|
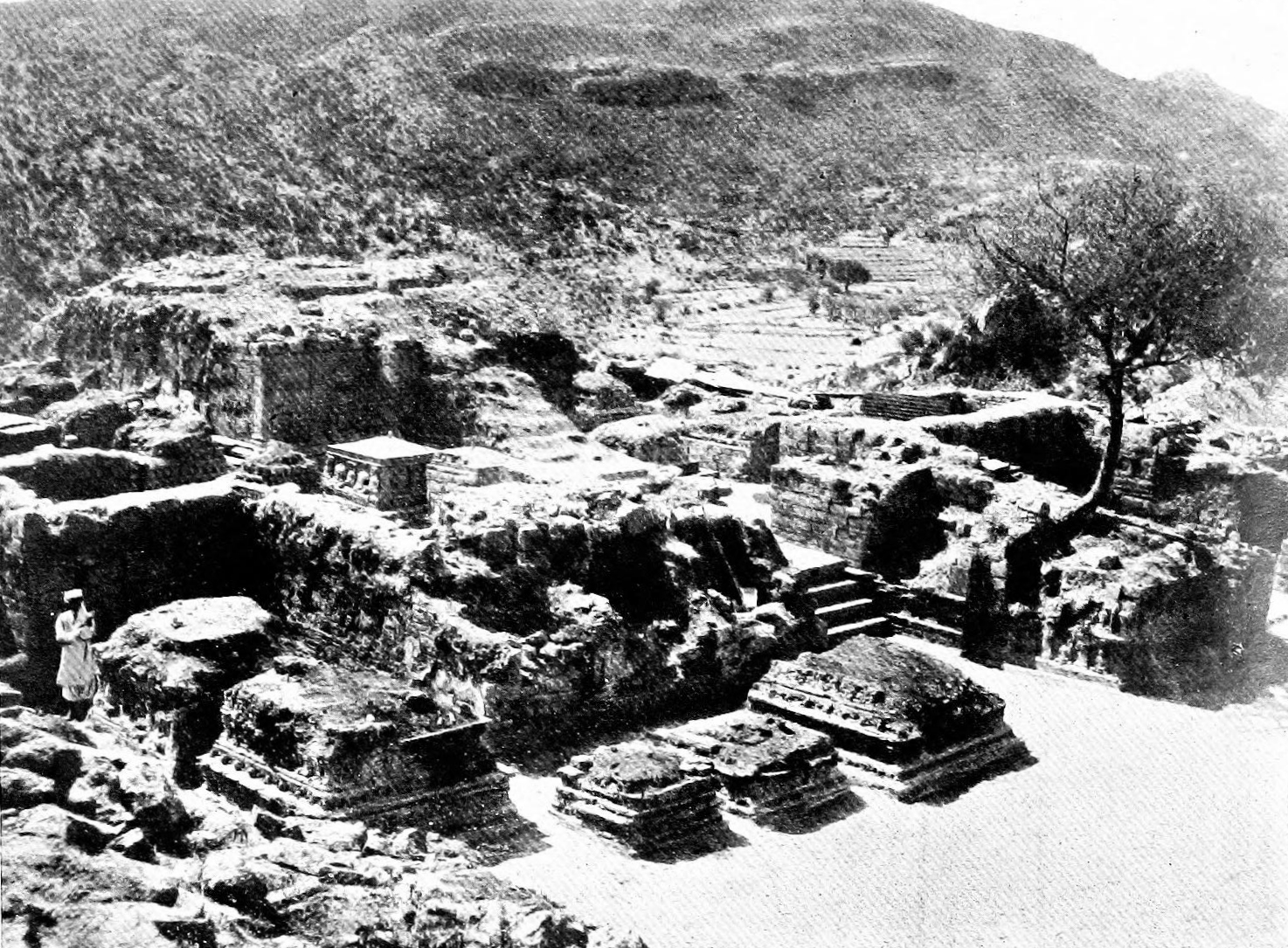
Jaulian
Jaulian (; meaning ''Seat of Saints'') is a ruined Buddhist monastery dating from the 2nd century CE, located in Taxila, in Pakistan. Jaulian, along with the nearby monastery at Mohra Muradu, form part of the Ruins of Taxila – a collection of excavations that were inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1980. Location Jaulian is located on a hill 100 metres above the nearby modern village of Jaulian. The cities of Rawalpindi and Islamabad are approximately 35 km and 45 km to the southeast, respectively and situated near Khanpur Taxila road; a picnic place near Khanpur Dam. Jaulian is located near the Mohra Muradu monastery, and the ancient Taxilan city of Sirsukh. Moreover, Piplan Remains, Badalpur Stupa and Jinnah Wali Dheri Stupa are nearby places. History Jaulian was built in the 2nd-century CE – around the same time as the nearby Mohra Muradu Jaulian, along with the rest of Ancient Taxila, was devastated in the 450s CE during the invasion of the White ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaulian Monastery Stupa Court
Jaulian (; meaning ''Seat of Saints'') is a ruined Buddhist monastery dating from the 2nd century Common era, CE, located in Taxila, in Pakistan. Jaulian, along with the nearby monastery at Mohra Muradu, form part of the Ruins of Taxila – a collection of excavations that were inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1980. Location Jaulian is located on a hill 100 metres above the nearby modern village of Jaulian. The cities of Rawalpindi and Islamabad are approximately 35 km and 45 km to the southeast, respectively and situated near Khanpur Taxila road; a picnic place near Khanpur Dam. Jaulian is located near the Mohra Muradu monastery, and the ancient Taxilan city of Sirsukh. Moreover, Piplan Remains, Badalpur Stupa and Jinnah Wali Dheri Stupa are nearby places. History Jaulian was built in the 2nd-century CE – around the same time as the nearby Mohra Muradu Jaulian, along with the rest of Taxila (ancient), Ancient Taxila, was devastated in the 450s CE during t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaulian Monastery Plan
Jaulian (; meaning ''Seat of Saints'') is a ruined Buddhist monastery dating from the 2nd century CE, located in Taxila, in Pakistan. Jaulian, along with the nearby monastery at Mohra Muradu, form part of the Ruins of Taxila – a collection of excavations that were inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1980. Location Jaulian is located on a hill 100 metres above the nearby modern village of Jaulian. The cities of Rawalpindi and Islamabad are approximately 35 km and 45 km to the southeast, respectively and situated near Khanpur Taxila road; a picnic place near Khanpur Dam. Jaulian is located near the Mohra Muradu monastery, and the ancient Taxilan city of Sirsukh. Moreover, Piplan Remains, Badalpur Stupa and Jinnah Wali Dheri Stupa are nearby places. History Jaulian was built in the 2nd-century CE – around the same time as the nearby Mohra Muradu Jaulian, along with the rest of Ancient Taxila, was devastated in the 450s CE during the invasion of the White ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruins Of Taxila
Taxila or Takshashila () is a city in the Pothohar region of Punjab, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil of Rawalpindi District, it lies approximately northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area and is just south of the Haripur District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. Established during the Vedic period, Old Taxila was for a time the capital city of ancient Gandhāra. It was situated on the eastern shore of the Indus River—the pivotal junction of the Indian subcontinent and Central Asia;Raymond Allchin, Bridget Allchin''The Rise of Civilization in India and Pakistan''.Cambridge University Press, 1982 p.127 it was possibly founded around 1000 BCE. Takshashila and Pushkalavati remained prominent cities in Gandhāra during the Mahajanapadas. The city was later conquered by the Achaemenid Empire and incorporated into the Hindush satrap, between 550 – 326 BCE. In 326 BCE, the city was claimed by Alexander the Great, after overthrowing the Achaemenids. He gained contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxila
Taxila or Takshashila () is a city in the Pothohar region of Punjab, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil of Rawalpindi District, it lies approximately northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area and is just south of the Haripur District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. Established during the Vedic period, Old Taxila was for a time the capital city of ancient Gandhāra. It was situated on the eastern shore of the Indus River—the pivotal junction of the Indian subcontinent and Central Asia;Raymond Allchin, Bridget Allchin''The Rise of Civilization in India and Pakistan''.Cambridge University Press, 1982 p.127 it was possibly founded around 1000 BCE. Takshashila and Pushkalavati remained prominent cities in Gandhāra during the Mahajanapadas. The city was later conquered by the Achaemenid Empire and incorporated into the Hindush satrap, between 550 – 326 BCE. In 326 BCE, the city was claimed by Alexander the Great, after overthrowing the Achaemenids. He gaine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Archaeological Sites And Monuments In Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
Following is the list of monuments and archaeological sites in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. A total 85 sites in the province were under the protection of the Federal Government. The list includes the only completely inscribed UNESCO World Heritage Site in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, the Buddhist Ruins of Takht-i-Bahi and Neighbouring City Remains at Sahr-i-Bahlol as well as sites which are part of the World Heritage Sites at Taxila. Protected/Unprotected sites Until the passing of the Eighteenth Amendment to the Constitution of Pakistan The Eighteenth Amendment to the Constitution of Pakistan (Urdu language, Urdu: آئین پاکستان میں اٹھارہویں ترمیم) was passed by the National Assembly of Pakistan on April 8, 2010, removing the power of the President of ..., the protected sites were under the Federal Government. Sites in what was previously FATA Ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirsukh
Sirsukh () is an ancient city that forms part of the ruins at Taxila, near the modern day city of Taxila, Punjab, Pakistan. City The city of Sirsukh is said to have been founded during the Kushan era after 80 CE, and is the last of the great ancient cities of Taxila. The invaders decided to abandon the older city of Sirkap and build a newer city on the other side of the Lundi-nala. The wall of the city is about 5 kilometers long and about 5.4 meters thick. The city wall covers an area of around 2300 x 1000 meters seen along the east-west direction, and is laid out in a typical Central Asian style, complete with suburbs. Sirsukh was left uninhabited when the White Huns invaded the Punjab at the end of the fifth century CE. To the north-east of the city flows the Harro river whereas to the south the Lundi-ravine is present. The ancient city was excavated only on a very small scale in 1915-16 CE, and further excavation work has been impeded by a high water table which threatens t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
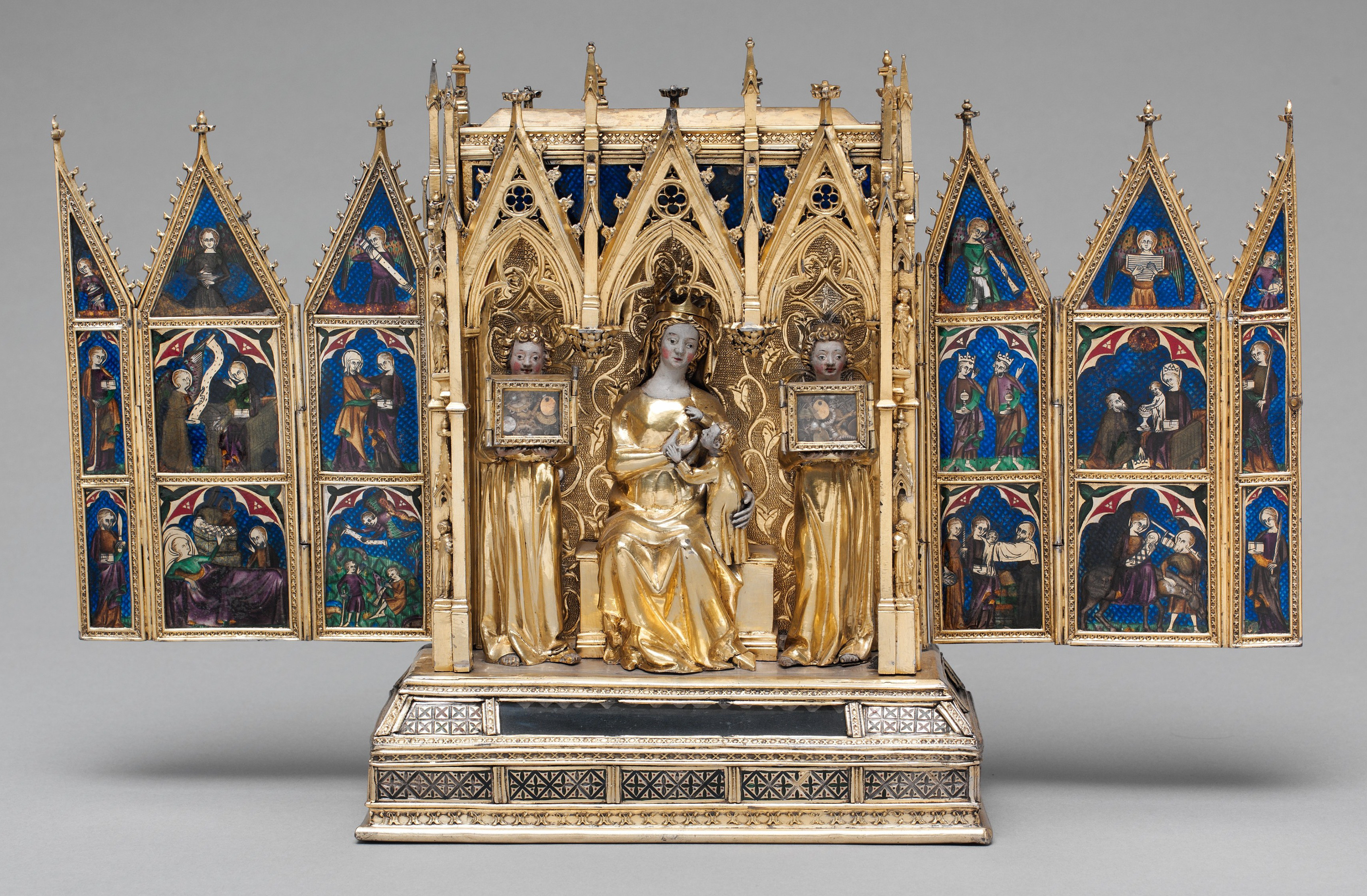
Dharmarajika Stupa
The Dharmarajika Stupa (Punjabi language, Punjabi, ), also referred to as the Great Stupa of Taxila, is a Buddhist stupa near Taxila (modern), Taxila, Pakistan. It was built over the relics of the Buddha by Ashoka, the Emperor of Magadha, in the 3rd century BCE. The stupa, along with the large monastic complex that later developed around it, forms part of the Ruins of Taxila - which were inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1980. History It is believed that the Dharmarajika Stupa was built over the remains of an even older stupa that had been built by the Mauryan emperor King ''Ashoka'' in the 3rd century BCE The stupa was believed to have been reestablished in the 2nd century CE during the Kushan Empire, Kushan era in order to house relics of the Buddha, which may have been sourced from earlier monuments. Buddhist texts mention that frankincense was used during religious services at Dharmarajika, while the complex was paved with colourful glass tiles. Indo-Greek coins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliquary
A reliquary (also referred to as a ''shrine'', ''Chasse (casket), chasse'', or ''phylactery'') is a container for relics. A portable reliquary, or the room in which one is stored, may also be called a ''feretory''. Relics may be the purported or actual physical remains of saints, and may comprise bones, pieces of clothing, or some object associated with saints or with other religious figures. The authenticity of any given relic is often a matter of debate; for that reason, some churches require documentation of a relic's provenance. Relics have long been important to Buddhism, Buddhists, Christianity , Christians, Hinduism , Hindus, and to followers of many other religions. These cultures often display reliquaries in shrines, churches, or temples to which the faithful make pilgrimages to gain blessings. The term is sometimes used in a looser sense to mean a container for the remains of any important figure, even non-religious ones. In particular, the kings of France often spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Scythian
The Indo-Scythians, also known as Indo-Sakas, were a group of nomadic people of Iranian peoples, Iranic Scythians, Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into the present-day regions of Afghanistan, Eastern Iran and the northwestern Indian subcontinent: present-day Pakistan and northern India. The migrations persisted from the middle of the second century BCE to the fourth century CE. The first Saka king in Greater India, India was Maues, Maues/Moga (first century BCE) who established Saka power in Gandhara, the Indus Valley, and other regions. The Indo-Scythians extended their supremacy over the north-western subcontinent, conquering the Indo-Greeks and other local peoples. They were apparently subjugated by the Kushan Empire's Kujula Kadphises or Kanishka. The Saka continued to govern as satrapies, forming the Northern Satraps and Western Satraps. The power of the Saka rulers began to decline during the 2nd century CE after the Indo-Scythians were defeated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Museum
The British Museum is a Museum, public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is the largest in the world. It documents the story of human culture from its beginnings to the present.Among the national museums in London, sculpture and decorative art, decorative and applied art are in the Victoria and Albert Museum; the British Museum houses earlier art, non-Western art, prints and drawings. The National Gallery holds the national collection of Western European art to about 1900, while art of the 20th century on is at Tate Modern. Tate Britain holds British Art from 1500 onwards. Books, manuscripts and many works on paper are in the British Library. There are significant overlaps between the coverage of the various collections. Established in 1753, the British Museum was the first public national museum. In 2023, the museum received 5,820,860 visitors, 42% more than the previous y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Statue Of Buddha With A Hole In The Navel
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, and others worldwide. Its name in English is '' a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version is often written in one of two forms: the double-storey and single-storey . The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English, '' a'' is the indefinite article, with the alternative form ''an''. Name In English, the name of the letter is the ''long A'' sound, pronounced . Its name in most other languages matches the letter's pronunciation in open syllables. History The earliest known ancestor of A is ''aleph''—the first letter of the Phoenician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |