|
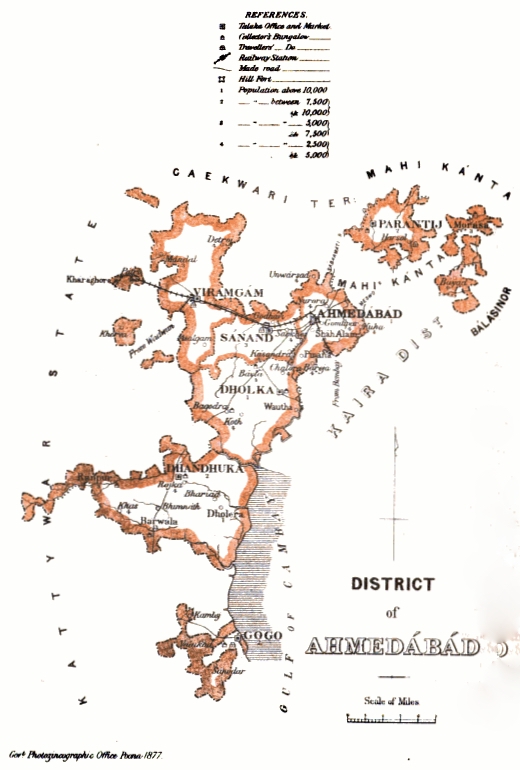
Jetalpur
Jetalpur is a town in the Ahmedabad district of the Indian state of Gujarat Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth .... It is the location of a Swaminarayan temple commissioned by Swaminarayan himself. An engineering college named Narnarayan Shastri Institute of Technology is situated in Jetalpur. References Map of Gujarat with Jetalpur marked on it Swaminarayan Sampradaya Cities and towns in Ahmedabad district {{Ahmedabad-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narnarayan Shastri Institute Of Technology
Narnarayan Shastri Institute of Technology is an engineering college in the town of Jetalpur very near to the city of Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India. The academic program of Narnarayan Shastri Institute of Technology is approved by the All India Council of Technical Education (AICTE) and is affiliated with Gujarat Technological University (GTU) About The institute is established in 2008. The institute is blessed by Acharya Shree Koshlendraprasadji Maharaj and Acharya Shree Tejendraprasadji Maharaj and is connected with Shree Swaminarayan Temple - Kalupur. It is functioning under "Swaminarayan Vividh Seva Niketan Trust - Jetalpur". It admits students from all over the Gujarat as well as other states of India to the Bachelor of Engineering. The academic program of NSIT is approved by the All India Council of Technical Education (AICTE) and is affiliated to Gujarat Technological University (GTU). At its establishment in 2008, the institute comprised Mechanical Engineering Electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
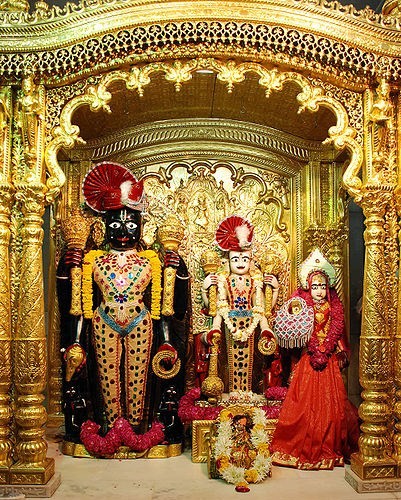
Swaminarayan Temple
Swaminarayan, the founder of the Swaminarayan Sampraday, established temples, known as ''mandirs'' (Devnagari: मन्दिर), as part of his philosophy of theism and deity worship. These mandirs are known as Swaminarayan Hindu temples. He constructed nine temples in the following cities; Ahmedabad, Bhuj, Muli, Vadtal, Junagadh, Dholera, Dholka, Gadhpur & Jetalpur. In these temples he installed images of various Hindu gods, such as NarNarayan Dev, LaxmiNarayan Dev, RadhaKrishna Dev, RadhaRaman Dev, Revti-Baldevji, Madan Mohan Dev etc. Each of these nine original temples fall either under the NarNarayan Dev Gadi, Ahmedabad or the LaxmiNarayan Dev Gadi, Vadtal depending on their geographical location. One of the most prominent features of the heritage of Swaminarayan is temple architecture. The images in the temples built by Swaminarayan are the evidence of the priority of Krishna. All of the temples constructed during his life show some form of Krishna, and all temples si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swaminarayan
Swaminarayan (IAST: ', 3 April 1781 – 1 June 1830), also known as Sahajanand Swami, was a yogi and Asceticism, ascetic, who is believed by followers to be a manifestation of God Krishna, or as the highest Theophany, manifestation of Brahman, Purushottam, and around whom the Swaminarayan Sampradaya developed. In 1800, he was initiated into the ''Uddhav'' ''sampradaya'' by his guru, Swami Ramanand, and was given the name Sahajanand Swami. Despite opposition, in 1802 Ramanand handed over the leadership of the Uddhav Sampraday to him before his death. According to the Swaminarayan-tradition, Sahajanand Swami became known as Swaminarayan, and the Uddhav Sampraday as the Swaminarayan Sampradaya, after a gathering in which he taught the Swaminarayan Mantra to his followers. He emphasized "moral, personal, and social betterment," and ''ahimsa'', and is also remembered within the sect for undertaking reforms for women and the poor, and performing non-violent yajna, yajñas (f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swaminarayan Sampradaya
The Swaminarayan Sampradaya, also known as Swaminarayan Hinduism and Swaminarayan movement, is a Hindu Vaishnava sampradaya rooted in Ramanuja's Vishishtadvaita, characterized by the worship of its charismatic founder Sahajanand Swami, better known as Swaminarayan (1781–1830), as an avatar of Krishna or as the highest manifestation of Purushottam, the supreme God. According to the tradition's lore, both the religious group and Sahajanand Swami became known as ''Swaminarayan'' after the Swaminarayan mantra, which is a compound of two Sanskrit words, swami ("master, lord") and Narayan (supreme God, Vishnu). During his lifetime, Swaminarayan institutionalized his charisma and beliefs in various ways. He constructed six mandirs to facilitate followers' devotional worship of God, and encouraged the creation of a scriptural tradition''.'' In 1826, in a legal document titled the Lekh, Swaminarayan created two dioceses, the Laxmi Narayan Dev Gadi (Vadtal Gadi) and Nar Nara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States And Territories Of India
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions. History Pre-independence The Indian subcontinent has been ruled by many different ethnic groups throughout its history, each instituting their own policies of administrative division in the region. The British Raj mostly retained the administrative structure of the preceding Mughal Empire. India was divided into provinces (also called Presidencies), directly governed by the British, and princely states, which were nominally controlled by a local prince or raja loyal to the British Empire, which held ''de facto'' sovereignty ( suzerainty) over the princely states. 1947–1950 Between 1947 and 1950 the territories of the princely states were politically integrated into the Indian union. Most were merged into existing provinces; others were organised into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth-most populous state, with a population of 60.4 million. It is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west. Gujarat's capital city is Gandhinagar, while its largest city is Ahmedabad. The Gujaratis are indigenous to the state and their language, Gujarati, is the state's official language. The state encompasses 23 sites of the ancient Indus Valley civilisation (more than any other state). The most important sites are Lothal (the world's first dry dock), Dholavira (the fifth largest site), and Gola Dhoro (where 5 uncommon seals were found). Lothal i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Districts Of India
A district ('' zila'') is an administrative division of an Indian state or territory. In some cases, districts are further subdivided into sub-divisions, and in others directly into ''tehsils'' or ''talukas''. , there are a total of 766 districts, up from the 640 in the 2011 Census of India and the 593 recorded in the 2001 Census of India. District officials include: *District Magistrate or Deputy Commissioner or District Collector, an officer of the Indian Administrative Service, in charge of administration and revenue collection *Superintendent of Police or Senior Superintendent of Police or Deputy Commissioner of Police, an officer belonging to the Indian Police Service, responsible for maintaining law and order *Deputy Conservator of Forests, an officer belonging to the Indian Forest Service, entrusted with the management of the forests, environment and wildlife of the district Each of these officials is aided by officers from the appropriate branch of the state governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmedabad District
{{Infobox settlement , name = Ahmedabad District , native_name = , native_name_lang = , settlement_type = District of Gujarat , image_skyline = Delhi Darwaja 1.jpg , imagesize = , HDI {{nobold, (2018) , blank_info_sec2 = {{increase 0.783{{cite web , title=Sub-national HDI – Area Database = 778(high) , image_alt = , image_caption = Delhi Darwaza, one of the gates to the old city , image_flag = , flag_alt = , image_seal = , seal_alt = , image_shield = , shield_alt = , nickname = Ahm , motto = save water drink beer , image_map = Ahmedabad in Gujarat (India).svg , map_alt = , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarati Language
Gujarati (; gu, ગુજરાતી, Gujarātī, translit-std=ISO, label=Gujarati script, ) is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Indian state of Gujarat and spoken predominantly by the Gujarati people. Gujarati is descended from Old Gujarati (). In India, it is one of the 22 scheduled languages of the Union. It is also the official language in the state of Gujarat, as well as an official language in the union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. As of 2011, Gujarati is the 6th most widely spoken language in India by number of native speakers, spoken by 55.5 million speakers which amounts to about 4.5% of the total Indian population. It is the 26th most widely spoken language in the world by number of native speakers as of 2007.Mikael Parkvall, "Världens 100 största språk 2007" (The World's 100 Largest Languages in 2007), in ''Nationalencyklopedin''. Asterisks mark th2010 estimatesfor the top dozen languages. Outside of Gujarat, Gujarati is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindi Language
Hindi (Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been described as a standardised and Sanskritised register of the Hindustani language, which itself is based primarily on the Khariboli dialect of Delhi and neighbouring areas of North India. Hindi, written in the Devanagari script, is one of the two official languages of the Government of India, along with English. It is an official language in nine states and three union territories and an additional official language in three other states. Hindi is also one of the 22 scheduled languages of the Republic of India. Hindi is the '' lingua franca'' of the Hindi Belt. It is also spoken, to a lesser extent, in other parts of India (usually in a simplified or pidginised variety such as Bazaar Hindustani or Haflong Hindi). Outside India, several ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Standard Time
Indian Standard Time (IST), sometimes also called India Standard Time, is the time zone observed throughout India, with a time offset of UTC+05:30. India does not observe daylight saving time or other seasonal adjustments. In military and aviation time, IST is designated E* ("Echo-Star"). It is indicated as Asia/Kolkata in the IANA time zone database. History After Independence in 1947, the Union government established IST as the official time for the whole country, although Kolkata and Mumbai retained their own local time (known as Calcutta Time and Bombay Time) until 1948 and 1955, respectively. The Central observatory was moved from Chennai to a location at Shankargarh Fort in Allahabad district, so that it would be as close to UTC+05:30 as possible. Daylight Saving Time (DST) was used briefly during the China–India War of 1962 and the Indo-Pakistani Wars of 1965 and 1971. Calculation Indian Standard Time is calculated from the clock tower in Mirzapur nearly exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postal Index Number
A Postal Index Number (PIN; sometimes redundantly a PIN code) refers to a six-digit code in the Indian postal code system used by India Post. On 15 August 2022, the PIN system celebrated its 50th anniversary. History The PIN system was introduced on 15 August 1972 by Shriram Bhikaji Velankar, an additional secretary in the Government of India's Ministry of Communications. The system was introduced to simplify the manual sorting and delivery of mail by eliminating confusion over incorrect addresses, similar place names, and different languages used by the public. PIN structure The first digit of a PIN indicates the zone, the second indicates the sub-zone, and the third, combined with the first two, indicates the sorting district within that zone. The final three digits are assigned to individual post offices within the sorting district. Postal zones There are nine postal zones in India, including eight regional zones and one functional zone (for the Indian Army). The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |