|
Jhalakati
Jhalokati, also spelled Jhalokathi, ( bn, ঝালকাঠি) is a district in southern Bangladesh. It is located in the Barisal Division and covers an area of 758.06 km2 It is bounded by Barisal district to the north and east, Barguna district and the Bishkhali river in the south, Lohagara Upazila and Pirojpur district to the west. Annual average temperatures: maximum 33.3 °C, minimum 12.1 °C; annual rainfall 2506 mm. The main rivers in this district are Bishkhali, Dhanshiri, Gabkhan, Sugandha, Jangalia, Bamanda and Bajitpur. "''পেয়ারা আর শীতলপাটি, এই নিয়ে ঝালকাঠি"'' "''(Jhalokathi, The land of tasty Guava and Shitolpati)"'' is the official moto of the district. History The 2021 Bangladesh ferry fire occurred on the Sugandha River near the town. Subdivisions The district is administratively subdivided into 4 upazilas, these are: # Jhalokati Sadar Upazila # Kathalia Upazila # Nalchity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jhalokati Sadar Upazila
Jhalakati Sadar (or Jhalokathi Sadar, bn, ঝালকাঠি সদর) is an upazila of Jhalokati District in the Division of Barisal, Bangladesh. Geography Jhalakathi Sadar is located at . It has 36,504 households and a total area 204.48 km2. History In the 17th-century, Kirtinarayan Basu, the former Raja of Chandradwip, settled in Jhalkathi's Keora village after converting to Islam. He founded the Baklai family of Keora who possessed land in the Chandradwip and Salimabad parganas and particularly, taluqs in Mathbaria and Morrelganj. His son and successor, Mahmud Hasan Taqi, founded a mosque in the village of Keora. Taqi had three sons; Mahmud Ghazanfar Ali, Mahmud Sadeq and Ejaz Mahmud. Mahmud Sadeq's son was Qutb Mahmud, whose son was Jan Mahmud, whose son was Rahmat Ali Baklai, whose son was Mahmud Ali Baklai, whose son was Amud Ali Baklai, whose son was Ahmad Ali Balkai, whose son was Abdul Majid Baklai. In total, Kirtinarayan's descendants number over one thou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabkhan Channel
Gabkhan Channel is a canal connecting Pirojpur District of Bangladesh with Jhalakati District. The canal was excavated during the British period in 1918 to connect the Sandha River Samdha is a village development committee in Mahottari District in the Janakpur Zone of south-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census The 1991 Nepal census was a widespread national census conducted by the Nepal Central Bureau of ... of Pirojpur district and the Sugandha River of Jhalakati district with a view to reducing the distance on the Dhaka-Mongla and Chittagong-Mongla river routes by about . This canal length is 18 kilometers. It is known as the Suez Canal of Bangladesh, starting from Kawkhali near the village of Ashoa. References Barishal Division {{Barisal-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barisal Division
Barishal Division is one of the eight administrative divisions of Bangladesh. Located in the south-central part of the country, it has an area of , and a population of 8,325,666 at the 2011 Census. It is the least populous Division within the entirety of Bangladesh. It is bounded by Dhaka Division on the north, the Bay of Bengal on the south, Chittagong Division on the east and Khulna Division on the west. The administrative capital, Barisal city, lies in the Padma River delta on an offshoot of the Arial Khan River. Barisal division is criss-crossed by numerous rivers that earned it the nickname ''Dhan-Nodi-Khal, Ei tin-e Borishal'' (rice, river and canal built Barishal). History Early Middle Ages In early times the Barisal region was composed of an amalgamation of marshlands formed by the merging of islands brought into existence and built up by alluvial soils washed down the great channels of the combined Brahmaputra-Ganges-Meghna river systems. In the early 13th centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nalchity Upazila
Nalchity ( bn, নলছিটি) is an upazila of Jhalokati District in the division of Barisal, Bangladesh. History Some family members of Isa Khan moved from Sarail to Nalchity. Abdul Ghani Khan, a 14th-generation descendant of Isa Khan, is the current head of this branch of the family. The region later became a free looting field and slave trading zone for Magh and Portuguese pirates. In 1654, Shah Shuja built two forts in one night in the village of Shujabad to better control the region, and to resist and suppress the piracy. One was built with mud, and the other with bricks. The ruins of the forts can be seen from the Barisal-Jhalokati highway. In 1924, the British authorities established a thana (police administrative headquarters) in Nalchity. On 7 March 1927, the British Raj police killed twenty Bengali Muslims in a mosque compound in the village of Kulkati. The event is now known as the Ponabalia Massacre. During the Bangladesh Liberation War of 1971, the Pakistan Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajapur Upazila
Rajapur ( bn, রাজাপুর) is an upazila (sub-district) of southern Bangladesh's Jhalokati District, part of the Barisal Division. Geography Rajapur is located at . It has 28,131 households and a total area of 164.33 km2. History The current Rajapur Upazila is home to many archeological sites such as forts and mosques. The Indrapasha Qila was thought to have been constructed during the reign of the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb in the late seventeenth century. It was a fort built to suppress the Maghs and Portuguese pirates around the Bay of Bengal. In 1664, Shaista Khan was appointed as the Mughal governor of Bengal to defeat the pirates. Khan constructed many forts with his accomplice, Muhammad Azam, including the Indrapasha Qila. The Qila no longer stands, existing only as a soil mound. In the same period, Keshwar Singh, who is thought to have been a Mughal general, constructed the triple mosques of Angaria Khan Bari. A triple mosque was also constructed in the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
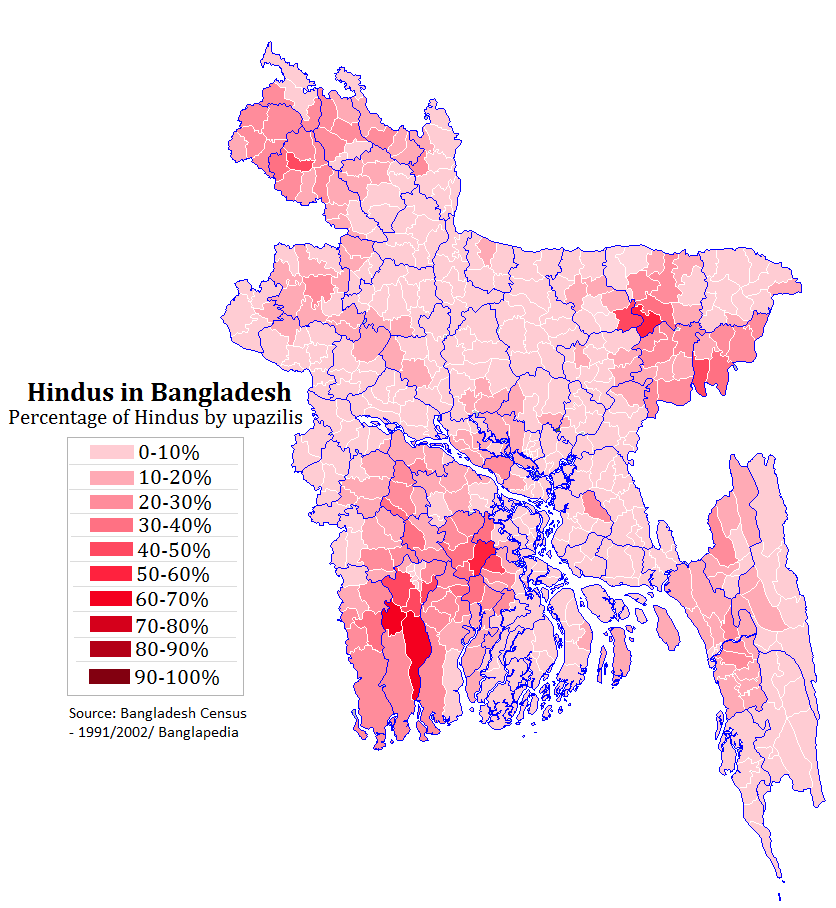
Hinduism In Bangladesh
Hinduism is the second largest religious affiliation in People's Republic of Bangladesh, as according to the Official 2022 Census of Bangladesh, approximately just 13.1 million people responded that they were Hindus, constituting 7.95% out of the total population of 165.15 million people. In terms of population, Bangladesh is the third-largest Hindu populated country of the world, just after India and Nepal. Hinduism is the second-largest religion in 61 out of 64 districts of Bangladesh, but there is no Hindu majority district in Bangladesh. Culture In nature, Bangladeshi Hinduism closely resembles the forms and customs of Hinduism practiced in the neighboring Indian state of West Bengal, with which Bangladesh (at one time known as East Bengal) was united until the partition of India in 1947. The vast majority of Hindus in Bangladesh are Bengali Hindus. Goddess ( Devi) – usually venerated as Durga or Kali – is widely revered, often alongside her consort Shiva. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangladesh Bureau Of Statistics
The Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (BBS) is the centralized official bureau in Bangladesh for collecting statistics on demographics, the economy, and other facts about the country and disseminating the information. History Although independent statistical programs had existed in the country before, they were often incomplete or produced inaccurate results, which led the Government of Bangladesh establishing an official bureau in August 1974, by merging four of the previous larger statistical agencies, the Bureau of Statistics, the Bureau of Agriculture Statistics, the Agriculture Census Commission and the Population Census Commission. In July 1975, the Statistics and Informatics Division was created under the Planning Ministry (Bangladesh) and tasked to oversee the BBS. Between 2002 and 2012, the division remained abolished but was later reinstated. The Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics is headquartered in Dhaka Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), formerly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam In Bangladesh
Islam is the state religion of the People's Republic of Bangladesh. According to the 2022 census, Bangladesh had a population of about 150 million Muslims, or 91.04% of its total population of million. The majority of Bangladeshis are Sunni, and follow the Hanafi school of fiqh. Religion is an integral part of Bangladeshi identity. Despite being a Muslim-majority country, Bangladesh is a ''de facto'' secular state. In the 9th century, Arab Muslims established commercial as well as religious connection within the region before the conquest, mainly through the coastal regions as traders and primarily via the ports of Chittagong. Region was largely inhabited by different animistic tribes. Arab navigation in the region was the result of the Muslim reign over the Indus delta. In the early 13th century, Muhammad bin Bakhtiyar Khalji conquered Western and part of Northern Bengal, and established the first Muslim kingdom in Bengal. Islamic missionaries in India achieved their grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being Rishabhadeva, whom the tradition holds to have lived millions of years ago, the twenty-third ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha, whom historians date to the 9th century BCE, and the twenty-fourth ''tirthankara'' Mahavira, around 600 BCE. Jainism is considered to be an eternal ''dharma'' with the ''tirthankaras'' guiding every time cycle of the cosmology. The three main pillars of Jainism are ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''anekāntavāda'' (non-absolutism), and ''aparigraha'' (asceticism). Jain monks, after positioning themselves in the sublime state of soul consciousness, take five main vows: ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''satya'' (truth), ''asteya'' (not stealing), ''brahmacharya'' (chastity), and ''aparigraha'' (non-possessiveness). These pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious .... It is the Major religious groups, world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in Christianity by country, 157 countries and territories, and believe that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God, whose coming as the Messiah#Christianity, messiah was Old Testament messianic prophecies quoted in the New Testament, prophesied in the Hebrew Bible (called the Old Testament in Christianity) and chronicled in the New Testamen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |