 |
Jie Of Xia
King Jie (; traditionally 1728–1675 BC) was the 17th and last ruler of the Xia dynasty of China. He is traditionally regarded as a tyrant and oppressor who brought about the collapse of a dynasty.劉煒/著. 002(2002) Chinese civilization in a new light 中華文明傳真#1 原始社會:東方的曙光. Publishing Company. . pg 150. Around 1600 BC, Jie was defeated by Tang of Shang, bringing an end to the Xia Dynasty that lasted about 500 years, and a rise to the new Shang Dynasty.王恆偉. (2005) (2006) 中國歷史講堂 #1 遠古至春秋. 中華書局. . p 26. Etymology ''Jié'' ( variant: ) (< : ) ( ZS) means "outstanding" and later "hero"; insides Chinese, it is cog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
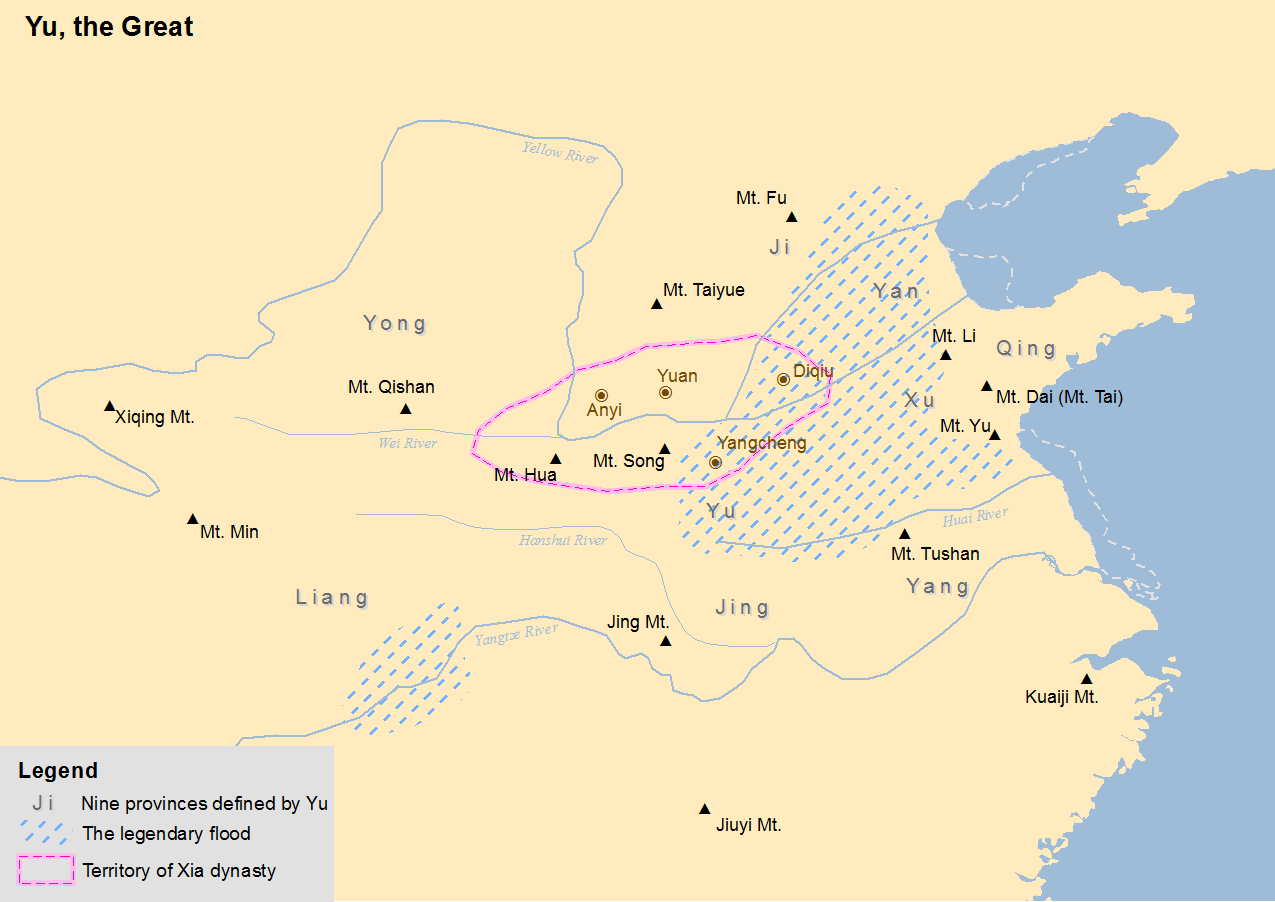 |
Xia Dynasty
The Xia dynasty () is the first dynasty in traditional Chinese historiography. According to tradition, the Xia dynasty was established by the legendary Yu the Great, after Shun, the last of the Five Emperors, gave the throne to him. In traditional historiography, the Xia was later succeeded by the Shang dynasty. There are no contemporaneous records of the Xia, who are not mentioned in the oldest Chinese texts, since the earliest oracle bone inscriptions date from the late Shang period (13th century BC). The earliest mentions occur in the oldest chapters of the ''Book of Documents'', which report speeches from the early Western Zhou period and are accepted by most scholars as dating from that time. The speeches justify the Zhou conquest of the Shang as the passing of the Mandate of Heaven and liken it to the succession of the Xia by the Shang. That political philosophy was promoted by the Confucian school in the Eastern Zhou period. The succession of dynasties was incorporat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Wei (state)
Wei (; ; Old Chinese: *') was one of the seven major states during the Warring States period of ancient China. It was created from the three-way Partition of Jin, together with Han and Zhao. Its territory lay between the states of Qin and Qi and included parts of modern-day Henan, Hebei, Shanxi, and Shandong. After its capital was moved from Anyi to Daliang (present-day Kaifeng) during the reign of King Hui, Wei was also called Liang (). History Foundation Surviving sources trace the ruling house of Wei to the Zhou royalty: Gao, Duke of Bi (), was a son of King Wen of Zhou. His descendants took their surname, Bi, from his fief. After the destruction of Bi, Bi Wan () escaped to Jin, where he became a courtier of Duke Xian's, accompanying his personal carriage. After a successful military expedition, Bi Wan was granted Wei, from which his own descendants then founded the house of Wei. Spring and Autumn period Jin's political structure was drastically changed aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Pyramid
A pyramid (from el, πυραμίς ') is a structure whose outer surfaces are triangular and converge to a single step at the top, making the shape roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be trilateral, quadrilateral, or of any polygon shape. As such, a pyramid has at least three outer triangular surfaces (at least four faces including the base). The square pyramid, with a square base and four triangular outer surfaces, is a common version. A pyramid's design, with the majority of the weight closer to the ground and with the pyramidion at the apex, means that less material higher up on the pyramid will be pushing down from above. This distribution of weight allowed early civilizations to create stable monumental structures. Civilizations in many parts of the world have built pyramids. The largest pyramid by volume is the Great Pyramid of Cholula, in the Mexican state of Puebla. For thousands of years, the largest structures on Earth were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Zhenxun
Zhenxun () was the last capital for the pre historical Chinese Xia dynasty. There is a consensus among many Chinese scholars that the Erlitou site about 20 km east of central Luoyang Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River (Henan), Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the ... is identified as Zhenxun. References Ancient Chinese capitals {{Portal, China, History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Da Liu Ren
Da Liu Ren is a form of Chinese calendrical astrology dating from the later Warring States period. It is also a member of the Three Styles () of divination, along with Qi Men Dun Jia () and Taiyi (). Li Yang describes Da Liu Ren as the highest form of divination in China. This divination form is called Da Liu Ren because the heavenly stem ''rén'' (), indicating "yang water", appears six times in the Sexagenary cycle. In order, it appears in ''rénshēn'' (), ''rénwǔ'' (), ''rénchén'' (), ''rényín'' (), ''rénzǐ'' (), and ''rénxū'' (). In the words of a contemporary Chinese master of Da Liu Ren, the six ''rén'' indicate an entire movement of the sexagenary cycle, during which an something may appear, rise to maturity and then decline and disappear. Thus the six ''rén'' indicate the life cycle of phenomena. There is a homonym in the Chinese language which carries the meaning of pregnancy, and so the six ''rén'' also carry the meaning of the birth of a phenomenon. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Duke Of Zhou
Dan, Duke Wen of Zhou (), commonly known as the Duke of Zhou (), was a member of the royal family of the early Zhou dynasty who played a major role in consolidating the kingdom established by his elder brother King Wu. He was renowned for acting as a capable and loyal regent for his young nephew King Cheng, and for successfully suppressing the Rebellion of the Three Guards and establishing firm rule of the Zhou dynasty over eastern China. He is also a Chinese culture hero credited with writing the ''I Ching'' and the ''Book of Poetry'', and establishing the ''Rites of Zhou''. Life His personal name was Dan (). He was the fourth son of King Wen of Zhou and Queen Tai Si. His eldest brother Bo Yikao predeceased their father (supposedly a victim of cannibalism); the second-eldest defeated the Shang Dynasty at the Battle of Muye around 1046 BC, ascending the throne as King Wu. King Wu distributed many fiefs to his relatives and followers and Dan received the ancestral territory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Posthumous Name
A posthumous name is an honorary name given mostly to the notable dead in East Asian culture. It is predominantly practiced in East Asian countries such as China, Korea, Vietnam, Japan, and Thailand. Reflecting on the person's accomplishments or reputation, the title is assigned after death and essentially replaces their name used during life. Although most posthumous names are assigned to royalty, some posthumous names are given to honor significant people without hereditary titles, such as courtiers or military generals. A posthumous name should not be confused with era names (年號), regnal names (尊號), or temple names (廟號). Format One or more adjectives are inserted before the deceased's title to make their posthumous name. Posthumous names are exclusively owned on the state level, although not necessarily on a broader national level. The name of the state or domain of the owner is added to avoid ambiguity from multiple similar posthumous names. The Chinese lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Rites Of Zhou
The ''Rites of Zhou'' (), originally known as "Officers of Zhou" () is a work on bureaucracy and organizational theory. It was renamed by Liu Xin to differentiate it from a chapter in the '' Book of History'' by the same name. To replace a lost work, it was included along with the '' Book of Rites'' and the '' Etiquette and Ceremonial'' becoming one of three ancient ritual texts (the "Three Rites") listed among the classics of Confucianism. In comparison with other works of its type, the Rite's ruler, though a sage, does not create the state, but merely organizes a bureaucracy. It could not have been composed during the Western Zhou, and was probably based on Warring States period societies. Michael Puett and Mark Edward Lewis compares its system of duties and ranks to the "Legalism" of Shang Yang. Authorship The book appeared in the middle of the 2nd century BC, when it was found and included in the collection of Old Texts in the library of Prince Liu De (; d. 130 BC), a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Kangxi Dictionary
The ''Kangxi Dictionary'' ( (Compendium of standard characters from the Kangxi period), published in 1716, was the most authoritative dictionary of Chinese characters from the 18th century through the early 20th. The Kangxi Emperor of the Qing dynasty ordered its compilation in 1710 in order to improve on earlier dictionaries, to show his concern for Confucian culture, and to foster the standardization of the writing system. The dictionary takes its name from the Emperor's era name. The dictionary was the largest of the traditional dictionaries, containing 47,035 characters. Some 40% of them are graphic variants, however, while others are dead, archaic, or found only once. Fewer than a quarter of the characters it contains are now in common use. The ''Kangxi Dictionary'' is available in many forms, from Qing dynasty block print editions, to reprints in traditional Chinese bookbinding, to modern revised editions with essays in Western-style hardcover, to a digitized Internet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |