|
Jerzy Radziwiłł (1556–1600)
Prince Jerzy Radziwiłł (; 31 May 1556 – 21 January 1600) was a Polish–Lithuanian magnate and Imperial Reichsfürst from the Radziwiłł family. He was ordained a Catholic priest and later rose through the ranks as Bishop of Vilnius eventually becoming a cardinal. He was a close friend and adviser of King Sigismund III and represented his interests in front of the Pope. Raised a Calvinist, Radziwiłł was educated at the University of Leipzig. In 1572 he converted to Catholicism and became associated with the Jesuits. He continued to study at Jesuit colleges in Poznań, Vilnius, and Rome. Radziwiłł began his duties as Bishop of Vilnius in 1579. He established Vilnius Seminary in the family palace (called Kardynalia Palace after him) and helped to obtain university status for the Jesuit Academy in Vilnius. He was ordained to the priesthood (10 April 1583) and was not consecrated bishop until 26 December 1583. He was elevated to the cardinalate by Pope Gregory XIII ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
His Eminence
His Eminence (abbreviation H.Em. or HE) is a style (manner of address), style of reference for high nobility, still in use in various religious contexts. Catholicism The style remains in use as the official style or standard form of address in reference to a cardinal (Catholicism), cardinal of the Catholic Church, reflecting his status as a Prince of the Church. A longer, and more formal, title is "His [or Your when addressing the cardinal directly] Most Reverend Eminence". Patriarchs of Eastern Catholic Churches who are also cardinals may be addressed as "His Eminence" or by the style particular to Catholic patriarchs, His Beatitude. When the Grand master (order), Grand Master of the Sovereign Military Order of Malta, the head of state of their sovereign territorial state comprising the island of Malta until 1797, who had already been made a Reichsfürst (i.e., prince of the Holy Roman Empire) in 1607, became (in terms of honorary order of precedence, not in the actual churc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichsfürst
Prince of the Holy Roman Empire (, , cf. ''Fürst'') was a title attributed to a hereditary ruler, nobleman or prelate recognised by the Holy Roman Emperor. Definition Originally, possessors of the princely title bore it as immediate vassals of the Emperor who held a fief (secular or ecclesiastical) that had no suzerain except the Emperor. However, by the time the Holy Roman Empire was abolished in 1806, there were a number of holders of Imperial princely titles who did not meet these criteria. Thus, there were two main types of princes: those who exercised ''Landeshoheit'' (sovereignty within one's territory while respecting the laws and traditions of the empire) as well as an individual or shared vote in the College of Princes, and those whose title was honorary (the possessor lacking an immediate Imperial fief and/or a vote in the Imperial Diet). The first came to be reckoned as "royalty" in the sense of being treated as sovereigns, entitled to inter-marry with reignin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Sixtus V
Pope Sixtus V (; 13 December 1521 – 27 August 1590), born Felice Piergentile, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 24 April 1585 to his death, in August 1590. As a youth, he joined the Franciscan order, where he displayed talents as a scholar and preacher, and enjoyed the patronage of Pius V, who made him a Cardinal (Catholic Church), cardinal. As a cardinal, he was known as Cardinal Montalto. As Pope, he energetically rooted out corruption and lawlessness across Rome, and launched a far-sighted rebuilding programme that continues to provoke controversy, as it involved the destruction of antiquities. The cost of these works was met by heavy taxation which caused much suffering. His foreign policy was regarded as over-ambitious; he excommunicated King Henry IV of France and renewed the excommunication of Queen Elizabeth I of England. He is recognized as a significant figure of the Counter-Reformation. He is the most recent pope to date to take on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1585 Papal Conclave
The 1585 papal conclave (21–24 April), convoked after the death of Pope Gregory XIII, elected Cardinal Felice Peretti, who took the name Sixtus V. Forty-two of the sixty cardinals participated in the conclave. The absence of thirty percent of the cardinalate makes this conclave one of the most sparsely attended in the history of the modern Roman Catholic Church. Fourteen of Gregory XIII's thirty cardinals failed to attend, a startlingly high number. Proceedings The conclave began in the Vatican on 21 April, Easter Sunday. At the opening ceremonies, out of sixty living cardinals thirty-nine were in attendance. Three more arrived later, in time to cast a vote: Andreas of Austria, Ludovico Madruzzo of Trent, and Guido Luca Ferrero of Vercelli. Two factions quickly formed. The first was led by Cardinal Ferdinando de' Medici and the second by Luigi d'Este (grandson of King Louis XII of France). They were willing to combine to make a pope, but it depended on whether they could agre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vilnius University
Vilnius University ( Lithuanian: ''Vilniaus universitetas'') is a public research university, which is the first and largest university in Lithuania, as well as one of the oldest and most prominent higher education institutions in Central and Eastern Europe. Today, it is Lithuania's leading research institution. The university was founded in 1579 as the Jesuit Academy (College) of Vilnius by Stephen Báthory. It was the third oldest university (after the Cracow Academy and the Albertina) in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Due to the failure of the November Uprising (1830–1831), the university was closed down and suspended its operation until 1919. In the aftermath of World War I, the university saw failed attempts to restart it by the local Poles, Lithuanians, and by invading Soviet forces. It finally resumed operations as Polish Stefan Batory University in August 1919. After the Soviet invasion of Poland in September 1939, the university was briefly administered by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kardynalia Palace
Kardynalia Palace is a no-longer-existing palace in Vilnius, located at the corner of Pilies Street, Pilies and St. John's Streets, right next to the university Church of St. Johns, Vilnius, Church of St. Johns. The palace was constructed between the 16th and 17th centuries for the Radziwiłł family. One of its owners at the time was Cardinal and Bishop of Vilnius Jerzy Radziwiłł (cardinal), Jerzy Radziwiłł, from whom the palace derived its name. The palace remained in the possession of the Radziwiłł family, Radziwiłłs for about 300 years, and in the 19th century, it became a government building. Damaged in 1944, it was not rebuilt after World War II, and in 1956, the palace's remnants were demolished to make way for residential buildings. History From 1540, Mikołaj Radziwiłł the Black rented a complex of buildings at the Castle and St. John's Streets from the Vilnius canons, previously occupied by the Bishop of Kyiv (Roman Catholic), Bishop of Kyiv Jan Filipowicz. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vilnius Seminary
The Vilnius St. Joseph Seminary is a Roman Catholic seminary in Vilnius, Lithuania. It traces its history to an institution founded by Cardinal Jerzy Radziwiłł (1556–1600), Jurgis Radvila in 1582. After being closed and reopened several times, it was re-established in 1993 by Audrys Bačkis, Juozas Bačkis, the archbishop of Vilnius, and moved to a new building in 1997. The seminary prepares candidates for priesthood in the Vilnius Archdiocese and the dioceses of Panevėžys and Kaišiadorys. Over the course of the six-year programme, candidates study philosophy, theology, sociology, church history and teachings, educational theory, singing, psychology, languages, art history, and rhetoric. Its graduates receive a baccalaureate from the Pontifical Lateran University. References External links Official website Universities and colleges in Vilnius Catholic seminaries in Lithuania 1582 establishments in Europe Educational institutions established in the 1580s {{C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
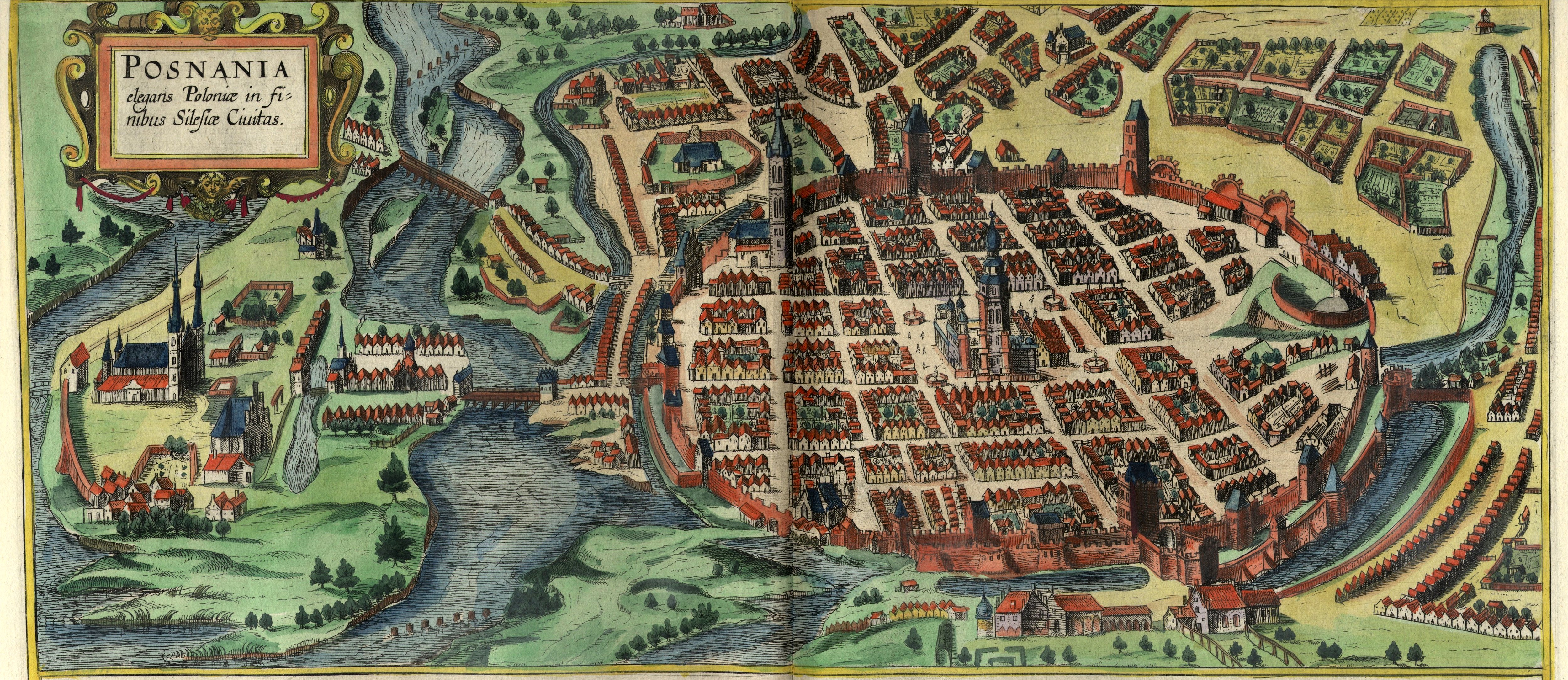
Poznań
Poznań ( ) is a city on the Warta, River Warta in west Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business center and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John's Fair, Poznań, Saint John's Fair (''Jarmark Świętojański''), traditional St. Martin's croissant, Saint Martin's croissants and a local dialect. Among its most important heritage sites are the Renaissance in Poland, Renaissance Old Town, Poznań Town Hall, Town Hall and Poznań Cathedral. Poznań is the fifth-largest List of cities and towns in Poland#Cities, city in Poland. As of 2023, the city's population is 540,146, while the Poznań metropolitan area (''Metropolia Poznań'') comprising Poznań County and several other communities is inhabited by over 1.029 million people. It is one of four historical capitals of medieval Poland and the ancient capital of the Greater Poland region, currently the administrative capital of the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesuits
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rome. It was founded in 1540 by Ignatius of Loyola and six companions, with the approval of Pope Paul III. The Society of Jesus is the largest religious order in the Catholic Church and has played significant role in education, charity, humanitarian acts and global policies. The Society of Jesus is engaged in evangelization and apostolic ministry in 112 countries. Jesuits work in education, research, and cultural pursuits. They also conduct retreats, minister in hospitals and parishes, sponsor direct social and humanitarian works, and promote Ecumenism, ecumenical dialogue. The Society of Jesus is consecrated under the patron saint, patronage of Madonna della Strada, a title of the Blessed Virgin Mary, and it is led by a Superior General of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.Gerald O'Collins, O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites#Churches, ''sui iuris'' (autonomous) churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and Eparchy, eparchies List of Catholic dioceses (structured view), around the world, each overseen by one or more Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishops. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the Papal supremacy, chief pastor of the church. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Leipzig
Leipzig University (), in Leipzig in Saxony, Germany, is one of the world's oldest universities and the second-oldest university (by consecutive years of existence) in Germany. The university was founded on 2 December 1409 by Frederick I, Elector of Saxony and his brother William II, Margrave of Meissen, and originally comprised the four scholastic faculties. Since its inception, the university has engaged in teaching and research for over 600 years without interruption. Famous alumni include Angela Merkel, Gottfried Wilhelm von Leibniz, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Leopold von Ranke, Friedrich Nietzsche, Robert Schumann, Richard Wagner, Tycho Brahe, Georgius Agricola. The university is associated with ten Nobel laureates, most recently with Svante Pääbo who won the Nobel Prize for Medicine in 2022. History Founding and development until 1900 The university was modelled on the University of Prague, from which the German-speaking faculty members withdrew to Leipzi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calvinist
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Protestantism, Continental Reformed Christian, Presbyterianism, Presbyterian, Congregationalism, Congregational, and Waldensians traditions, as well as parts of the Calvinistic Methodist, Methodist, Reformed Anglican Church, Anglican (known as "Episcopal" in some regions) and Reformed Baptists, Baptist traditions. Reformed theology emphasizes the Biblical authority, authority of the Bible and the Sovereignty of God in Christianity, sovereignty of God, as well as covenant theology, a framework for understanding the Bible based on God's covenants with people. Reformed churches emphasize simplicity in worship. Several forms of ecclesiastical polity are exercised by Reformed churches, including presbyterian polity, presbyterian, Congregational polity, congregational, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |