|
Jehosophat
Jehoshaphat (; alternatively spelled Jehosaphat, Josaphat, or Yehoshafat; ; el, Ἰωσαφάτ, Iosafát; la, Josaphat), according to 1 Kings 22:41, was the son of Asa, and the fourth king of the Kingdom of Judah, in succession to his father. His children included Jehoram, who succeeded him as king. His mother was Azubah. Historically, his name has sometimes been connected with the Valley of Josaphat. Reign 2 Chronicles chapters 17 to 21 are devoted to the reign of Jehoshaphat. 1 Kings 15:24 mentions him as successor to Asa, and 1 Kings 22:1-50 summarizes the events of his life. The Jerusalem Bible states that "the Chronicler sees Asa as a type of the peaceful, Jehoshaphat of the strong king". According to these passages, Jehoshaphat ascended the throne at the age of thirty-five and reigned for twenty-five years. He "walked in the ways" of his father or ancestor, King David. He spent the first years of his reign fortifying his kingdom against the Kingdom of Israel. Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Israel (Samaria)
The Kingdom of Israel (), or the Kingdom of Samaria, was an Israelite kingdom in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. The kingdom controlled the areas of Samaria, Galilee and parts of Transjordan. Its capital, for the most part, was Samaria (modern Sebastia). The Hebrew Bible depicts the Kingdom of Israel as one of two successor states to the former United Kingdom of Israel ruled by King David and his son Solomon, the other being the Kingdom of Judah; most historians and archaeologists, however, do not believe in the existence of a United Kingdom as depicted in the Bible.The debate is described in Amihai Mazar, "Archaeology and the Biblical Narrative: The Case of the United Monarchy" (see bibliography), p.29 fn.2: "For conservative approaches defining the United Monarchy as a state “from Dan to Beer Sheba” including “conquered kingdoms” (Ammon, Moab, Edom) and “spheres of influence” in Geshur and Hamath cf. e.g. Ahlström (1993), 455–542; Meyers (1998); Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kings Of Judah
The Kings of Judah were the monarchs who ruled over the ancient Kingdom of Judah. According to the biblical account, this kingdom was founded after the death of Saul, when the tribe of Judah elevated David to rule over it. After seven years, David became king of a reunited Kingdom of Israel. However, in about 930 BCE the united kingdom split, with ten of the twelve Tribes of Israel rejecting Solomon's son Rehoboam as their king. The tribes of Judah and Benjamin remained loyal to Rehoboam, and re-formed the Kingdom of Judah, while the other entity continued to be called the Kingdom of Israel, or just Israel. The capital of the Kingdom of Judah was Jerusalem. All of the kings of Judah lived and died in Judah except for Ahaziah (who died at Megiddo in Israel), Jehoahaz (who died a prisoner in Egypt) and Jeconiah and Zedekiah who were deported as part of the Babylonian captivity. Judah was conquered in 587 or 586 BC, by the Neo-Babylonian Empire under Nebuzaradan, captain of Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shmita
The sabbath year (shmita; he, שמיטה, literally "release"), also called the sabbatical year or ''shǝvi'it'' (, literally "seventh"), or "Sabbath of The Land", is the seventh year of the seven-year agricultural cycle mandated by the Torah in the Land of Israel and is observed in Judaism. During ''shmita'', the land is left to lie fallow and all agricultural activity, including plowing, planting, pruning and harvesting, is forbidden by ''halakha'' (Jewish law). Other cultivation techniques (such as watering, fertilizing, weeding, spraying, trimming and mowing) may be performed as a preventive measure only, not to improve the growth of trees or other plants. Additionally, any fruits or herbs which grow of their own accord and where no watch is kept over them are deemed ''hefker'' (ownerless) and may be picked by anyone. A variety of laws also apply to the sale, consumption and disposal of ''shmita'' produce. All debts, except those of foreigners, were to be remitted. Chapt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesha
King Mesha ( Moabite: 𐤌𐤔𐤏 *''Māšaʿ''; Hebrew: מֵישַׁע ''Mēšaʿ'') was a king of Moab in the 9th century BC, known most famously for having the Mesha Stele inscribed and erected at Dibon. In this inscription he calls himself "Mesha, son of Kemosh- .. the king of Moab, the Dibonite." The two main records: Mesha Stele and the Bible The two main sources for the existence and history of King Mesha are the Mesha Stele and the Hebrew Bible. Per the Mesha Stele, Mesha's father was also a king of Moab. His name is not totally preserved in the inscription, only the theophoric first element ''Chemosh''(-...) surviving; throughout the years scholars have proposed numerous reconstructions, including ''Chemosh-gad'', ''Chemosh-melek'', and ''Chemosh-yat(ti)'', the latter of which has found some acceptance, as a Moabite king named ''Chemosh-yat'' is known from the Kerak Inscription. In the Books of Samuel account, Moab is said to have been conquered by David (tradition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moab
Moab ''Mōáb''; Assyrian: 𒈬𒀪𒁀𒀀𒀀 ''Mu'abâ'', 𒈠𒀪𒁀𒀀𒀀 ''Ma'bâ'', 𒈠𒀪𒀊 ''Ma'ab''; Egyptian: 𓈗𓇋𓃀𓅱𓈉 ''Mū'ībū'', name=, group= () is the name of an ancient Levantine kingdom whose territory is today located in the modern state of Jordan. The land is mountainous and lies alongside much of the eastern shore of the Dead Sea. The existence of the Kingdom of Moab is attested to by numerous archaeological findings, most notably the Mesha Stele, which describes the Moabite victory over an unnamed son of King Omri of Israel, an episode also noted in 2 Kings . The Moabite capital was Dibon. According to the Hebrew Bible, Moab was often in conflict with its Israelite neighbours to the west. Etymology The etymology of the word Moab is uncertain. The earliest gloss is found in the Koine Greek Septuagint () which explains the name, in obvious allusion to the account of Moab's parentage, as ἐκ τοῦ πατρός μου ("from my ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jehoram Of Israel
Jehoram ( ''Yəhōrām''; also Joram) was the ninth king of the northern Kingdom of Israel ( 2 Kings 8:16, 2 Kings 8:25–28). He was the son of Ahab and Jezebel, and brother to Ahaziah and Athaliah. According to 2 Kings, 2 Kings 8:16, in the fifth year of Jehoram of Israel, (another) Jehoram became king of Judah. The author of Kings speaks of both Jehoram of Israel and Jehoram of Judah in the same passage. Reign Jehoram began to reign in Israel in the 18th year of Jehoshaphat of Judah and ruled 12 years ( 2 Kings 3:1). William F. Albright dated his reign to 849–842 BCE, whereas E. R. Thiele proposed 852–841 BCE. Unlike his predecessors, Jehoram did not worship Ba'al, and he removed the pillar of Baal, probably a special pillar which Ahab had erected near his palace at Jezreel for his own and Jezebel's worship. However, the writer of 2 Kings says that he still "followed in the ways of Jeroboam, son of Nebat, who led the Israelites to sin". With Jehoshaphat of Judah, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophir
Ophir (; ) is a port or region mentioned in the Bible, famous for its wealth. King Solomon received a shipment from Ophir every three years (1 Kings 10:22) which consisted of gold, silver, sandalwood, pearls, ivory, apes, and peacocks. Biblical references Ophir in Genesis 10 (the Table of Nations) is said to be the name of one of the sons of Joktan. The Books of Kings and Chronicles tell of a joint expedition to Ophir by King Solomon and the Tyrian king Hiram I from Ezion-Geber, a port on the Red Sea, that brought back large amounts of gold, precious stones and ' algum wood' and of a later failed expedition by king Jehoshaphat of Judah. The famous 'gold of Ophir' is referenced in several other books of the Hebrew Bible. In the Septuagint, other variants of the name are mentioned: ''Ōpheír'', ''Sōphír'', ''Sōpheír'' and ''Souphír''. The New Testament apocrypha book ''Cave of Treasures'' contains a passage: "And the children of Ophir, that is, Send, appointed to be the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahaziah Of Israel
Ahaziah (, " Yah has grasped"; also gr, Ὀχοζίας, ''Ochozias'' in the Septuagint and the Douai-Rheims translation) was the eighth king of the northern Kingdom of Israel and the son of Ahab and Jezebel. Like his father, he reigned from Samaria. William F. Albright has dated his reign to 850-849 BC, while E. R. Thiele offers the dates 853-852 BC. The author of the '' Books of Kings'' criticized him for following the ways of his father Ahab and his mother Jezebel, and for making Israel sin "in the way of Jeroboam the son of Nebat". Biblical commentator Albert Barnes notes that the phrase "in the way of his mother" does not occur anywhere else in the Hebrew Bible, and demonstrates the strong feeling of the writer of the Books of Kings as to the influence of Jezebel. Reign During his reign the Moabites revolted against his authority (). This event is recorded on the Mesha stele, an extensive inscription written in the Moabite language. Ahaziah formed a business par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idolatry
Idolatry is the worship of a cult image or "idol" as though it were God. In Abrahamic religions (namely Judaism, Samaritanism, Christianity, the Baháʼí Faith, and Islam) idolatry connotes the worship of something or someone other than the Abrahamic god as if it were God. In these monotheistic religions, idolatry has been considered as the "worship of false gods" and is forbidden by texts such as the Ten Commandments. Other monotheistic religions may apply similar rules. For instance, the phrase ''false god'' is a derogatory term used in Abrahamic religions to indicate cult images or deities of non-Abrahamic Pagan religions, as well as other competing entities or objects to which particular importance is attributed. Conversely, followers of animistic and polytheistic religions may regard the gods of various monotheistic religions as "false gods" because they do not believe that any real deity possesses the properties ascribed by monotheists to their sole deity. Atheists, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanani
The word Hanani ( he, חנני ''Ḥănānî'') means "God has gratified me" or "God is gracious". Hanani is the name of four men mentioned in the Hebrew Bible: * One of the sons of Heman (1 Chronicles 25:4, 25). * A "seer" or prophet who was sent to rebuke king Asa of Judah for entering into a league with Ben-Hadad I Ben-Hadad I ( he, בן הדד, translit=bn hdd; arc, בר הדד, translit=br hdd), son of Tabrimmon and grandson of Hezion, was king of Aram-Damascus between 885 BC and 865 BC. Ben-Hadad I was reportedly a contemporary of kings Baasha of the ..., List of Syrian monarchs, king of Syria, against the Northern Kingdom of Israel, northern kingdom of Israel. Hanani was imprisoned in stocks by Asa (2 Chronicles 16:7-10). This Hanani was also probably the father of the prophet Jehu (prophet), Jehu, who rebuked Baasha of Israel, Baasha, king of the northern kingdom (1 Kings 16:1-4, 7) and Jehoshaphat , king of the southern kingdom (2 Chronicles 19:1-3). The Pulpit Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jehu (prophet)
Jehu (, ; he, יֵהוּא , "Yah is He") son of Hanani was a prophet mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, who was active during the 9th century BC. Biblical account According to the Bible, Jehu condemned Baasha, king of Israel, and the House of Baasha (1 Kings 16:7), accusing him of leading the people into the sin of idolatry like his predecessor Jeroboam. Jehu foretold that: :''surely odwill take away the posterity of Baasha and the posterity of his house, and ... will make your house like the house of Jeroboam the son of Nebat. The dogs shall eat whoever belongs to Baasha and dies in the city, and the birds of the air shall eat whoever dies in the fields.'' () His words were fulfilled in the reign of Elah, Baasha's son, when the traitor Zimri assassinated Elah and murdered all of Baasha's family and associates. () Jehu also challenged Jehoshaphat, king of Judah. Jehoshaphat's alliance with Ahab ended in the latter's death at the Battle of Ramoth-Gilead. Jehoshaphat returned s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
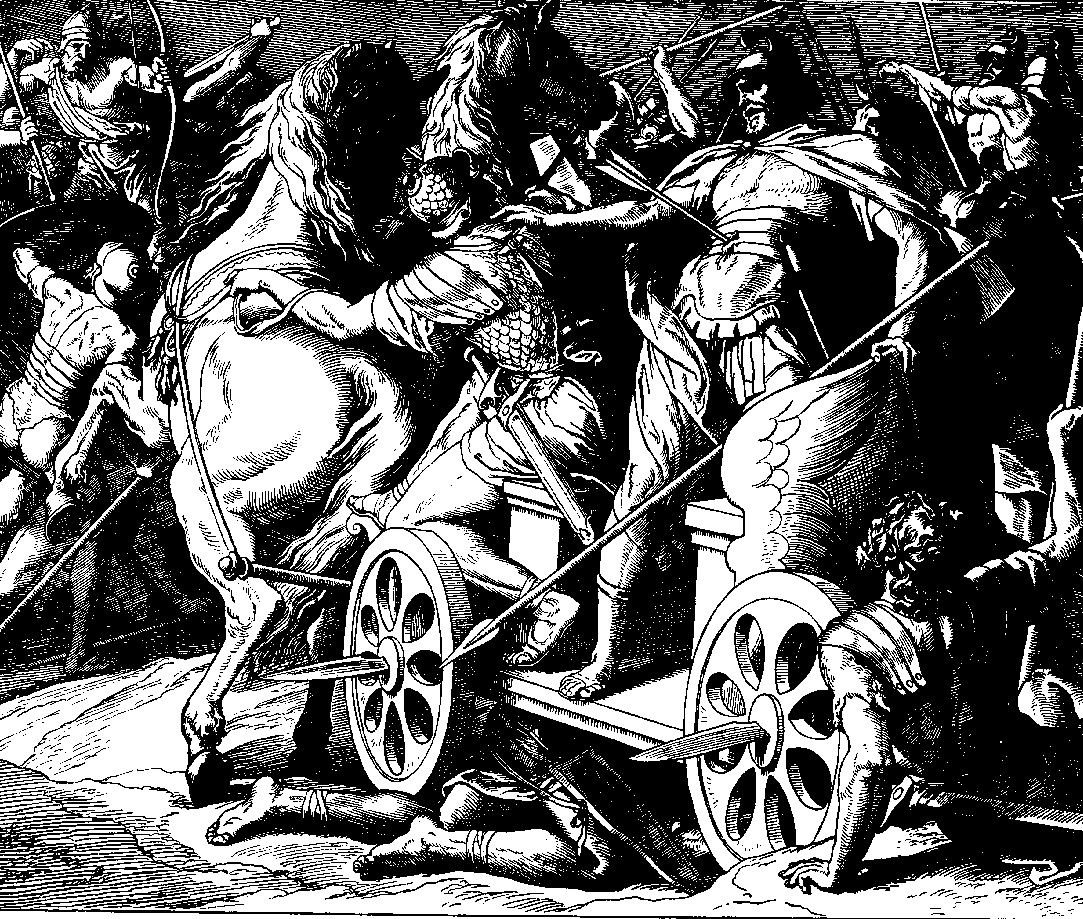
Ramoth-Gilead
Ramoth-Gilead ( he, רָמֹת גִּלְעָד, meaning "Heights of Gilead"), was a Levitical city and city of refuge east of the Jordan River in the Hebrew Bible, also called "Ramoth in Gilead" (; ; ) or "Ramoth Galaad" in the Douay–Rheims Bible. It was located in the tribal territorial allotment of the tribe of Gad. Biblical events According to (), Ramothgilead was the base of Ben-Geber, one of King Solomon's regional governors. He was responsible for ("to him belonged") the towns of Jair the son of Manasseh, in Gilead and the region of Argob in Bashan: sixty large cities with walls and bronze gate-bars. It appears to have been lost to Syria (Aram-Damascus) during the battles between the northern kingdom of Israel and Syria, as Ahab, King of Israel, proposed to go to battle to win it back. After consulting prophets about the prospects of success, Ahab went to fight for Ramoth in Gilead, aided by Jehoshaphat, King of Judah. During the battle, Ahab was wounded by an arrow. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |