|
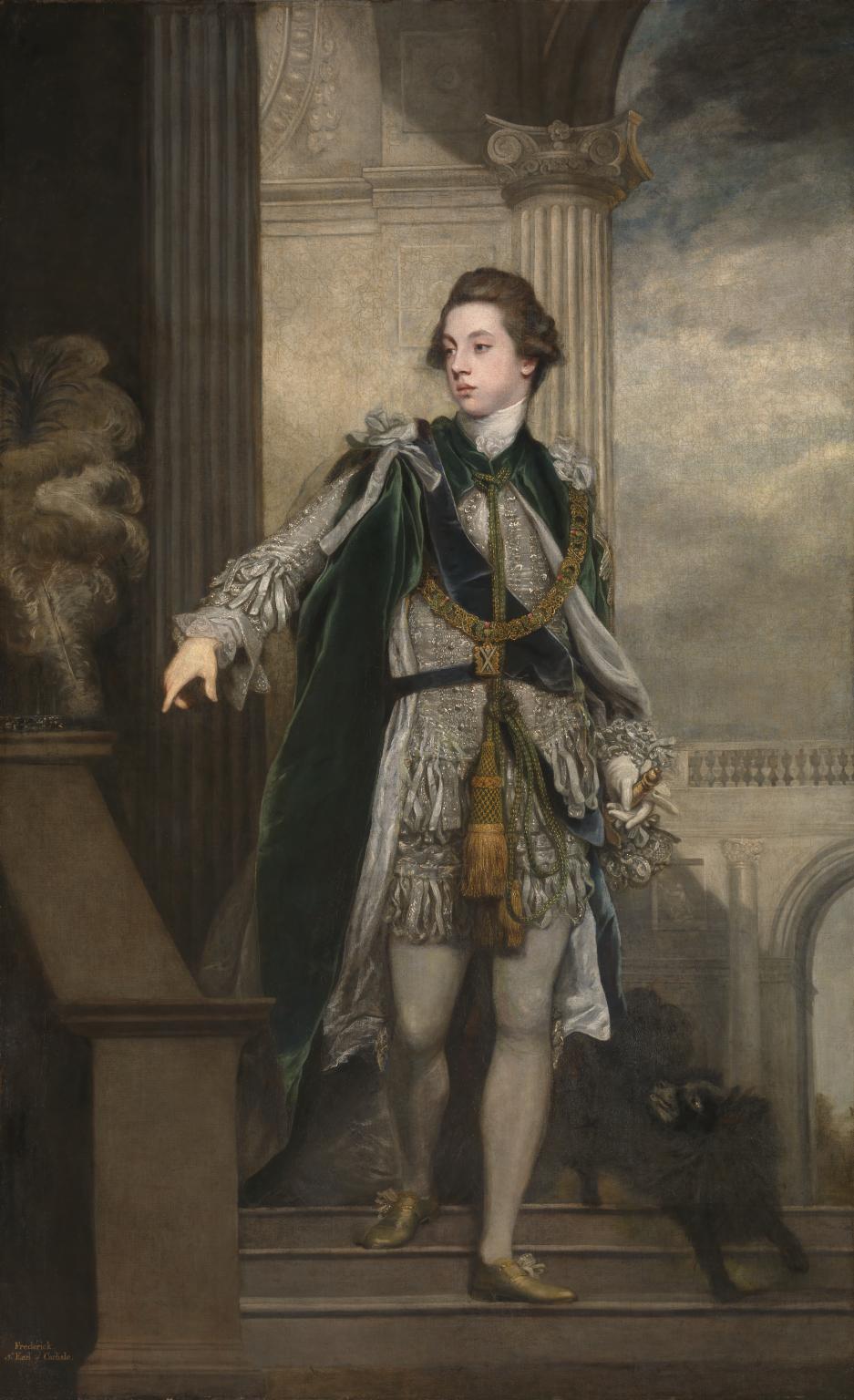
John Elliot (Royal Navy Officer)
John Elliot (1732 – 20 September 1808) was a Scottish officer of the Royal Navy who served during the Seven Years' War and the American War of Independence. He rose to the rank of admiral, and served briefly as colonial governor of Newfoundland. Elliot was born into the gentry in Scotland, and entered the navy. Little is known about his early service, but he received a promotion to post-captain during the Seven Years' War, and commanded the 32-gun frigate with distinction, first capturing a small French frigate, and then taking command of a squadron of three ships and bringing to action the notorious privateer François Thurot, who had been raiding the coast of Ireland in 1760. After a short but bitter engagement, Thurot was killed and his ships captured. Elliot was widely hailed as a hero and he and his captains received several rewards. He commanded several other ships during the remainder of the war, and after a period of unemployment during the peace, returned to acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Florida
West Florida ( es, Florida Occidental) was a region on the northern coast of the Gulf of Mexico that underwent several boundary and sovereignty changes during its history. As its name suggests, it was formed out of the western part of former Spanish Florida ( East Florida formed the eastern part, with the Apalachicola River as the border), along with lands taken from French Louisiana; Pensacola became West Florida's capital. The colony included about two thirds of what is now the Florida Panhandle, as well as parts of the modern U.S. states of Louisiana, Mississippi, and Alabama. Great Britain established West and East Florida in 1763 out of land acquired from France and Spain after the Seven Years' War. As the newly acquired territory was too large to govern from one administrative center, the British divided it into two new colonies separated by the Apalachicola River. British West Florida included the part of formerly Spanish Florida which lay west of the Apalachicola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Elliot
Jean Elliot (April 1727 – 29 March 1805), also known as Jane Elliot, was a Scottish poet. She wrote one of the most famous versions of ''The Flowers of the Forest'', a song lamenting the Scottish army's defeat in the Battle of Flodden. Published in 1776, it is her only surviving work. The lyrics are set to an earlier tune c. 1615–1625 in the John Skene of Halyards Manuscript as "Flowres of the Forrest." Biography Daughter of Sir Gilbert Elliot, Jean was born in 1727 at Minto House in Teviotdale. During the Jacobite rising of 1745, when a party of Jacobites came to arrest her influential father, Jean received and entertained the unwelcomed officers at Minto House with such calmness, courtesy and composure that she was able to convince them that her father was not within reach when he was actually hiding himself among Minto crags, not far from the Minto House. While Miss Elliot had many admirers, she never married. From 1782 to 1804 she resided in Brown's Square, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city status in the United Kingdom, city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council. Portsmouth is the most densely populated city in the United Kingdom, with a population last recorded at 208,100. Portsmouth is located south-west of London and south-east of Southampton. Portsmouth is mostly located on Portsea Island; the only English city not on the mainland of Great Britain. Portsea Island has the third highest population in the British Isles after the islands of Great Britain and Ireland. Portsmouth also forms part of the regional South Hampshire, South Hampshire conurbation, which includes the city of Southampton and the boroughs of Eastleigh, Fareham, Gosport, Havant and Waterlooville. Portsmouth is one of the world's best known ports, its history can be traced to Roman Britain, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Naval Academy
The Royal Naval Academy was a facility established in 1733 in Portsmouth Dockyard to train officers for the Royal Navy. The founders' intentions were to provide an alternative means to recruit officers and to provide standardised training, education and admission. In 1806 it was renamed the Royal Naval College and in 1816 became the Royal Naval College and the School for Naval Architecture. It was closed as a training establishment for officer entrants in 1837. Training In 1733, a shoreside facility was established in the dockyard for 40 recruits. A comprehensive syllabus provided theoretical and practical experience in the dockyard and at sea. Graduates of the Academy could earn two years of sea time as part of their studies, and would be able to take the lieutenant's examination after four years at sea instead of six. The Academy did not, however, achieve the objective of becoming the preferred path to becoming a naval officer; the traditional means of a sea-going "apprentic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Kempenfelt
Rear-Admiral Richard Kempenfelt (1718 – 29 August 1782) was a British rear admiral who gained a reputation as a naval innovator. He is best known for his victory against the French at the Second Battle of Ushant and for his death when accidentally sank at Portsmouth the following year. He was born at Westminster. His father, a Swede, was a professional soldier in the British service. Naval career Richard Kempenfelt was commissioned a lieutenant in January 1741. He saw service in the West Indies, taking part in the capture of Portobelo during the War of Jenkins' Ear. In 1746 he returned to Britain, and from then until 1780, when he was made rear admiral, he saw active service in the East Indies with Sir George Pocock and in various quarters of the world. In 1779 he was made Chief of Staff or Captain of the Fleet under Admiral Sir Charles Hardy on which was to lead a hastily assembled fleet to oppose an invasion of England set to begin with the destruction of the Ports ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Brydges Rodney, 1st Baron Rodney
Admiral George Brydges Rodney, 1st Baron Rodney, KB ( bap. 13 February 1718 – 24 May 1792), was a British naval officer. He is best known for his commands in the American War of Independence, particularly his victory over the French at the Battle of the Saintes in 1782. It is often claimed that he was the commander to have pioneered the tactic of breaking the line. Rodney came from a distinguished but poor background, and went to sea at the age of fourteen. His first major action was the Second Battle of Cape Finisterre in 1747. He made a large amount of prize money during the 1740s, allowing him to purchase a large country estate and a seat in the House of Commons of Great Britain. During the Seven Years' War, Rodney was involved in a number of amphibious operations such as the raids on Rochefort and Le Havre and the Siege of Louisbourg. He became well known for his role in the capture of Martinique in 1762. Following the Peace of Paris, Rodney's financial situat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlisle Peace Commission
The Carlisle Peace Commission was a group of British peace commissioners who were sent to North America in 1778 to negotiate terms with the rebellious Continental Congress during the American Revolutionary War. The commission carried an offer of self-rule, including parliamentary representation within the British Empire. The Second Continental Congress, aware that British troops were about to be withdrawn from Philadelphia, insisted on demanding full independence, which the commission was not authorised to grant. The Peace Commission marked the first time that the British government formally agreed to negotiate with Congress. A previous informal attempt at negotiation, now known as the Staten Island Peace Conference, had taken place in 1776. Background The first attempt at negotiation between Great Britain and the rebellious Thirteen Colonies after the outbreak in April 1775 of the American War of Independence took place in September 1776, when a committee from the Second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of the United States, fighting began on April 19, 1775, followed by the Lee Resolution on July 2, 1776, and the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776. The American Patriots were supported by the Kingdom of France and, to a lesser extent, the Dutch Republic and the Spanish Empire, in a conflict taking place in North America, the Caribbean, and the Atlantic Ocean. Established by royal charter in the 17th and 18th centuries, the American colonies were largely autonomous in domestic affairs and commercially prosperous, trading with Britain and its Caribbean colonies, as well as other European powers via their Caribbean entrepôts. After British victory over the French in the Seven Years' War in 1763, tensions between the motherla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the List of islands of the British Isles, second-largest island of the British Isles, the List of European islands by area, third-largest in Europe, and the List of islands by area, twentieth-largest on Earth. Geopolitically, Ireland is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Ireland), which covers five-sixths of the island, and Northern Ireland, which is part of the United Kingdom. As of 2022, the Irish population analysis, population of the entire island is just over 7 million, with 5.1 million living in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million in Northern Ireland, ranking it the List of European islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
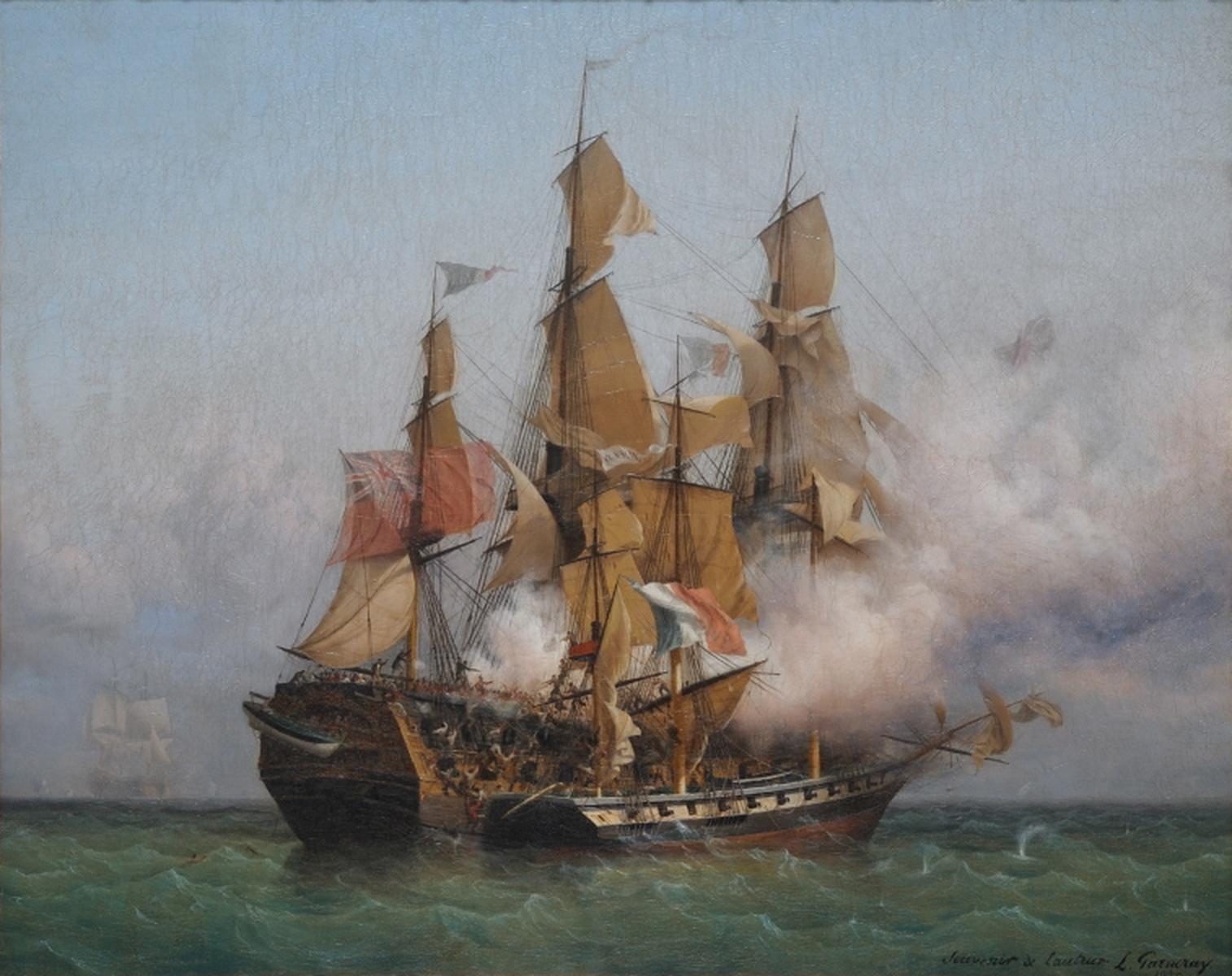
François Thurot
François Thurot (22 July 1727 at Nuits-Saint-Georges near Dijon in eastern France – 28 February 1760 off the Isle of Man) was a French privateer, merchant naval captain and smuggler who raided British shipping during the Seven Years' War. Early years He may have been the son of the postmaster at Nuits-St-GeorgesThurot family tree by Danièle Calder accessed 2007-12-04 or his grandfather was Captain O'Farrell from who had served in the Irish Brigade of the French army. As a teenager Thurot rebelled against a [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or delegated authority issued commissions, also referred to as a letter of marque, during wartime. The commission empowered the holder to carry on all forms of hostility permissible at sea by the usages of war. This included attacking foreign vessels and taking them as prizes, and taking prize crews as prisoners for exchange. Captured ships were subject to condemnation and sale under prize (law), prize law, with the proceeds divided by percentage between the privateer's sponsors, shipowners, captains and crew. A percentage share usually went to the issuer of the commission (i.e. the sovereign). Privateering allowed sovereigns to raise revenue for war by mobilizing privately owned armed ships and sailors to supplement state power. For participants, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied somewhat. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), armoured frigates were developed as powerful ironclad warships, the term frigate was used because of their single gun deck. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the frigate designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War the name 'frigate' was reintroduced to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2009.jpg)







