|
Jerzy Neyman
Jerzy Neyman (April 16, 1894 – August 5, 1981; born Jerzy Spława-Neyman; ) was a Polish mathematician and statistician who spent the first part of his professional career at various institutions in Warsaw, Poland and then at University College London, and the second part at the University of California, Berkeley. Neyman first introduced the modern concept of a confidence interval into statistical hypothesis testing and co-revised Ronald Fisher's null hypothesis testing (in collaboration with Egon Pearson). Life and career He was born into a Polish family in Bendery, in the Bessarabia Governorate of the Russian Empire, the fourth of four children of Czesław Spława-Neyman and Kazimiera Lutosławska. His family was Roman Catholic and Neyman served as an altar boy during his early childhood. Later, Neyman would become an agnostic. Neyman's family descended from a long line of Polish nobles and military heroes. He graduated from the Kamieniec Podolski gubernial gymnasium for boys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bendery
Bender (, Moldovan Cyrillic: Бендер) or Bendery (russian: Бендеры, , uk, Бендери), also known as Tighina ( ro, Tighina), is a city within the internationally recognized borders of Moldova under ''de facto'' control of the unrecognized Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic (Transnistria) (PMR) since 1992. It is located on the western bank of the river Dniester in the Romanian historical region of Bessarabia. Together with its suburb Proteagailovca, the city forms a municipality, which is separate from Transnistria (as an administrative unit of Moldova) according to Moldovan law. Bender is located in the buffer zone established at the end of the 1992 War of Transnistria. While the Joint Control Commission has overriding powers in the city, Transnistria has ''de facto'' administrative control. The fortress of Tighina was one of the important historic fortresses of the Principality of Moldova until 1812. Name First mentioned in 1408 as ''Tyagyanyakyacha'' (Тя ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erich Leo Lehmann
Erich Leo Lehmann (20 November 1917 – 12 September 2009) was a German-born American statistician, who made a major contribution to nonparametric hypothesis testing. He is one of the eponyms of the Lehmann–Scheffé theorem and of the Hodges–Lehmann estimator of the median of a population. Early life Lehmann was born in Strasbourg, Alsace-Lorraine in 1917 to a family of Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry. He grew up in Frankfurt am Main, Germany, until the Machtergreifung in 1933 his family fled to Switzerland to escape the Nazis. He graduated from high school in Zurich, and studied mathematics for two years at Trinity College, Cambridge. Following that, he emigrated to the United States, arriving in New York in late 1940. He enrolled in University of California, Berkeley as a post-graduate student—albeit without a prior degree—in 1941. Career Lehmann obtained his MA in mathematics in 1942 and his PhD (under Jerzy Neyman) in 1946, at the University of California, Berkeley, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous member state of the European Union. Warsaw is the nation's capital and largest metropolis. Other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, Gdańsk, and Szczecin. Poland has a temperate transitional climate and its territory traverses the Central European Plain, extending from Baltic Sea in the north to Sudeten and Carpathian Mountains in the south. The longest Polish river is the Vistula, and Poland's highest point is Mount Rysy, situated in the Tatra mountain range of the Carpathians. The country is bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukraine to the east, Slovakia and the Czech Republic to the south, and Germany to the west. It also shares maritime boundaries with Denmark and Sweden. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officially estimated at 1.86 million residents within a greater metropolitan area of 3.1 million residents, which makes Warsaw the 7th most-populous city in the European Union. The city area measures and comprises 18 districts, while the metropolitan area covers . Warsaw is an Alpha global city, a major cultural, political and economic hub, and the country's seat of government. Warsaw traces its origins to a small fishing town in Masovia. The city rose to prominence in the late 16th century, when Sigismund III decided to move the Polish capital and his royal court from Kraków. Warsaw served as the de facto capital of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1795, and subsequently as the seat of Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biographical Memoirs Of Fellows Of The Royal Society
The ''Biographical Memoirs of Fellows of the Royal Society'' is an academic journal on the history of science published annually by the Royal Society. It publishes obituaries of Fellows of the Royal Society. It was established in 1932 as ''Obituary Notices of Fellows of the Royal Society'' and obtained its current title in 1955, with volume numbering restarting at 1. Prior to 1932, obituaries were published in the ''Proceedings of the Royal Society''. The memoirs are a significant historical record and most include a full bibliography of works by the subjects. The memoirs are often written by a scientist of the next generation, often one of the subject's own former students, or a close colleague. In many cases the author is also a Fellow. Notable biographies published in this journal include Albert Einstein, Alan Turing, Bertrand Russell, Claude Shannon, Clement Attlee, Ernst Mayr, and Erwin Schrödinger. Each year around 40 to 50 memoirs of deceased Fellows of the Royal Soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellow Of The Royal Society
Fellowship of the Royal Society (FRS, ForMemRS and HonFRS) is an award granted by the judges of the Royal Society of London to individuals who have made a "substantial contribution to the improvement of natural science, natural knowledge, including mathematics, engineering science, and medical science". Fellow, Fellowship of the Society, the oldest known scientific academy in continuous existence, is a significant honour. It has been awarded to many eminent scientists throughout history, including Isaac Newton (1672), Michael Faraday (1824), Charles Darwin (1839), Ernest Rutherford (1903), Srinivasa Ramanujan (1918), Albert Einstein (1921), Paul Dirac (1930), Winston Churchill (1941), Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar (1944), Dorothy Hodgkin (1947), Alan Turing (1951), Lise Meitner (1955) and Francis Crick (1959). More recently, fellowship has been awarded to Stephen Hawking (1974), David Attenborough (1983), Tim Hunt (1991), Elizabeth Blackburn (1992), Tim Berners-Lee (2001), Venki R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Medal Of Science
The National Medal of Science is an honor bestowed by the President of the United States to individuals in science and engineering who have made important contributions to the advancement of knowledge in the fields of behavioral and social sciences, biology, chemistry, engineering, mathematics and physics. The twelve member presidential Committee on the National Medal of Science is responsible for selecting award recipients and is administered by the National Science Foundation (NSF). History The National Medal of Science was established on August 25, 1959, by an act of the Congress of the United States under . The medal was originally to honor scientists in the fields of the "physical, biological, mathematical, or engineering sciences". The Committee on the National Medal of Science was established on August 23, 1961, by executive order 10961 of President John F. Kennedy. On January 7, 1979, the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) passed a resolution propo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy Medal
The Guy Medals are awarded by the Royal Statistical Society in three categories; Gold, Silver and Bronze. The Silver and Bronze medals are awarded annually. The Gold Medal was awarded every three years between 1987 and 2011, but is awarded biennially as of 2019. They are named after William Guy. *The Guy Medal in Gold is awarded to fellows or others who are judged to have merited a signal mark of distinction by reason of their innovative contributions to the theory or application of statistics. *The Guy Medal in Silver is awarded to any fellow or, in exceptional cases, to two or more fellows in respect of a paper/papers of special merit communicated to the Society at its ordinary meetings, or in respect of a paper/papers published in any of the journals of the Society. General contributions to statistics may also be taken into account. *The Guy Medal in Bronze is awarded to fellows, or to non-fellows who are members of a section or a local group, in respect of a paper or papers rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newcomb Cleveland Prize
The Newcomb Cleveland Prize of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) is annually awarded to author(s) of outstanding scientific paper published in the Research Articles or Reports sections of ''Science''. Established in 1923, funded by Newcomb Cleveland who remained anonymous until his death in 1951, and for this period it was known as the AAAS Thousand Dollar Prize. "The prize was inspired by Mr. Cleveland's belief that it was the scientist who counted and who needed the encouragement an unexpected monetary award could give." The present rules were instituted in 1975, previously it had gone to the author(s) of noteworthy papers, representing an outstanding contribution to science, presented in a regular session, sectional or societal, during the AAAS Annual Meeting. It is now sponsored by the Fodor Family Trust and includes a prize of $25,000. Recipients List of winners Current rules Previous rules See also * AAAS Award for Science Diplomacy * AAA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy Clusters
A galaxy cluster, or a cluster of galaxies, is a structure that consists of anywhere from hundreds to thousands of galaxies that are bound together by gravity, with typical masses ranging from 1014 to 1015 solar masses. They are the second-largest known gravitationally bound structures in the universe after galaxy filaments and were believed to be the largest known structures in the universe until the 1980s, when superclusters were discovered. One of the key features of clusters is the intracluster medium (ICM). The ICM consists of heated gas between the galaxies and has a peak temperature between 2–15 keV that is dependent on the total mass of the cluster. Galaxy clusters should not be confused with ''galactic clusters'' (also known as open clusters), which are star clusters ''within'' galaxies, or with globular clusters, which typically orbit galaxies. Small aggregates of galaxies are referred to as galaxy groups rather than clusters of galaxies. The galaxy groups and clus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neyman–Pearson Lemma
In statistics, the Neyman–Pearson lemma was introduced by Jerzy Neyman and Egon Pearson in a paper in 1933. The Neyman-Pearson lemma is part of the Neyman-Pearson theory of statistical testing, which introduced concepts like errors of the second kind, power function, and inductive behavior.The Fisher, Neyman-Pearson Theories of Testing Hypotheses: One Theory or Two?: Journal of the American Statistical Association: Vol 88, No 424The Fisher, Neyman-Pearson Theories of Testing Hypotheses: One Theory or Two?: Journal of the American Statistical Association: Vol 88, No 424/ref>Wald: Chapter II: The Neyman-Pearson Theory of Testing a Statistical HypothesisWald: Chapter II: The Neyman-Pearson Theory of Testing a Statistical Hypothesis/ref>The Empire of ChanceThe Empire of Chance/ref> The previous Fisherian theory of significance testing postulated only one hypothesis. By introducing a competing hypothesis, the Neyman-Pearsonian flavor of statistical testing allows investigating the two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
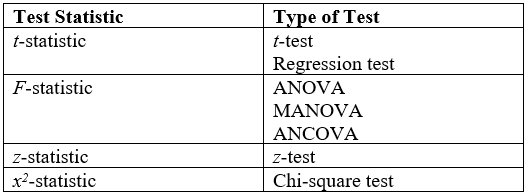
Hypothesis Testing
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of statistical inference used to decide whether the data at hand sufficiently support a particular hypothesis. Hypothesis testing allows us to make probabilistic statements about population parameters. History Early use While hypothesis testing was popularized early in the 20th century, early forms were used in the 1700s. The first use is credited to John Arbuthnot (1710), followed by Pierre-Simon Laplace (1770s), in analyzing the human sex ratio at birth; see . Modern origins and early controversy Modern significance testing is largely the product of Karl Pearson ( ''p''-value, Pearson's chi-squared test), William Sealy Gosset ( Student's t-distribution), and Ronald Fisher ("null hypothesis", analysis of variance, "significance test"), while hypothesis testing was developed by Jerzy Neyman and Egon Pearson (son of Karl). Ronald Fisher began his life in statistics as a Bayesian (Zabell 1992), but Fisher soon grew disenchanted with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |