|
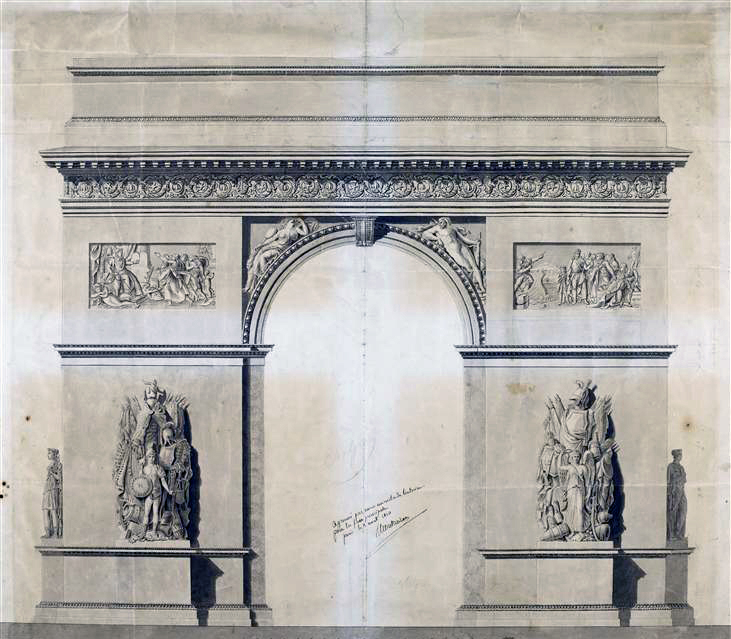
Jean Chalgrin
Jean-François-Thérèse Chalgrin (1739 – 21 January 1811) was a French architect, best known for his design for the Arc de Triomphe, Paris. Biography His neoclassic orientation was established from his early studies with the prophet of neoclassicism Giovanni Niccolò Servandoni and with the radical classicist Étienne-Louis Boullée in Paris and through his Prix de Rome sojourn (November 1759 – May 1763) as a pensionnaire of the French Academy in Rome. His time in Rome coincided with a fervent new interest in Classicism among the young French ''pensionnaires'', under the influences of Piranesi and the publications of Winckelmann. Returning to Paris, he was quickly given an appointment as an inspector of public works for the city of Paris, under the architect Pierre-Louis Moreau-Desproux, whose own time at the French Academy in Rome had predisposed him to the new style. In this official capacity he oversaw the construction of Ange-Jacques Gabriel's Hôtel Saint-Florent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Chalgrin
Jean-François-Thérèse Chalgrin (1739 – 21 January 1811) was a French architect, best known for his design for the Arc de Triomphe, Paris. Biography His neoclassic orientation was established from his early studies with the prophet of neoclassicism Giovanni Niccolò Servandoni and with the radical classicist Étienne-Louis Boullée in Paris and through his Prix de Rome sojourn (November 1759 – May 1763) as a pensionnaire of the French Academy in Rome. His time in Rome coincided with a fervent new interest in Classicism among the young French ''pensionnaires'', under the influences of Piranesi and the publications of Winckelmann. Returning to Paris, he was quickly given an appointment as an inspector of public works for the city of Paris, under the architect Pierre-Louis Moreau-Desproux, whose own time at the French Academy in Rome had predisposed him to the new style. In this official capacity he oversaw the construction of Ange-Jacques Gabriel's Hôtel Saint-Florent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis XVIII Of France
Louis XVIII (Louis Stanislas Xavier; 17 November 1755 – 16 September 1824), known as the Desired (), was King of France from 1814 to 1824, except for a brief interruption during the Hundred Days in 1815. He spent twenty-three years in exile: during the French Revolution and the First French Empire (1804–1814), and during the Hundred Days. Until his accession to the throne of France, he held the title of Count of Provence as brother of King Louis XVI. On 21 September 1792, the National Convention abolished the monarchy and deposed Louis XVI, who was later executed by guillotine. When his young nephew Louis XVII died in prison in June 1795, the Count of Provence proclaimed himself (titular) king under the name Louis XVIII. Following the French Revolution and during the Napoleonic era, Louis XVIII lived in exile in Prussia, England, and Russia. When the Sixth Coalition finally defeated Napoleon in 1814, Louis XVIII was placed in what he, and the French royalists, con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Nicolas Huyot
Jean-Nicholas Huyot (December 25, 1780, Paris – August 2, 1840, Paris) was a French architect, best known for his 1833 continuation of the Arc de Triomphe from the plans of Jean Chalgrin. Biography Son of a builder, Huyot attended the École nationale supérieure des Beaux-Arts in Paris, and won the Prix de Rome in 1807. Following his study in Rome, between 1817 and 1821 Huyot traveled in Asia Minor, Egypt, and Greece. He developed significant credentials as an antiquarian. He was part of the ''Cléopâtra'' expedition under Louis Nicolas Philippe Auguste de Forbin in 1817, and Huyot sent to Jean-François Champollion a collection of inscriptions he found in the temple of Ramses II at Abu Simbel; this contribution was helpful in Champollion's work in deciphering hieroglyphics. Huyot also provided technical archeological assistance to the Fine Arts section of the French scientific Morea expedition into Greece in 1823. In 1822 Huyot was elected a member of the Academy of Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Arnaud Raymond
Jean-Arnaud Raymond (4 April 1742, Toulouse - 28 January 1811, Paris) was a French architect in the Palladian style. Biography He was born to a family of carpenters. In 1759, he began his architectural studies at the new , then went to Paris, where he attended the Académie Royale d'Architecture, under the direction of Jacques-François Blondel and Jacques-Germain Soufflot. He won the Prix de Rome in 1766, with his design for the portal of a cathedral, then spent eight years in Italy where he developed a strong attachment to the work of Andrea Palladio.Aurélie Lacourarie, L’Influence de Palladio dans l’œuvre de l’architecte toulousain Jean-Arnaud Raymond à la fin du XVIIIe siècle', in Les Cahiers du Framespa, 2010 On his way back to Paris, he was appointed architect for the Estates of Languedoc. In this capacity, he directed work on the in Montpellier. In 1783, he was called to the reconstruction site of the Notre-Dame-de-Prouille Monastery, to proceed with inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First French Empire
The First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire (; Latin: ) after 1809, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Europe at the beginning of the 19th century. It lasted from 18 May 1804 to 11 April 1814 and again briefly from 20 March 1815 to 7 July 1815. Although France had already established a colonial empire overseas since the early 17th century, the French state had remained a kingdom under the Bourbons and a republic after the French Revolution. Historians refer to Napoleon's regime as the ''First Empire'' to distinguish it from the restorationist ''Second Empire'' (1852–1870) ruled by his nephew Napoleon III. The First French Empire is considered by some to be a " Republican empire." On 18 May 1804, Napoleon was granted the title Emperor of the French (', ) by the French and was crowned on 2 December 1804, signifying the end of the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led successful campaigns during the Revolutionary Wars. He was the ''de facto'' leader of the French Republic as First Consul from 1799 to 1804, then Emperor of the French from 1804 until 1814 and again in 1815. Napoleon's political and cultural legacy endures to this day, as a highly celebrated and controversial leader. He initiated many liberal reforms that have persisted in society, and is considered one of the greatest military commanders in history. His wars and campaigns are studied by militaries all over the world. Between three and six million civilians and soldiers perished in what became known as the Napoleonic Wars. Napoleon was born on the island of Corsica, not long af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directoire
The Directory (also called Directorate, ) was the governing five-member committee in the French First Republic from 2 November 1795 until 9 November 1799, when it was overthrown by Napoleon Bonaparte in the Coup of 18 Brumaire and replaced by the Consulate. ''Directoire'' is the name of the final four years of the French Revolution. Mainstream historiography also uses the term in reference to the period from the dissolution of the National Convention on 26 October 1795 (4 Brumaire) to Napoleon's coup d’état. The Directory was continually at war with foreign coalitions, including Britain, Austria, Prussia, the Kingdom of Naples, Russia and the Ottoman Empire. It annexed Belgium and the left bank of the Rhine, while Bonaparte conquered a large part of Italy. The Directory established 196 short-lived sister republics in Italy, Switzerland and the Netherlands. The conquered cities and states were required to send France huge amounts of money, as well as art treasures, which we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palais Du Luxembourg
The Luxembourg Palace (french: Palais du Luxembourg, ) is at 15 Rue de Vaugirard in the 6th arrondissement of Paris. It was originally built (1615–1645) to the designs of the French architect Salomon de Brosse to be the royal residence of the regent Marie de' Medici, mother of King Louis XIII. After the Revolution it was refashioned (1799–1805) by Jean Chalgrin into a legislative building and subsequently greatly enlarged and remodeled (1835–1856) by Alphonse de Gisors. The palace has been the seat of the upper houses of the various French national legislatures (excepting only the unicameral National Assembly of the Second Republic) since the establishment of the ''Sénat conservateur'' during the Consulate; as such, it has been home to the Senate of the Fifth Republic since its establishment in 1958. Immediately west of the palace on the Rue de Vaugirard is the Petit Luxembourg, now the residence of the Senate President; and slightly further west, the Musée du Luxembo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collège De France
The Collège de France (), formerly known as the ''Collège Royal'' or as the ''Collège impérial'' founded in 1530 by François I, is a higher education and research establishment (''grand établissement'') in France. It is located in Paris near La Sorbonne. The Collège de France is considered to be France's most prestigious research establishment. Research and teaching are closely linked at the Collège de France, whose ambition is to teach "the knowledge that is being built up in all fields of literature, science and the arts". It offers high-level courses that are free, non-degree-granting and open to all without condition or registration. This gives it a special place in the French intellectual landscape. Overview The Collège is considered to be France's most prestigious research establishment. As of 2021, 21 Nobel Prize winners and 9 Fields Medalists have been affiliated with the Collège. It does not grant degrees. Each professor is required to give lectures where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exposition Des Produits De L'industrie Française
The Exposition des produits de l'industrie française (Exhibition of Products of French Industry) was a public event organized in Paris, France, from 1798 to 1849. The purpose was "to offer a panorama of the productions of the various branches of industry with a view to emulation". It was a precursor to the Great Exhibition of 1851 in London. Background The Paris industrial expositions between 1798 and 1849 can trace their origins to the fairs that were held in several cities of Europe in the Middle Ages. After the start of the French Revolution of 1789–98 the authorities staged a series of festivals in Paris, starting with the Festival of the Federation on 14 July 1790 and followed by events such as the Festival of Law (1792), Festival of Reason (1793), Festival of the Supreme Being (1794), and Festival of the Foundation of the Republic (1796). These celebrations of the new republic helped to unite the people and win acceptance of the new order. The Directory launched the fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considered fundamental principles of liberal democracy, while phrases like ''liberté, égalité, fraternité'' reappeared in other revolts, such as the 1917 Russian Revolution, and inspired campaigns for the abolition of slavery and universal suffrage. The values and institutions it created dominate French politics to this day. Its causes are generally agreed to be a combination of social, political and economic factors, which the ''Ancien Régime'' proved unable to manage. In May 1789, widespread social distress led to the convocation of the Estates General, which was converted into a National Assembly in June. Continuing unrest culminated in the Storming of the Bastille on 14 July, which led to a series of radical measures by the Assembly, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Sulpice (Paris)
, image = Paris Saint-Sulpice Fassade 4-5 A.jpg , image_size = , pushpin map = Paris , pushpin label position = , coordinates = , location = Place Saint-Sulpice 6th arrondissement, Paris , country = France , denomination = Roman Catholic , religious institute = Society of the Priests of Saint Sulpice , website = , bull date = , founded date = , founder = , dedication = Sulpitius the Pious , dedicated date = , consecrated date = , relics = , status = Parish church , functional status = Active , heritage designation = , architect = , style = Baroque , years built = , groundbreaking = 1646 , completed date = 1870 , capacity = , length = , width ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |