|
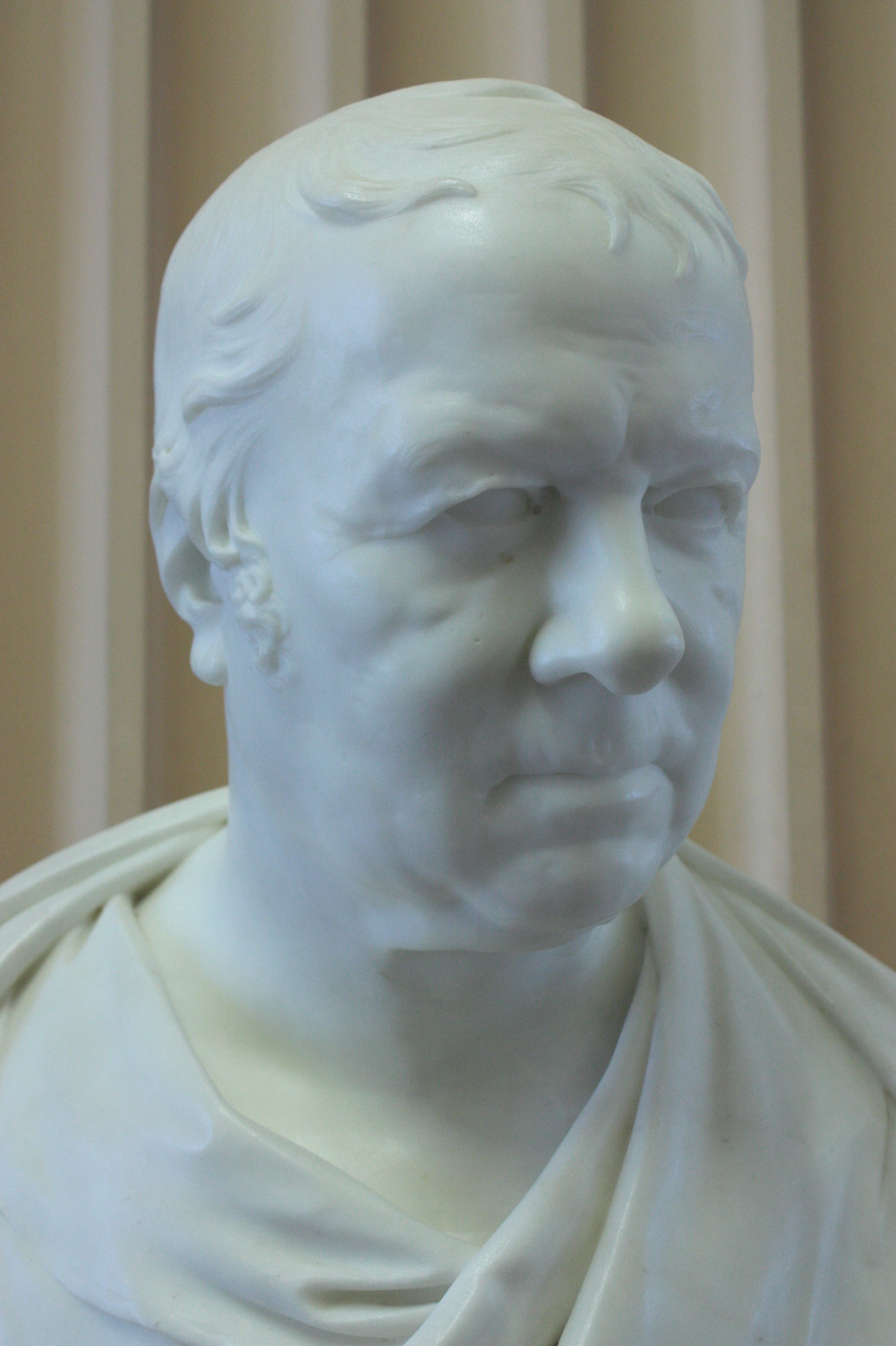
John Gordon (anatomist)
Dr John Gordon FRSE FRCSE (19 April 1786 – 14 June 1818) was a short-lived but influential Scottish anatomist. In 1806 he served as President of the Royal Medical Society. In 1815 he caused an international stir by debunking the new science of phrenology and publicly criticising its principal European exponents, Johann Spurzheim and Franz Joseph Gall. Life He was born on 19 April 1786 in Forres in northern Scotland the son of John Gordon a wine-merchant and banker. He studied medicine at the University of Edinburgh under Dr John Barclay and philosophy under Dugald Stewart. He gained his doctorate MD in 1805 aged 19. He then did further studies in Anatomy in London. A prodigy, he served as President of the Royal Medical Society in 1806 aged just 20. On return to Edinburgh he taught anatomy and physiology at his anatomy school at 9 Surgeons' Square, one of the earliest teachers in the Edinburgh Extramural School of Medicine. he served as a surgeon at the Edinburgh Royal Infir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19 Castle Street, Edinburgh
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album ''63/19'' by Kool A.D. * '' Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album ''Refugee'' * "Nineteen", a song by Karma to Burn from the 2001 album ''Almost Heathen''. * "Nineteen" (song), a 2007 song by American singer Billy Ray Cyrus. * "Nineteen", a song by Tegan and Sara from the 2007 album '' The Con''. * "XIX" (song), a 2014 song by Slipk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical and physical functions in a living system. According to the classes of organisms, the field can be divided into medical physiology, animal physiology, plant physiology, cell physiology, and comparative physiology. Central to physiological functioning are biophysical and biochemical processes, homeostatic control mechanisms, and communication between cells. ''Physiological state'' is the condition of normal function. In contrast, ''pathological state'' refers to abnormal conditions, including human diseases. The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for exceptional scientific achievements in physiology related to the field of medicine. Foundations Cells Although there are differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1818 Deaths
Events January–March * January 1 ** Battle of Koregaon: Troops of the British East India Company score a decisive victory over the Maratha Empire. ** Mary Shelley's ''Frankenstein'' is published anonymously in London. * January 2 – The British Institution of Civil Engineers is founded. * January 3 (21:52 UTC) – Venus occults Jupiter. It is the last occultation of one planet by another before November 22, 2065. * January 6 – The Treaty of Mandeswar brings an end to the Third Anglo-Maratha War, ending the dominance of Marathas, and enhancing the power of the British East India Company, which controls territory occupied by 180 million Indians. * January 11 – Percy Bysshe Shelley's ''Ozymandias'' is published pseudonymously in London. * January 12 – The Dandy horse (''Laufmaschine'' bicycle) is invented by Karl Drais in Mannheim. * February 3 – Jeremiah Chubb is granted a British patent for the Chubb detector lock. * February 5 – Upon his death, King Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1786 Births
Events January–March * January 3 – The third Treaty of Hopewell is signed, between the United States and the Choctaw. * January 6 – The outward bound East Indiaman '' Halsewell'' is wrecked on the south coast of England in a storm, with only 74 of more than 240 on board surviving. * February 2 – In a speech before The Asiatic Society in Calcutta, Sir William Jones notes the formal resemblances between Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit, laying the foundation for comparative linguistics and Indo-European studies. * March 1 – The Ohio Company of Associates is organized by five businessmen at a meeting at the Bunch-of-Grapes Tavern in Boston, to purchase land from the United States government to form settlements in what is now the U.S. state of Ohio. * March 13 – Construction begins in Dublin on the Four Courts Building, with the first stone laid down by the United Kingdom's Viceroy for Ireland, the Duke of Rutland. April–June * Apri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Thomson Gordon
John Thomson Gordon FRSE (1813-1865) was a Scottish advocate who served as Rector of Marischal College 1849-50 and Sheriff of Aberdeen 1847-48 and Edinburgh 1848–>1852. Life He was born on 19 March 1813 at 14 Buccleuch Place in Edinburgh the son of Dr John Gordon. His mother was the sister of Andrew Rutherfurd, Lord Rutherfurd. The family moved to 19 Castle Street in the New Town when he was five. He was educated at Edinburgh Academy then studied law at Edinburgh University. He became an advocate in 1835. He was Sheriff of Aberdeen in 1847-48. In 1849 he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. His proposer was John Gordon of Cairnbulg. From 1848 he became Sheriff of Edinburgh based at Midlothian Chambers in Edinburgh. He died in Caen in northern France on 21 September 1865. Family In 1837 he married Mary Wilson (d.1873), daughter of John Wilson. Her sister, Jane Emily Wilson, was married to William Edmondstoune Aytoun William Edmondstoune Aytoun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Rutherfurd, Lord Rutherfurd
The Right Hon. Andrew Rutherfurd, Lord Rutherfurd, (born Andrew Greenfield; 21 June 1791 – 13 December 1854) was a Scottish advocate, judge and politician. Early life Rutherfurd was born at Bristo Port (near Greyfriars Kirkyard) in Edinburgh on 21 June 1791 to Janet Rutherfurd Bervie, and Reverend William Greenfield. In 1799, after his father was disgraced in a sex scandal, the family changed their name to Rutherfurd, his maternal grandmother's maiden name. His main house was Lauriston Castle near Cramond just north-west of the city. His sister married John Gordon FRSE, father of John Thomson Gordon FRSE. He was educated at the High School in Edinburgh then studied law at the University of Edinburgh. He became an advocate in 1812. Career In the 1830s he is listed as an advocate living at 9, St Colme Street, on the Moray Estate in Edinburgh's west end. His house was remodelled by William Notman in 1835, whilst working in the offices of William Henry Playfair. He was appo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greyfriars Kirkyard
Greyfriars Kirkyard is the graveyard surrounding Greyfriars Kirk in Edinburgh, Scotland. It is located at the southern edge of the Old Town, adjacent to George Heriot's School. Burials have been taking place since the late 16th century, and a number of notable Edinburgh residents are interred at Greyfriars. The Kirkyard is operated by City of Edinburgh Council in liaison with a charitable trust, which is linked to but separate from the church. The Kirkyard and its monuments are protected as a category A listed building. History Greyfriars takes its name from the Franciscan friary on the site (the friars of which wear grey habits), which was dissolved in 1560. The churchyard was founded in August 1562 after Royal sanction was granted to replace the churchyard at St Giles' Cathedral in Edinburgh. The latter burial ground was not used after around 1600. The Kirkyard was involved in the history of the Covenanters. The Covenanting movement began with signing of the National Cov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
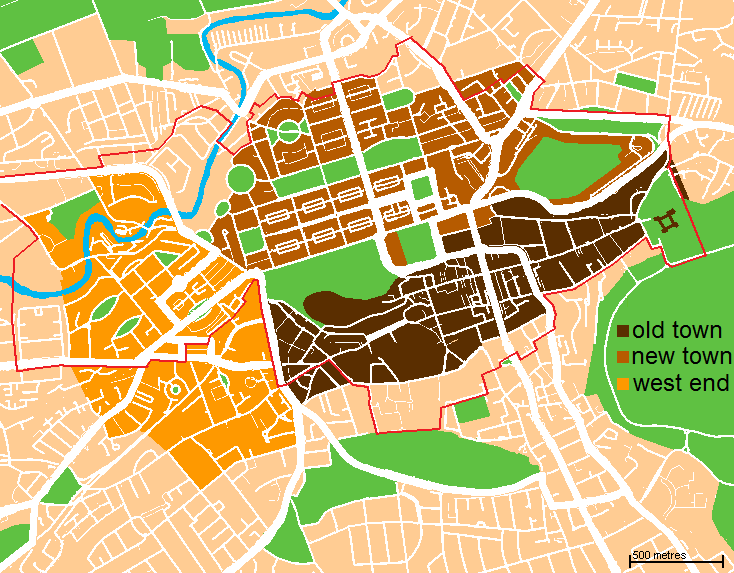
New Town, Edinburgh
The New Town is a central area of Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. It was built in stages between 1767 and around 1850, and retains much of its original neo-classical and Georgian period architecture. Its best known street is Princes Street, facing Edinburgh Castle and the Old Town across the geological depression of the former Nor Loch. Together with the West End, the New Town was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site alongside the Old Town in 1995. The area is also famed for the New Town Gardens, a heritage designation since March 2001. Proposal and planning The idea of a New Town was first suggested in the late 17th century when the Duke of Albany and York (later King James VII and II), when resident Royal Commissioner at Holyrood Palace, encouraged the idea of having an extended regality to the north of the city and a North Bridge. He gave the city a grant:That, when they should have occasion to enlarge their city by purchasing ground without the town, or to build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Christian Reil
Johann Christian Reil (20 February 1759 – 22 November 1813) was a German physician, physiologist, anatomist, and psychiatrist. He coined the term psychiatry – ''Psychiatrie'' in German – in 1808. Medical conditions and anatomical features named after him include Reil's finger (later called ''digitus mortuus'' or Raynaud syndrome) and the Islands of Reil in the cerebral cortex. In 1809, he was the first to describe the white fibre tract now called the arcuate fasciculus.Catani M, Mesulam M. (2008). The arcuate fasciculus and the disconnection theme in language and aphasia: history and current state. Cortex. 44(8):953-61. He is frequently and erroneously crediting with discovering the locus coeruleus,Maeda T. (2000). The Locus coeruleus: history. Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy. 18:57–64. which was first described by Félix Vicq-d'Azyr. In 1779 and 1780, Reil became acquainted with the scientist Johann Friedrich Blumenbach while Reil was studying medicine in Götting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Allan (mineralogist)
Thomas Allan of Lauriston FRS FRSE FSA FLS (17 July 1777 – 12 September 1833) was a British mineralogist. Life Allan was born in Edinburgh, Scotland, on 17 July 1777, the son of Robert Allan (1748–1818), a banker. He was educated at the High School of Edinburgh and took up banking as profession; but he is remembered today for his contributions to mineral science. At an early age Allan became fascinated with minerals and he began to accumulate a large mineral collection that was subsequently bequeathed to his son Robert Allan FRSE. This collection was later incorporated into Robert Greg's, which was ultimately acquired by the British Museum of Natural History in the mid-nineteenth century. In 1813, Allan was influential in securing a mineralogy post in the Dublin Philosophical Society for the German mineralogist Karl Ludwig Giesecke (1761–1833). Allan was elected as Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh in 1805, his proposers being Sir James Hall, William Wright and J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Playfair
John Playfair FRSE, FRS (10 March 1748 – 20 July 1819) was a Church of Scotland minister, remembered as a scientist and mathematician, and a professor of natural philosophy at the University of Edinburgh. He is best known for his book ''Illustrations of the Huttonian Theory of the Earth'' (1802), which summarised the work of James Hutton. It was through this book that Hutton's principle of uniformitarianism, later taken up by Charles Lyell, first reached a wide audience. Playfair's textbook ''Elements of Geometry'' made a brief expression of Euclid's parallel postulate known now as Playfair's axiom. In 1783 he was a co-founder of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. He served as General Secretary to the society 1798–1819. Life Born at Benvie, slightly west of Dundee to Margaret Young (1719/20 – 1805) and Reverend James Playfair (died 1772), the kirk minister of Liff and Benvie. Playfair was educated at home until the age of 14, when he entered the University of St Andrews to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Thomson (advocate)
Thomas Thomson FRSE FSA Scot (10 November 1768 – 2 October 1852) was a Scottish advocate, antiquarian and archivist who served as Principal Clerk of Session (1828–1852) and as secretary of the literary section of the Royal Society of Edinburgh (1812–20). Life Thomas Thomson was born in Dailly manse on 10 November 1768, the eldest son of Rev Thomas Thomson, minister of Dailly in Ayrshire, and his second wife, Mary, daughter of Francis Hay. John Thomson was a younger brother. After attending the parish school of Dailly, he entered the University of Glasgow at age 13, where he graduated with an MA on 27 April 1789. He attended classes in theology and law at the University of Edinburgh from 1789 to 1791. He passed the Scottish bar as an advocate on 10 December 1793. His early Edinburgh address was 19 North Castle Street. Here he was a neighbour and close friend to Walter Scott, at that time also a fellow advocate. Thomson acquired a practice at the bar, particularly in cases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_painted_by_JW_Gordon.jpg)

