|
Jiyin Commandery
Jiyin Commandery ( zh, 濟陰郡) was a commandery in historical China from Han dynasty to Tang dynasty The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdo ..., located in what is now southwestern Shandong province. In 144 BC, the Liang Kingdom was divided into five states. Jiyin, one of the successor kingdoms, was ruled by Liu Bushi. Bushi died only one year later, and his kingdom was converted to a commandery under imperial administration. In 25 BC, Liu Kang (劉康), the second son of Emperor Yuan of Han, Emperor Yuan, was granted title "King of Dingtao", as the territory of Jiyin became the Dingtao Kingdom (定陶國). Kang's son Xin succeeded to the imperial throne in 8 BC as the Emperor Ai of Han, Emperor Ai, and Dingtao was granted to Liu Jing (劉景), another member of the imperi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commandery (China)
A jùn (郡) was a historical administrative division of China from the Eastern Zhou (c. 7th century BCE) until the early Tang dynasty (c. 7th century CE). It is usually translated as a commandery. Countries around China have adopted administrative divisions based on or named after the ''jùn''. History and development China Eastern Zhou During the Eastern Zhou's Spring and Autumn period from the 8th to 5th centuries BCE, the larger and more powerful of the Zhou's vassal states—including Qin, Jin and Wei—began annexing their smaller rivals. These new lands were not part of their original fiefs and were instead organized into counties (''xiàn''). Eventually, jun were developed as marchlands between the major realms. Despite having smaller populations and ranking lower on the official hierarchies, the jun were larger and boasted greater military strength than the counties. As each state's territory gradually took shape in the 5t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Later Han
The ''Book of the Later Han'', also known as the ''History of the Later Han'' and by its Chinese name ''Hou Hanshu'' (), is one of the Twenty-Four Histories and covers the history of the Han dynasty from 6 to 189 CE, a period known as the Later or Eastern Han. The book was compiled by Fan Ye and others in the 5th century during the Liu Song dynasty, using a number of earlier histories and documents as sources. Background In 23 CE, Han dynasty official Wang Mang was overthrown by a peasants' revolt known as the Red Eyebrows. His fall separates the Early (or Western) Han Dynasty from the Later (or Eastern) Han Dynasty. As an orthodox history, the book is unusual in being completed over two hundred years after the fall of the dynasty. Fan Ye's primary source was the ''Dongguan Han Ji'' (東觀漢記; "Han Records of the Eastern Lodge"), which was written during the Han dynasty itself. Contents References Citations Sources ; General * Chavannes, Édouard (1906) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Song
The ''Book of Song'' (''Sòng Shū'') is a historical text of the Liu Song Dynasty of the Southern Dynasties of China. It covers history from 420 to 479, and is one of the Twenty-Four Histories, a traditional collection of historical records. It was written in 492–493 by Shen Yue from the Southern Qi dynasty (479–502). The work contained 100 volumes at the time that it was written, but some volumes were already missing by the time of the Song Dynasty. Later editors reconstructed those volumes by taking material from the '' History of the Southern Dynasties'', plus a few works such as the ''Historiette of Gao'' by Gao Jun, though many of those volumes were no longer in their original condition. History The ''Book of Song'' was based on records compiled beginning in the Liu Song. He Chentian 何承天 (370-447) was commissioned by the imperial court of the time in 439. He compiled biographies and also treatises on astronomy and music. Compilation was later continued by S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Wei
Wei (), known in historiography as the Northern Wei (), Tuoba Wei (), Yuan Wei () and Later Wei (), was founded by the Tuoba (Tabgach) clan of the Xianbei. The first of the Northern dynasties, it ruled northern China from 386 to 535 during the period of the Northern and Southern dynasties. Described as "part of an era of political turbulence and intense social and cultural change", the Northern Wei dynasty is particularly noted for unifying northern China in 439, bringing to an end the chaotic Sixteen Kingdoms period, and strengthening imperial control over the rural landscape via reforms in 485. This was also a period of introduced foreign ideas, such as Buddhism, which became firmly established. The Northern Wei were referred to as "Plaited Barbarians" (索虜 ''suolu'') by writers of the Southern dynasties, who considered themselves the true upholders of Chinese culture. During the Taihe period (477–499), Empress Dowager Feng and Emperor Xiaowen instituted sweeping re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Wen Of Song
Emperor Wen of (Liu) Song ((劉)宋文帝, (Liu) Song Wen-di) (407 – 16 March 453), personal name Liu Yilong (劉義隆), childhood name Che'er (車兒), was an emperor of the Liu Song dynasty of China. He was the third son of the dynastic founder Emperor Wu (Liu Yu). After his father's death in 422, Liu Yilong's eldest brother Liu Yifu took the throne as Emperor Shao. In 424, a group of officials, believing Emperor Shao to be unfit to be emperor, deposed Emperor Shao and placed Liu Yilong on the throne as Emperor Wen. In his 29 years of rule, Emperor Wen largely continued the grand plan of his father and some of the land policies of the Jin Dynasty. The period, called the " Yuanjia administration" (), is seen as a period of prosperity and strength, because of the emperor's diligence and ability to find capable and honest officials to serve in his administration. However, Emperor Wen was faulted for making repeated failed attempts to attack rival Northern Wei and using the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Song
Song, known as Liu Song (), Former Song (前宋) or Song of (the) Southern Dynasty (南朝宋) in historiography, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China and the first of the four Northern and Southern dynasties#Southern dynasties, Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period. It succeeded the Jin dynasty (266–420)#Eastern Jin (317–420), Eastern Jin dynasty and preceded the Southern Qi, Southern Qi dynasty. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Wu of Song, Liu Yu (Emperor Wu; 363–422 CE), whose surname together with "Song" forms the common name for the dynasty, the Liu Song. This appellation is used to distinguish it from a later dynasty of the same name, the Song dynasty (960–1279 CE, ruled by the House of Zhao). Although the Liu Song has also at times been referred to as the "Southern Song", the name is now mainly used to refer to the Song dynasty after 1127 CE. The Liu Song was a time when there was much internal turmoil. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor An Of Jin
Emperor An of Jin (; 383 – 28 January 419), personal name Sima Dezong (), was an emperor of the Eastern Jin Dynasty (266–420) in China. He was described as so developmentally disabled that he was unable to speak, clothe himself, or be able to express whether he was hungry or full. He was created crown prince in 387 and ascended the throne in 397. Because of his disability, the actual power was controlled by his uncle, Sima Daozi, Prince of Kuaiji. During his reign, regents and warlords dominated the Jin regime. Revolts by various governors also ravaged the land. From 398 to 403, there were constant revolts and civil war campaigns. In 403, the Jin regime was usurped by the warlord Huan Xuan, and while Emperor An was restored in 404, the Jin Dynasty was nearing its end. With the warlord Liu Yu as the actual power, Jin destroyed Southern Yan and Later Qin, greatly expanding its territory. However, with Liu Yu up in the north, the renegade governor of Guang Province (廣州, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
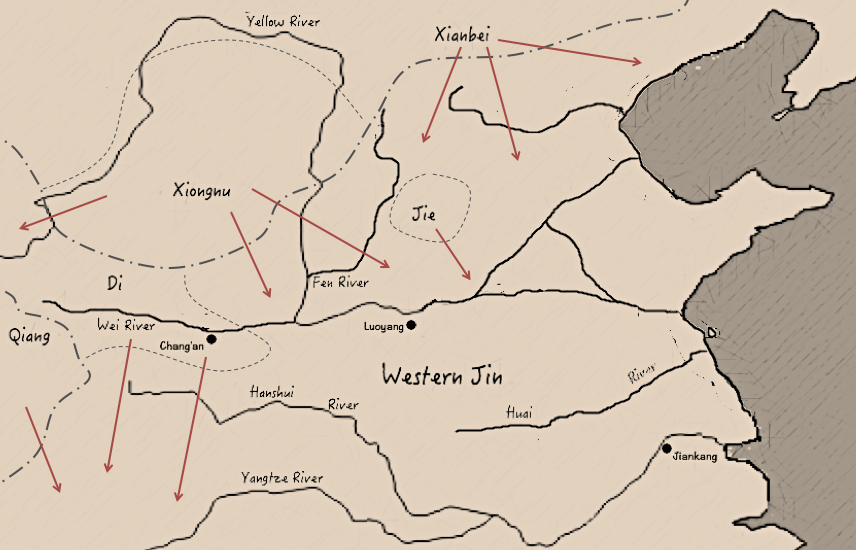
Sixteen Kingdoms
The Sixteen Kingdoms (), less commonly the Sixteen States, was a chaotic period in Chinese history from AD 304 to 439 when northern China fragmented into a series of short-lived dynastic states. The majority of these states were founded by the " Five Barbarians", non- Han peoples who had settled in northern and western China during the preceding centuries, and had launched a series of rebellions and invasions against the Western Jin dynasty in the early 4th century. However, several of the states were founded by the Han people, and all of the states—whether ruled by Xiongnu, Xianbei, Di, Jie, Qiang, Han, or others—took on Han-style dynastic names. The states frequently fought against both one another and the Eastern Jin dynasty, which succeeded the Western Jin in 317 and ruled southern China. The period ended with the unification of northern China in 439 by the Northern Wei, a dynasty established by the Xianbei Tuoba clan. This occurred 19 years after the Easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disaster Of Yongjia
The Disaster of Yongjia () refers to an event in Chinese history that occurred in 311 CE (5th year of the ''Yongjia'' era of the reign of Emperor Huai of Jin, hence the name), when forces of the Xiongnu-led Han Zhao dynasty captured and sacked Luoyang, the capital of the Western Jin dynasty. After this victory, Han Zhao's army committed a massacre of the city's inhabitants, killing the Jin crown prince, a host of ministers, and over 30,000 civilians. They also burnt down the palaces and dug up the Jin dynasty's mausoleums. This was a pivotal event during the Upheaval of the Five Barbarians and the early Sixteen Kingdoms era, and it played a major role in the fall of the Western Jin dynasty in 316 CE. The Disaster of Yongjia was a major impetus for the mass migration and expansion of Han people into southern China. Many clan genealogies ascribe this event in particular as the reason why their ancestors moved from the north to places in Fujian, Guangdong, etc. See also *Invasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jin Dynasty (265–420)
Jin is a toneless pinyin romanization of various Chinese names and words. These have also been romanized as Kin and Chin (Wade–Giles). "Jin" also occurs in Japanese and Korean. It may refer to: States Jìn 晉 * Jin (Chinese state) (晉國), major state of the Zhou dynasty, existing from the 11th century BC to 376 BC * Jin dynasty (266–420) (晉朝), also known as Liang Jin and Sima Jin * Jin (Later Tang precursor) (晉國; 907–923), Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period * Later Jin (Five Dynasties) (後晉; 936–947), Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period Jīn 金 * Jin dynasty (1115–1234) (金朝), also known as the Jurchen Jin * Later Jin (1616–1636) (後金; 1616–1636), precursor of the Qing dynasty Others * Jin (Korean state) (辰國), precursor of the Jinhan Confederation * Balhae (698–713), originally known as Jin (震) Places * Jin Prefecture (Shanxi) (晉州), a former Chinese prefecture centered on present-day Linfen, Shanxi * Jin Prefecture ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jian'an Era
Emperor Xian of Han (2 April 181 – 21 April 234), personal name Liu Xie (劉協), courtesy name Bohe, was the 14th and last emperor of the Eastern Han dynasty in China. He reigned from 28 September 189 until 11 December 220. Liu Xie was a son of Liu Hong (Emperor Ling) and was a younger half-brother of his predecessor, Liu Bian (Emperor Shao). In 189, at the age of eight, he became emperor after the warlord Dong Zhuo, who had seized control of the Han central government, deposed Emperor Shao and replaced him with Liu Xie. The newly enthroned Liu Xie, historically known as Emperor Xian, was in fact a puppet ruler under Dong Zhuo's control. In 190, when a coalition of regional warlords launched a punitive campaign against Dong Zhuo in the name of freeing Emperor Xian, Dong Zhuo ordered the destruction of the imperial capital, Luoyang, and forcefully relocated the imperial capital along with its residents to Chang'an. After Dong Zhuo's assassination in 192, Emperor Xian fell un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |