|
Johann Eglof Von Knöringen
Johann Eglof von Knöringen (25 July 1537 – 4 June 1575) was Prince-Bishop of Augsburg from 1573 to 1575. Biography Johann Eglof von Knöringen was born in Kreßberg on July 25, 1537. 1537 was the same year that the Catholic clergy were expelled from the city of Augsburg.Artikel „Johann Eglof von Knoeringen“ von Friedrich Roth in: Allgemeine Deutsche Biographie , herausgegeben von der Historischen Kommission bei der Bayerischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, Band 50 (1905), S. 683–684, Digitale Volltext-Ausgabe in Wikisource , URL: http://de.wikisource.org/w/index.php?title=ADB:Johann_Eglof_von_Knoeringen&oldid=1016538 (Version vom 27. Oktober 2011, 04:54 Uhr UTC) When he was 13 years old, he was sent to the University of Ingolstadt. He later studied at the University of Freiburg, where he studied under Heinrich Glarean and Johann Hartung. In 1553, he received rich benefices in Würzburg, Freising, and Augsburg. In the 1550s, he traveled widely in Rome, Vienna, northern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince-Bishopric Of Augsburg
The Prince-Bishopric of Augsburg (german: Fürstbistum Augsburg; Hochstift Augsburg) was one of the prince-bishoprics of the Holy Roman Empire, and belonged to the Swabian Circle. It should not be confused with the larger diocese of Augsburg, over which the prince-bishop exercised only spiritual authority. The city of Augsburg proper, after it gained free imperial status, was a separate entity and constitutionally and politically independent of the prince-bishopric of the same name. The prince-bishopric covered some 2365 km2 and had approximately 100,000 inhabitants at the time it was annexed to Bavaria in the course of the German mediatization. History Medieval period Nothing authentic is known about the history of the Augsburg Church during the centuries immediately succeeding the collapse of Roman power in Germany and the turbulence of the great migrations, but it survived. It is true that two catalogues of the Bishops of Augsburg, dating from the eleventh and twelfth c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
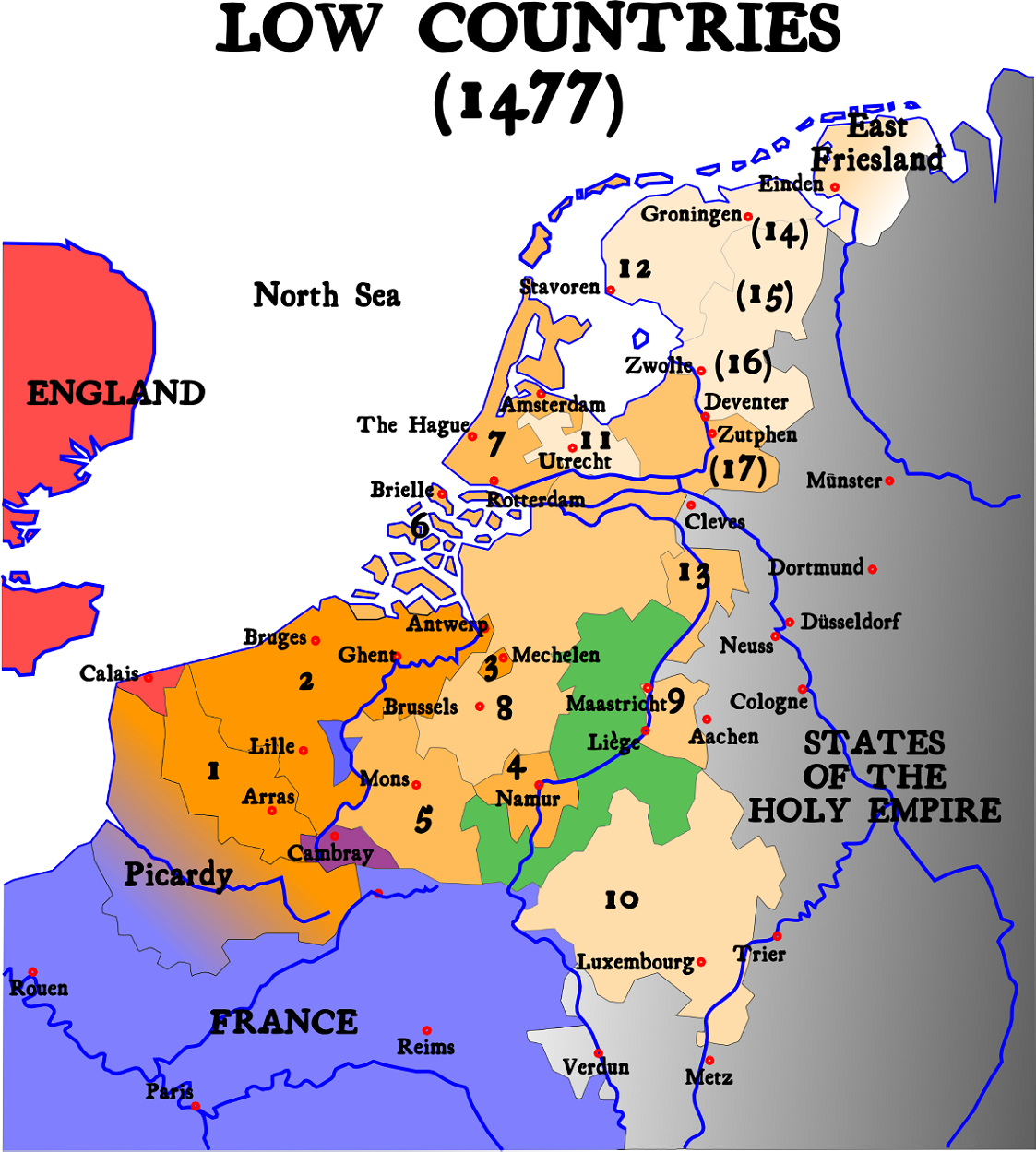
Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord (French Flanders and French Hainaut) and Pas-de-Calais (Artois). Also within this area were semi-independent fiefdoms, mainly ecclesiastical ones, such as Liège, Cambrai and Stavelot-Malmedy. The Seventeen Provinces arose from the Burgundian Netherlands, a number of fiefs held by the House of Valois-Burgundy and inherited by the Habsburg dynasty in 1482, and held by Habsburg Spain from 1556. Starting in 1512, the Provinces formed the major part of the Burgundian Circle. In 1581, the Seven United Provinces seceded to form the Dutch Republic. Composition After the Habsburg emperor Charles V had re-acquired the Duchy of Guelders from Duke William of Jülich-Cleves-Berg by the 1543 Treaty of Venlo, the Seventeen Provinces comprised: #th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1537 Births
__NOTOC__ Year 1537 ( MDXXXVII) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events January–June * January ** Bigod's Rebellion, an uprising by Roman Catholics against Henry VIII of England, is crushed. ** Battle of Ollantaytambo: Emperor Manco Inca Yupanqui is victorious against the Spanish and their Indian allies led by Hernando Pizarro. * March – Diego de Almagro successfully charges Manco Inca's siege of Cuzco, thereby saving his antagonists, the Pizarro brothers. * March 12 – Recife is founded by the Portuguese, in Brazil. * April – Spanish conquest of the Muisca: Bacatá, the main settlement of the Muisca Confederation, is conquered by Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada, effectively ending the Confederation in the Colombian Eastern Andes. * April 1 – The Archbishop of Norway Olav Engelbrektsson flees from Trondheim to Lier, Belgium. * June 2 – Pope Paul III publishes the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marquard Von Berg
Marquard von Berg (1528 – 29 January 1591) was Prince-Bishopric of Augsburg, Prince-Bishop of Augsburg from 1575 to 1591. Biography Marquard von Berg was born in Öpfingen in 1528. At the age of 13, he was sent to study at the University of Ingolstadt, where he remained until 1545.:de:Marquard II. vom Berg, Article from German Wikipedia Starting in 1548, he studied law at the University of Padua and the University of Pavia. In 1551, he interrupted his studies to take over the parish church in Langweid am Lech. He then completed his studies, graduating in 1554. In 1559 he became Provost (religion), provost of Bamberg Cathedral. He was elected Prince-Bishopric of Augsburg, Prince-Bishop of Augsburg on 26 July 1575 and Pope Gregory XIII confirmed his appointment on 24 September 1575. He was Holy Orders, ordained as a Priesthood (Catholic Church), priest on 8 December 1575. Michael Dornvogel, auxiliary bishop of Augsburg, consecrated him as a bishop on 15 January 1576. He died ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Truchsess Von Waldburg
Otto Truchsess von Waldburg (25 February 1514 – 2 April 1573) was Prince-Bishop of Augsburg from 1543 until his death and a Cardinal of the Catholic Church. Childhood and Education Otto was born at Scheer Castle to the Swabian noble House of Waldburg, which, for their support in the German Peasants' War was vested with the title of a hereditary Imperial Seneschal (''Truchsess'') by Emperor Charles V in 1526. Designated for an ecclesiastical career, he studied at the Universities of Tübingen, Dole, Padua, Bologna, where he received his degree of Doctor of Theology in 1534, and Pavia. He was a fellow student of Cristoforo Madruzzo, Stanislaus Hosius and Viglius van Zwichem. At an early age he had received canonries at Trent, Speyer, and Augsburg. In 1541 he was appointed Imperial councillor and acted as a strong advocate of the Catholic faith against the Protestant Reformation at the 1542 Reichstag of Speyer. Thereafter, while on an embassy to Rome, was made a papal chamberla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is called episcopacy. Organizationally, several Christian denominations utilize ecclesiastical structures that call for the position of bishops, while other denominations have dispensed with this office, seeing it as a symbol of power. Bishops have also exercised political authority. Traditionally, bishops claim apostolic succession, a direct historical lineage dating back to the original Twelve Apostles or Saint Paul. The bishops are by doctrine understood as those who possess the full priesthood given by Jesus Christ, and therefore may ordain other clergy, including other bishops. A person ordained as a deacon, priest (i.e. presbyter), and then bishop is understood to hold the fullness of the ministerial priesthood, given responsibility b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consecrated
Consecration is the solemn dedication to a special purpose or service. The word ''consecration'' literally means "association with the sacred". Persons, places, or things can be consecrated, and the term is used in various ways by different groups. The origin of the word comes from the Latin stem ''consecrat'', which means dedicated, devoted, and sacred. A synonym for consecration is sanctification; its antonym is desecration. Buddhism Images of the Buddha and bodhisattvas are ceremonially consecrated in a broad range of Buddhist rituals that vary depending on the Buddhist traditions. Buddhābhiseka is a Pali and Sanskrit term referring to these consecration rituals. Christianity In Christianity, consecration means "setting apart" a person, as well as a building or object, for God. Among some Christian denominations there is a complementary service of "deconsecration", to remove a consecrated place of its sacred character in preparation for either demolition or sale for s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dillingen An Der Donau
Dillingen or Dillingen an der Donau (Dillingen at the Danube) is a town in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany. It is the administrative center of the district of Dillingen. Besides the town of Dillingen proper, the municipality encompasses the villages of Donaualtheim, Fristingen, Hausen, Kicklingen, Schretzheim and Steinheim. Schretzheim is notable for its 6th to 7th century Alemannic cemetery, 630 row graves in an area of 100 by 140 metres. History The counts of Dillingen ruled from the 10th to the 13th century; in 1258 the territory was turned over to the Prince Bishops of Augsburg. After the Reformation, the prince-bishops of Augsburg moved to the Catholic city of Dillingen and made it one of the centers of the Counter-Reformation. In 1800, during the War of the Second Coalition, the armies of the French First Republic, under command of Jean Victor Moreau, fought Habsburg regulars and Württemberg contingents, under the general command of Pál Kray. Kray had taken refuge in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
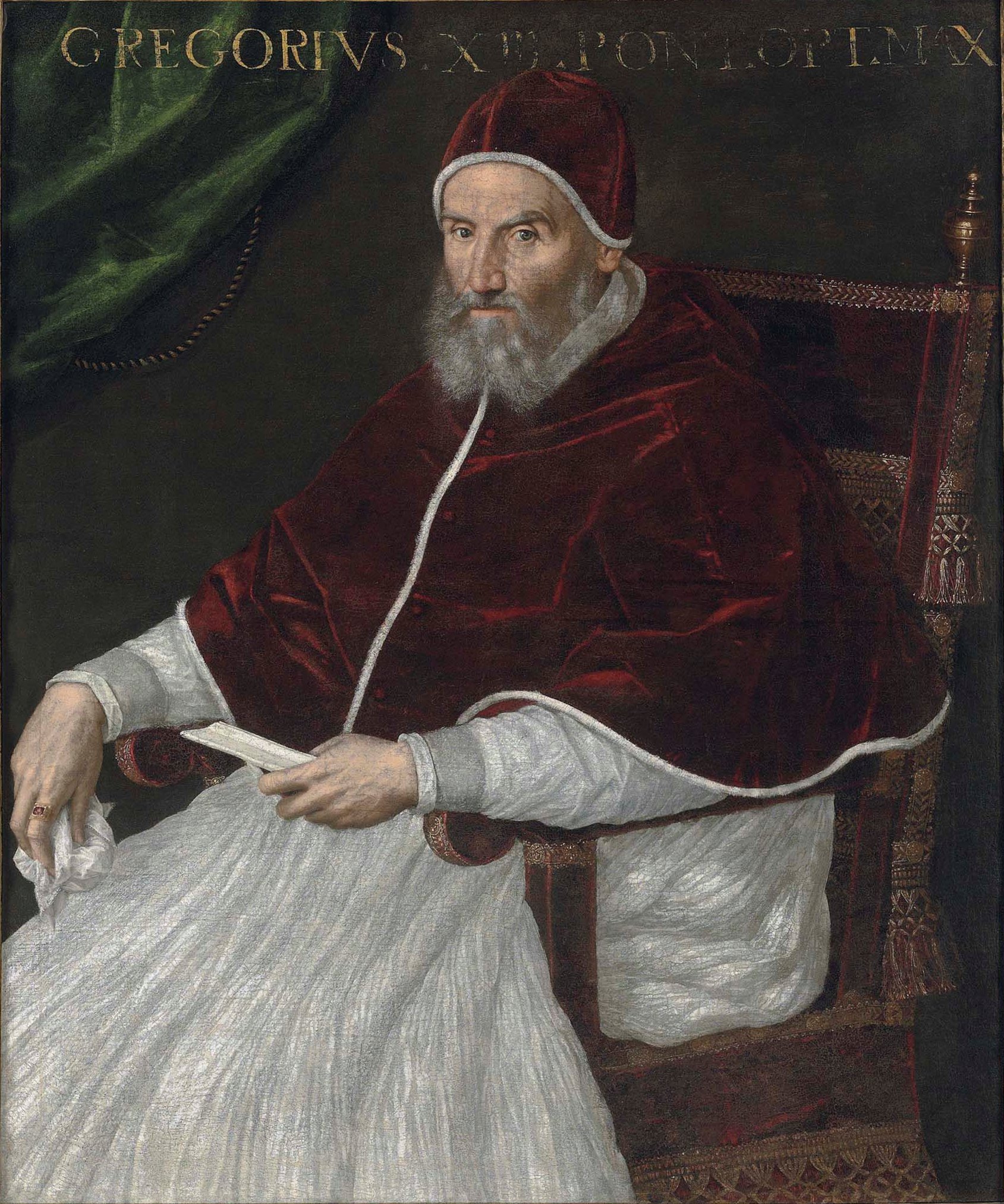
Pope Gregory XIII
Pope Gregory XIII ( la, Gregorius XIII; it, Gregorio XIII; 7 January 1502 – 10 April 1585), born Ugo Boncompagni, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 13 May 1572 to his death in April 1585. He is best known for commissioning and being the namesake for the Gregorian calendar, which remains the internationally accepted civil calendar to this day. Early biography Youth Ugo Boncompagni was born the son of Cristoforo Boncompagni (10 July 1470 – 1546) and of his wife Angela Marescalchi in Bologna, where he studied law and graduated in 1530. He later taught jurisprudence for some years, and his students included notable figures such as Cardinals Alexander Farnese, Reginald Pole and Charles Borromeo. He had an illegitimate son after an affair with Maddalena Fulchini, Giacomo Boncompagni, but before he took holy orders, making him the last Pope to have left issue. Career before papacy At the age of 36 he was summoned to Rome by Pope Paul III (1534� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesuits
The Society of Jesus ( la, Societas Iesu; abbreviation: SJ), also known as the Jesuits (; la, Iesuitæ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rome. It was founded in 1540 by Ignatius of Loyola and six companions, with the approval of Pope Paul III. The society is engaged in evangelization and apostolic ministry in 112 nations. Jesuits work in education, research, and cultural pursuits. Jesuits also give retreats, minister in hospitals and parishes, sponsor direct social and humanitarian ministries, and promote Ecumenism, ecumenical dialogue. The Society of Jesus is consecrated under the patron saint, patronage of Madonna della Strada, a title of the Blessed Virgin Mary, and it is led by a Superior General of the Society of Jesus, Superior General. The headquarters of the society, its Curia, General Curia, is in Rome. The historic curia of Ignatius is now part of the attached to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protonotary Apostolic
In the Roman Catholic Church, protonotary apostolic (PA; Latin: ''protonotarius apostolicus'') is the title for a member of the highest non-episcopal college of prelates in the Roman Curia or, outside Rome, an honorary prelate on whom the pope has conferred this title and its special privileges. An example is Prince Georg of Bavaria (1880–1943), who became in 1926 Protonotary by papal decree. History In late antiquity, there were in Rome seven regional notaries who, on the further development of the papal administration and the accompanying increase of the notaries, remained the supreme palace notaries of the papal chancery (''notarii apostolici'' or ''protonotarii''). In the Middle Ages, the protonotaries were very high papal officials and were often raised directly from this office to the cardinalate. Originally numbering seven, Pope Sixtus V (1585–90) increased their number to twelve. Their importance gradually diminished, and at the time of the French Revolution, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Pius V
Pope Pius V ( it, Pio V; 17 January 1504 – 1 May 1572), born Antonio Ghislieri (from 1518 called Michele Ghislieri, O.P.), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1566 to his death in May 1572. He is venerated as a saint of the Catholic Church. He is chiefly notable for his role in the Council of Trent, the Counter-Reformation, and the standardization of the Roman Rite within the Latin Church. Pius V declared Thomas Aquinas a Doctor of the Church. As a cardinal, Ghislieri gained a reputation for putting orthodoxy before personalities, prosecuting eight French bishops for heresy. He also stood firm against nepotism, rebuking his predecessor Pope Pius IV to his face when he wanted to make a 13-year-old member of his family a cardinal and subsidize a nephew from the papal treasury. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |