|
Jezreelite
Tel Jezreel ( he, יִזְרְעֶאל ''Yīzrə‘e’l'', "God will sow") is an archaeological site in the eastern Jezreel Valley in northern Israel. The city of Jezreel served as a main fortress of the Kingdom of Israel under king Ahab in the 9th century BCE. Biblical references Prior to the division of the United Kingdom of Israel, the city was the hometown of Ahinoam, second wife of King David, Michal, Saul's daughter, being the first, Ahinoam being his second, and Abigail, widow of Nabal, being his third (). According to the First Book of Kings, the royal palace of King Ahab, "one of the most famous of the royal residences of the kings of Israel", was in Jezreel, adjacent to the vineyard of Naboth (). Ahab's capital remained in Samaria. According to , following the prophet Elijah's victory over the prophets of Ba'al at Mount Carmel, Elijah instructs Ahab to return home to Jezreel, where he would be reporting on events to Jezebel, his wife, but "the hand of the Lord wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
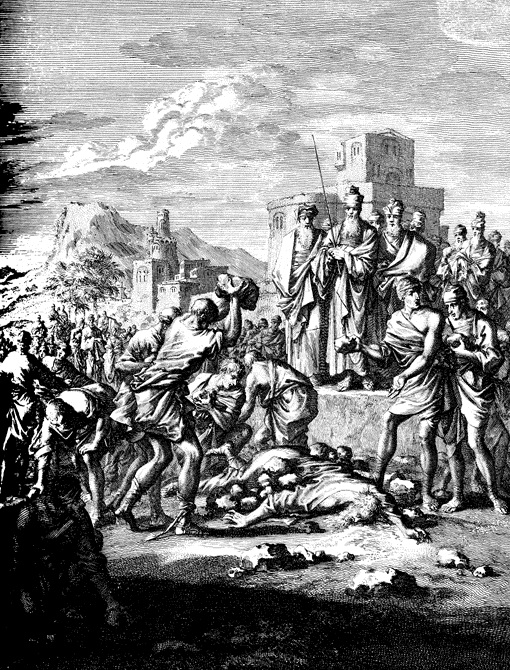
Naboth
Naboth ( he, נבות) was a citizen of Jezreel. According to the Book of Kings in the Hebrew Bible, he was executed by Queen Jezebel so that her husband Ahab could possess his vineyard. Narrative 1 Kings 21:1-16 states that Naboth owned a vineyard, in proximity to King Ahab's palace in the city of Jezreel. Because of this, Ahab desired to acquire the vineyard so that he could use it for a vegetable (or herb) garden. Since he inherited the land from his ancestors, Naboth refused to sell it to Ahab. According to the Mosaic law, the law forbade the permanent selling of land. Frustrated at not being able to procure the vineyard, Ahab returned to his palace and went to bed without eating anything. His wife, Jezebel, after learning the reason for his being upset, asked mockingly, "Are you not the king?" She then said that she would obtain the vineyard for him. To do so, she sent a letter, under Ahab's name, to the elders and nobles of Naboth's city, instructing them to entrap Nabo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jehoram Of Israel
Jehoram ( ''Yəhōrām''; also Joram) was the ninth king of the northern Kingdom of Israel ( 2 Kings 8:16, 2 Kings 8:25–28). He was the son of Ahab and Jezebel, and brother to Ahaziah and Athaliah. According to 2 Kings, 2 Kings 8:16, in the fifth year of Jehoram of Israel, (another) Jehoram became king of Judah. The author of Kings speaks of both Jehoram of Israel and Jehoram of Judah in the same passage. Reign Jehoram began to reign in Israel in the 18th year of Jehoshaphat of Judah and ruled 12 years ( 2 Kings 3:1). William F. Albright dated his reign to 849–842 BCE, whereas E. R. Thiele proposed 852–841 BCE. Unlike his predecessors, Jehoram did not worship Ba'al, and he removed the pillar of Baal, probably a special pillar which Ahab had erected near his palace at Jezreel for his own and Jezebel's worship. However, the writer of 2 Kings says that he still "followed in the ways of Jeroboam, son of Nebat, who led the Israelites to sin". With Jehoshaphat of Judah, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Ussishkin
David Ussishkin (Hebrew: דוד אוסישקין; born 1935) is an Israeli archaeologist and professor emeritus of archaeology. Biography David Ussishkin was born in Jerusalem. Ussishkin is the grandson of the Zionist leader Menachem Ussishkin. He studied at Gymnasia Rehavia, in Rehavia and served in the Israel Defense Forces between 1953 and 1955 in the Giv'ati Brigade. He studied archaeology and Jewish History at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem between 1955 and 1966. Received his B.A. in 1958, his Master of Arts degree in Archaeology and Jewish History in 1962 (with distinction) and his Ph. D. in 1966. His Doctoral Thesis on "The Neo-Hittite Monuments, their Dating and Style" was written under the guidance of professor Yigael Yadin. Beginning in 1966 and until his retirement in 2004 he taught archaeology of Israel and Hittite art at the University of Tel Aviv, receiving full professorship in 1985. Academic and archaeology career From 1966 to 2004, he taught archaeology at Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Books Of Kings
The Book of Kings (, '' Sēfer Məlāḵīm'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Kings) in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. It concludes the Deuteronomistic history, a history of Israel also including the books of Joshua, Judges and Samuel. Biblical commentators believe the Books of Kings were written to provide a theological explanation for the destruction of the Kingdom of Judah by Babylon in c. 586 BCE and to provide a foundation for a return from Babylonian exile.Sweeney, p1/ref> The two books of Kings present a history of ancient Israel and Judah, from the death of King David to the release of Jehoiachin from imprisonment in Babylon—a period of some 400 years (). Scholars tend to treat the books as consisting of a first edition from the late 7th century BCE and of a second and final edition from the mid-6th century BCE.Fretheim, p. 7 Contents The Jerusalem Bible divides the two Books of Kings into eight sections: *1 Kings 1:1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abigail
Abigail () was an Israelite woman in the Hebrew Bible married to Nabal; she married the future King David after Nabal's death ( 1 Samuel ). Abigail was David's second wife, after Saul and Ahinoam's daughter, Michal, whom Saul later married to Palti, son of Laish, when David went into hiding. Abigail became the mother of one of David's sons, who is listed in the Book of Chronicles under the name ''Daniel'', in the Masoretic Text of the Books of Samuel as ''Chileab,'' and in the Septuagint text of 2 Samuel 3:3 as Δαλουια, ''Dalouia''. Her name is spelled Abigal in in the American Standard Version. Name Derived from the Hebrew word ''ab,'' "father", and the Hebrew root ''g-y-l'', "to rejoice," the name Abigail has a variety of possible meanings including "my father's joy" and "source of joy". Biblical narrative In 1 Samuel 25, Nabal demonstrates ingratitude towards David, the son of Jesse (from the tribe of Judah), and Abigail attempts to placate David, in order to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vineyard
A vineyard (; also ) is a plantation of grape-bearing vines, grown mainly for winemaking, but also raisins, table grapes and non-alcoholic grape juice. The science, practice and study of vineyard production is known as viticulture. Vineyards are often characterised by their ''terroir'', a French term loosely translating as "a sense of place" that refers to the specific geographical and geological characteristics of grapevine plantations, which may be imparted to the wine itself. History The earliest evidence of wine production dates from between 6000 and 5000 BC. Wine making technology improved considerably with the ancient Greeks but it wasn't until the end of the Roman Empire that cultivation techniques as we know them were common throughout Europe. In medieval Europe the Church was a staunch supporter of wine, which was necessary for the celebration of the Mass. During the lengthy instability of the Middle Ages, the monasteries maintained and developed viticultural prac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samaria (ancient City)
Samaria ( he, שֹׁמְרוֹן, translit=Šōmrōn; grc, Σαμάρεια, ''Samareia''; ar, السامرة, ''as-Samira'') was a city in the historical region of Samaria that served as the capital of the northern Kingdom of Israel during the 9th and 8th centuries BCE. Towards the end of the 8th century BCE, possibly in 722 BCE, Samaria was captured by the Neo-Assyrian Empire and became an administrative center under Assyrian, Babylonian, and Persian rule. During the early Roman period, the city was expanded and fortified by Herod the Great, who renamed it “ Sebastia” in honor of emperor Augustus. The ancient city's hill is where the modern Palestinian village of Sebastia, which retains its Roman name, is located. The archeological site, subject to a shared Israeli-Palestinian control, is located on the hill's eastern slope. Etymology Samaria's biblical name, ''Šōmrōn'' (שֹׁמְרוֹן), means "watch" or "watchman" in Hebrew. The Bible derives the name from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baal
Baal (), or Baal,; phn, , baʿl; hbo, , baʿal, ). ( ''baʿal'') was a title and honorific meaning "owner", "lord" in the Northwest Semitic languages spoken in the Levant during Ancient Near East, antiquity. From its use among people, it came to be applied to gods. Scholars previously associated the theonym with solar god, solar cults and with a variety of unrelated patron deity, patron deities but inscriptions have shown that the name Ba'al was particularly associated with the storm god, storm and fertility god Hadad and his local manifestations. The Hebrew Bible includes use of the term in reference to various Levantine mythology, Levantine deities, often with application towards Hadad, who was decried as a false god. That use was taken over into Christianity and Islam, sometimes under the form Beelzebub in demonology. Etymology The spelling of the English term "Baal" derives from the Koine Greek, Greek ''Báal'' ( which appears in the New Testament and Septuagint, and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Carmel
Mount Carmel ( he, הַר הַכַּרְמֶל, Har haKarmel; ar, جبل الكرمل, Jabal al-Karmil), also known in Arabic as Mount Mar Elias ( ar, link=no, جبل مار إلياس, Jabal Mār Ilyās, lit=Mount Saint Elias/Elijah), is a coastal mountain range in northern Israel stretching from the Mediterranean Sea towards the southeast. The range is a UNESCO biosphere reserve. A number of towns are situated there, most notably the city of Haifa, Israel's third largest city, located on the northern and western slopes. Etymology The word ''karmel'' means "garden-land" and is of uncertain origin. It is either a compound of ''kerem'' and ''el'', meaning "vineyard of El (deity), God" or a clipping of ''kar male,'' meaning "full kernel." Martin Jan Mulder suggested a third etymology, that of ''kerem + l'' with the lamed a wiktionary:sufformative, sufformative, but this is considered unlikely as evidence for the existence of a lamed sufformative is weak. Geography and geology T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yizre'el
Yizre'el ( he, יִזְרְעֶאל) is a kibbutz in north-eastern Israel. Located in the Jezreel Valley near Afula, it falls under the jurisdiction of Gilboa Regional Council. In it had a population of . History After the Mamluks took control of the area in the late 13th century, the Mamluk sultan Zahir Baybars defeated the Mongols in the Battle of Ain Jalut at a site just west of what was then Zir'in, where Yizre'el now stands. The kibbutz was established in August 1948 by demobilised Palmach soldiers in the remains of the depopulated Palestinian village of Zir'in. In 1950, it moved North-West of the Zir'in village site. It was one of the first kibbutzim to abandon the system of children sleeping in communal houses, instead allowing them to live with their parents. It was named after the ancient city of Jezreel, which was located in the area allotted to the tribe of Issachar (Joshua 19:18). Economy A major branch of the kibbutz economy is Maytronics, which manufactures a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google Maps
Google Maps is a web mapping platform and consumer application offered by Google. It offers satellite imagery, aerial photography, street maps, 360° interactive panoramic views of streets ( Street View), real-time traffic conditions, and route planning for traveling by foot, car, bike, air (in beta) and public transportation. , Google Maps was being used by over 1 billion people every month around the world. Google Maps began as a C++ desktop program developed by brothers Lars and Jens Rasmussen at Where 2 Technologies. In October 2004, the company was acquired by Google, which converted it into a web application. After additional acquisitions of a geospatial data visualization company and a real-time traffic analyzer, Google Maps was launched in February 2005. The service's front end utilizes JavaScript, XML, and Ajax. Google Maps offers an API that allows maps to be embedded on third-party websites, and offers a locator for businesses and other organizations in numero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eunuch
A eunuch ( ) is a male who has been castrated. Throughout history, castration often served a specific social function. The earliest records for intentional castration to produce eunuchs are from the Sumerian city of Lagash in the 2nd millennium BCE. Over the millennia since, they have performed a wide variety of functions in many different cultures: courtiers or equivalent domestics, for espionage or clandestine operations, castrato singers, concubines, or sexual partners, religious specialists, soldiers, royal guards, government officials, and guardians of women or harem servants. Eunuchs would usually be servants or slaves who had been castrated to make them less threatening servants of a royal court where physical access to the ruler could wield great influence. Seemingly lowly domestic functions—such as making the ruler's bed, bathing him, cutting his hair, carrying him in his litter, or even relaying messages—could, in theory, give a eunuch "the ruler's ear" and impa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |