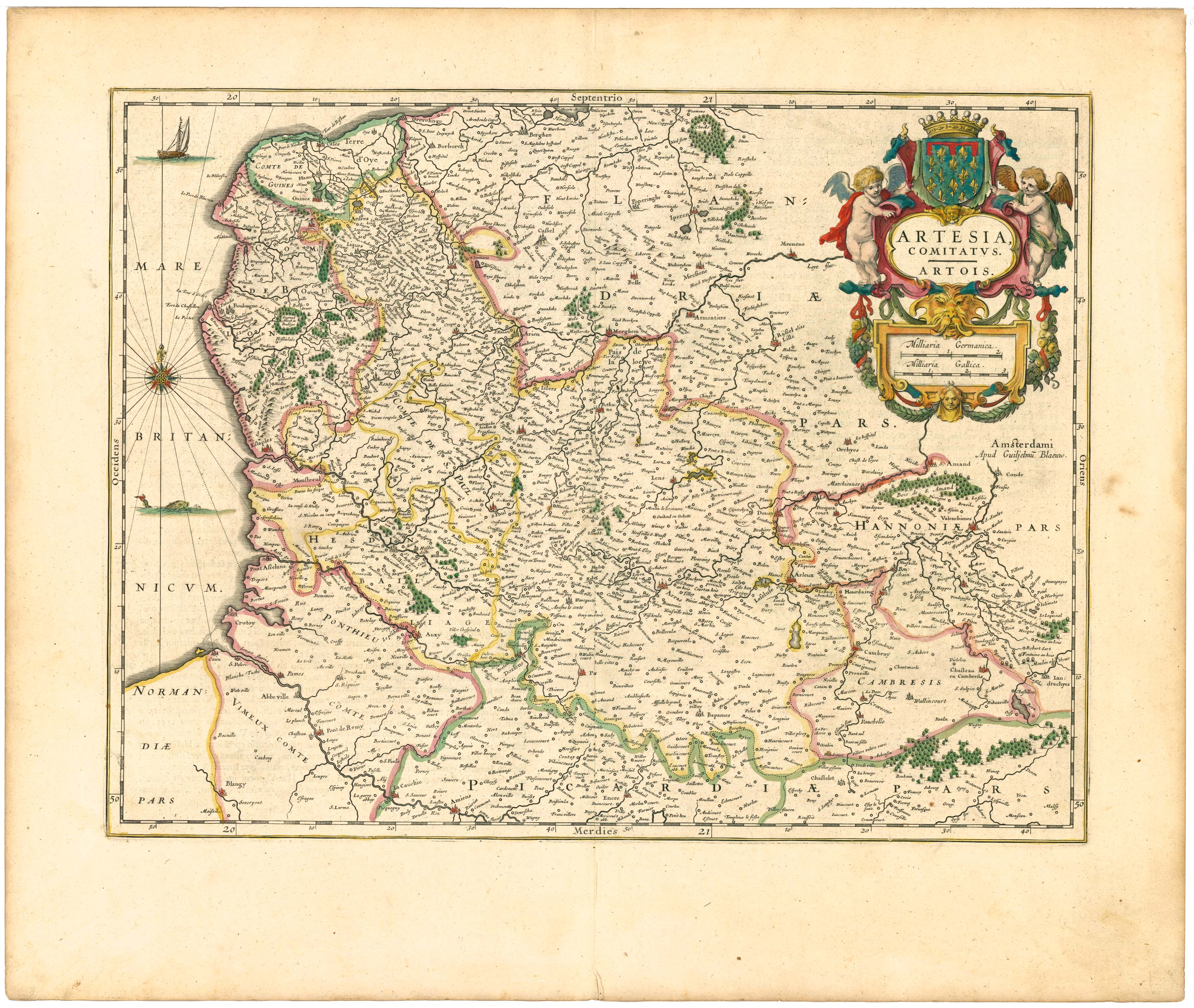
County Of Artois
The County of Artois (, , ) was a historic province of the Kingdom of France, held by the Dukes of Burgundy from 1384 until 1477/82, and a state of the Holy Roman Empire from 1493 until 1659. Present-day Artois lies in northern France, near the border with Belgium. Its territory has an area of around and a population of about one million. Its principal cities include Arras (), Calais (), Boulogne-sur-Mer (), Saint-Omer (, Lens and Béthune. It forms the interior of the French département of Pas-de-Calais. In northern Gaul the Belgic tribe of the Atrebates lived in the future area of Artois, the name of which () reflects theirs. A Carolingian feudal county in its own right from the late 8th century, Artois was annexed by the County of Flanders (898 onwards). It came to France in 1180 as the dowry of a 10-year-old Flemish noblewoman, Isabelle of Hainaut, and was again made a separate county in 1237 for Robert, a grandson of Isabelle. Through inheritance, Artois once a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are linked by 438 bridges. The islands are in the shallow Venetian Lagoon, an enclosed bay lying between the mouths of the Po River, Po and the Piave River, Piave rivers (more exactly between the Brenta (river), Brenta and the Sile (river), Sile). As of 2025, 249,466 people resided in greater Venice or the Comune of Venice, of whom about 51,000 live in the historical island city of Venice (''centro storico'') and the rest on the mainland (''terraferma''). Together with the cities of Padua, Italy, Padua and Treviso, Italy, Treviso, Venice is included in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area (PATREVE), which is considered a statistical metropolitan area, with a total population of 2.6 million. The name is derived from the ancient Adr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Bulgarian Empire
The Second Bulgarian Empire (; ) was a medieval Bulgarians, Bulgarian state that existed between 1185 and 1422. A successor to the First Bulgarian Empire, it reached the peak of its power under Tsars Kaloyan of Bulgaria, Kaloyan and Ivan Asen II before gradually being conquered by the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans in the late 14th century. Until 1256, the Second Bulgarian Empire was the dominant power in the Balkans, defeating the Byzantine Empire in several major battles. In 1205, Emperor Kaloyan of Bulgaria, Kaloyan defeated the newly established Latin Empire in the battle of Adrianople (1205), Battle of Adrianople. His nephew Ivan Asen II defeated the Despotate of Epiros and made Bulgaria a regional power again. During his reign, Bulgaria spread from the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic to the Black Sea and the economy flourished. In the late 13th century, however, the Empire declined under constant invasions by Mongols, Byzantine Empire, Byzantines, Hungarians, and Serbia in the Middle Ages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick II (, , , ; 26 December 1194 – 13 December 1250) was King of Sicily from 1198, King of Germany from 1212, King of Italy and Holy Roman Emperor from 1220 and King of Jerusalem from 1225. He was the son of Emperor Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor, Henry VI of the Hohenstaufen dynasty (the second son of Emperor Frederick Barbarossa) and Queen Constance I of Sicily of the Hauteville dynasty. Frederick was one of the most powerful figures of the Middle Ages and ruled a vast area, beginning with Sicily and stretching through Italy all the way north to Germany. Viewing himself as a direct successor to the Roman emperors of antiquity, he was Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of the Romans from his papal coronation in 1220 until his death; he was also a claimant to the title of King of the Romans from 1212 and unopposed holder of that monarchy from 1215. As such, he was King of Germany, King of Italy, of Italy, and King of Burgundy, of Burgundy. At the age of three, he was crowned King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Of Brienne
John of Brienne ( 1170 – 19–23 March 1237), also known as John I, was the king of Jerusalem from 1210 to 1225 and Latin emperor of Constantinople from 1229 to 1237. He was the youngest son of Erard II of Brienne, a wealthy nobleman in Champagne (province), Champagne. John, originally destined for an ecclesiastical career, became a knight and owned small estates in Champagne around 1200. After the death of his brother Walter III, Count of Brienne, Walter III, he ruled the County of Brienne on behalf of his minor nephew Walter IV, Count of Brienne, Walter IV, who lived in Italy. The barons of the Kingdom of Jerusalem proposed that John marry their queen, Maria of Montferrat, Maria. With the consent of Philip II of France and Pope Innocent III, he left France for the Holy Land and married Queen Maria; the couple were crowned in 1210. After Maria's death in 1212 John administered the kingdom as regent for their infant daughter Isabella II of Jerusalem, Isabella II; an influenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baldwin II, Latin Emperor
Baldwin II, also known as Baldwin of Courtenay (; ; late 1217 – October 1273), was the last Latin Emperor ruling from Constantinople. He was the only Latin Emperor born in Constantinople. Biography Baldwin II was born in Constantinople, a younger son of Yolanda of Flanders, sister of the first two emperors, Baldwin I and Henry of Flanders. Her husband, Peter of Courtenay, was third emperor of the Latin Empire, and had been followed by his son Robert of Courtenay, on whose death in 1228 the succession passed to Baldwin, then an 11-year-old boy. The barons chose John of Brienne as Baldwin's co-ruler for life. Baldwin was also to marry Marie of Brienne, daughter of John and his third wife Berenguela of Leon, and on John's death to enjoy the full imperial sovereignty. The marriage contract was carried out in 1234. Since the death of Baldwin's uncle Emperor Henry in 1216, the Latin Empire had declined and the Byzantine ( Nicene) power advanced; and the hopes that John of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Empire Of Constantinople
The Latin Empire, also referred to as the Latin Empire of Constantinople, was a feudal Crusader state founded by the leaders of the Fourth Crusade on lands captured from the Byzantine Empire. The Latin Empire was intended to replace the Byzantine Empire as the Western-recognized Roman Empire in the east, with a Catholic emperor enthroned in place of the Eastern Orthodox Roman emperors. The main objective to form a Latin Empire was planned over the course of the Fourth Crusade, promoted by crusade leaders such as Boniface of Montferrat, as well as the Republic of Venice. The Fourth Crusade had originally been called to retake the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, but a sequence of economic and political events culminated in the Crusader army sacking the city of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire. Originally, the plan had been to restore the deposed Byzantine Emperor Isaac II Angelos, who had been usurped by Alexios III Angelos, to the throne. The crusaders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encre
Albert () is a Communes of France, commune in the Somme (department), Somme Department in France, department in Hauts-de-France in northern France. It is located about halfway between Amiens and Bapaume. History Albert was founded as a Roman outpost, in about 54 BC. After being known by various forms of the name of the local river, the Ancre, it was renamed to Albert after it passed to Charles d'Albert, duc de Luynes. It was a key location in the Battle of the Somme in World War I, and World War I tourism is important for the town. During World War I, the statue of Mary and the infant Jesus – designed by sculptor Albert Roze and dubbed the ''Golden Virgin'' – on top of the Basilica of Our Lady of Brebières was hit by a shell on 15 January 1915 and slumped to a near-horizontal position, where however it remained until further shelling in 1918 destroyed the tower. In his letters home to his wife, Rupert Inglis, who was a former rugby international and now a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Of Andres
William (c.1177–1234) was a Benedictine monk and historian from the Kingdom of France. He served from 1207 as the proctor for his abbey in its legal battles and then from 1211 as the abbot of the abbey of , a position he held until his death. Beginning in the 1220s, he wrote a long chronicle of his abbey, the ''Chronicon Andrense''. Life Almost all that is known about William comes from his chronicle. He was probably born not far from the abbey. He says he was about thirty years old when elected abbot, which puts his birth around 1177. He was educated in the monastery before joining it as a monk. He was a monk under Abbot Peter II for two years. Since Peter died in 1195, he must have become a monk in 1193 when he was around sixteen. Given the popularity of William in the region at the time, securely identifying the abbot with a William mentioned in the documentary sources is impossible. Nevertheless, it has been speculated on the basis of some documents that he was born into a bou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anchin Abbey
Anchin Abbey was a Rule of St. Benedict, Benedictine monastery founded in 1079 in the commune of Pecquencourt in what is now the Nord (French department), Nord department of France. Geography Aquicintum then Aquacignium , Anchin (or Chisho) is an island of 25 hectares, part of the territory of Pecquencourt and surrounded by marshes, the river Scarpe (river), Scarpe and the stream of Bouchart. History ''Aquicintum'', later ''Aquacignium'' and then Anchin (or ''Enchin''), was a 25 hectare island forming part of the territory of Pecquencourt, between the ''marsh, marais'', the river Scarpe (river), Scarpe and the Bouchart brook. The hermit and confessor Gordaine built his hermitage on the island in the 8th century and is sometimes considered the abbey's founder: an anonymous 17th-century painting in the church of Saint-Gilles at Pecquencourt shows his miracles. In 1096, the abbey was the site of a large tournament, the ''Tournoi d'Anchin'', at which 300 knights from Ostrevent, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homage (feudal)
Homage (/ˈhɒmɪdʒ/ or ) (from Medieval Latin , lit. "pertaining to a man") in the Middle Ages was the ceremony in which a feudal tenant or vassal pledged reverence and submission to his feudal lord, receiving in exchange the symbolic title to his new position ( investiture). It was a symbolic acknowledgement to the lord that the vassal was, literally, his man (''homme''). The oath known as "fealty" implied lesser obligations than did "homage". Further, one could swear "fealty" to many different overlords with respect to different land holdings, but "homage" could only be performed to a single liege, as one could not be "his man" (i.e., committed to military service) to more than one "liege lord". The ceremony of homage was used in many regions of Europe to symbolically bind two men together. The vassal to-be would go down on their knee and place their palms together as if praying. The lord to-be would place his hands over the hands of the vassal, while the vassal made a short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |