|
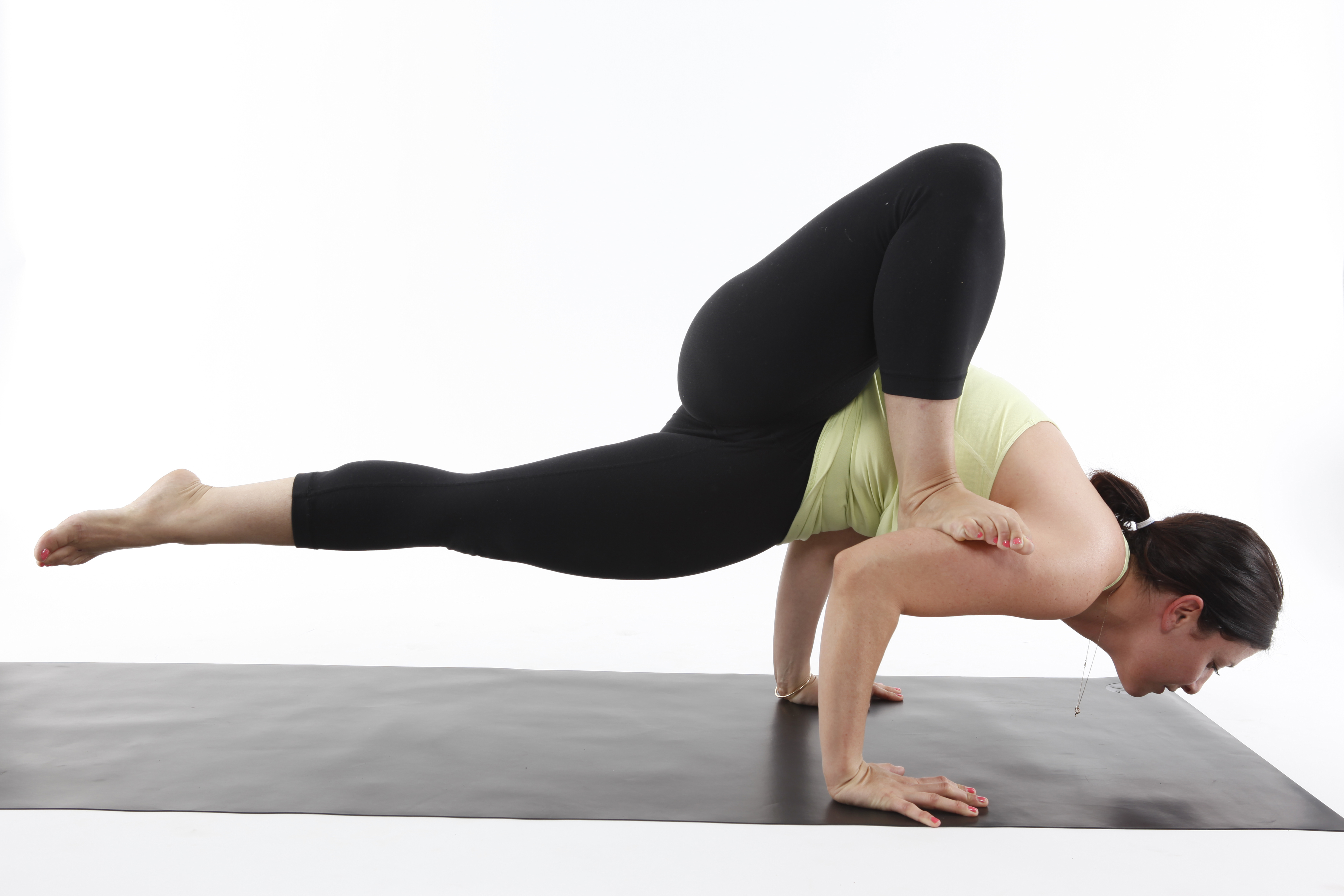
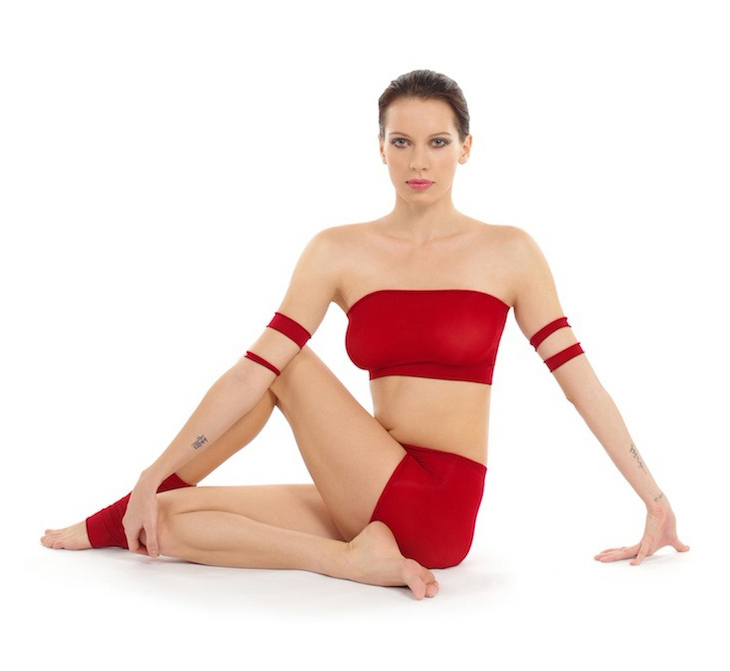
Jathara Parivartanasana
Jathara Parivartanasana (Sanskrit ञठर परिवर्तनासन), Revolved Abdomen pose, Belly twist, or Spinal twist is a reclining twist ''asana'' in modern yoga as exercise. Etymology and origins The name is from the Sanskrit ञठर ''Jaṭhara'', stomach or abdomen; परिवर्तन ''Parivartana'', to turn around; and आसन ''āsana'', posture or seat. The pose is not found in medieval hatha yoga texts, but is described in 20th century manuals including B. K. S. Iyengar's 1966 ''Light on Yoga''. Description The full pose, sometimes called Jathara Parivartanasana B, is entered from a supine position, with the arms outspread on the ground, level with the shoulders. For the full pose, the legs are raised straight up and then lowered to one side, keeping the opposite shoulder on the ground. In Ashtanga Vinyasa Yoga, the pose is used cautiously, in combination with deep muscle exercises, to help relieve low back pain: it is not sufficient on its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
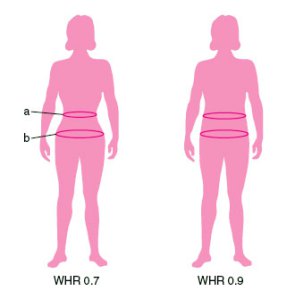
Waist Rotating Pose
The waist is the part of the Human abdomen, abdomen between the rib cage and Hip (anatomy), hips. On people with slim bodies, the waist is the narrowest part of the torso. ''Waistline'' refers to the horizontal line where the waist is narrowest, or to the general appearance of the waist. Structure Because of this and because the waist is often synonymous with the stomach, one can become confused as to the exact location of the waist. Another confusing factor is that the waistline differs on different people. A study showed that self-reported measurements as opposed to measurement done by a technician, underestimated waist circumference and this underestimation increased with increased body size. In the study, waist circumference measured at the level of the umbilicus was larger than that measured at the natural waist. To locate the natural waistline, one need simply stand upright and then tilt over to the side keeping the legs and hips straight. Where the torso creases is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting impact on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Old Indo-Aryan language varieties. The most archaic of these is the Vedic Sanskrit found in the Rig Veda, a colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matsyendrasana
Matsyendrasana ( sa, मत्स्येन्द्रासन; IAST: ''Matsyendrāsana''), Matsyendra's Pose or Lord of the Fishes Pose, is a seated twisting asana in hatha yoga and modern yoga as exercise. The full form is the difficult Paripurna Matsyendrasana. A common and easier variant is Ardha Matsyendrasana. The asana has many variations, and in its half form is one of the twelve basic asanas in many systems of hatha yoga. Etymology and origins The name comes from the Sanskrit words परिपूर्ण ''Paripurna'', perfected; मत्स्येन्द् '' Matsyendra'', one of the founders of hatha yoga, whose name in turn means "lord of the fishes"; and आसन '' asana'', posture or seat; अर्ध ''ardha'' means half. The asana is medieval, described in the 15th century ''Haṭha Yoga Pradīpikā'' 1.26-7, which states that it destroys many diseases, and the 17th century '' Gheraṇḍa Saṃhitā'' 2.22-23. Yogi Ghamande chose the asana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
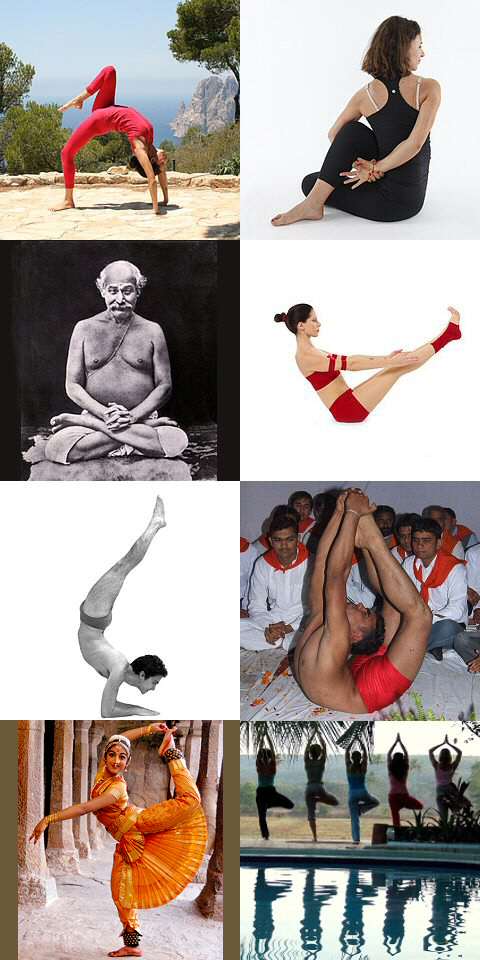
Asana
An asana is a body posture, originally and still a general term for a sitting meditation pose,Verse 46, chapter II, "Patanjali Yoga sutras" by Swami Prabhavananda, published by the Sri Ramakrishna Math p. 111 and later extended in hatha yoga and modern yoga as exercise, to any type of position, adding reclining, standing, inverted, twisting, and balancing poses. The ''Yoga Sutras of Patanjali'' define "asana" as " position thatis steady and comfortable". Patanjali mentions the ability to sit for extended periods as one of the eight limbs of his system. Patanjali ''Yoga sutras'', Book II:29, 46 Asanas are also called yoga poses or yoga postures in English. The 10th or 11th century '' Goraksha Sataka'' and the 15th century '' Hatha Yoga Pradipika'' identify 84 asanas; the 17th century ''Hatha Ratnavali'' provides a different list of 84 asanas, describing some of them. In the 20th century, Indian nationalism favoured physical culture in response to colonialism. In that enviro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
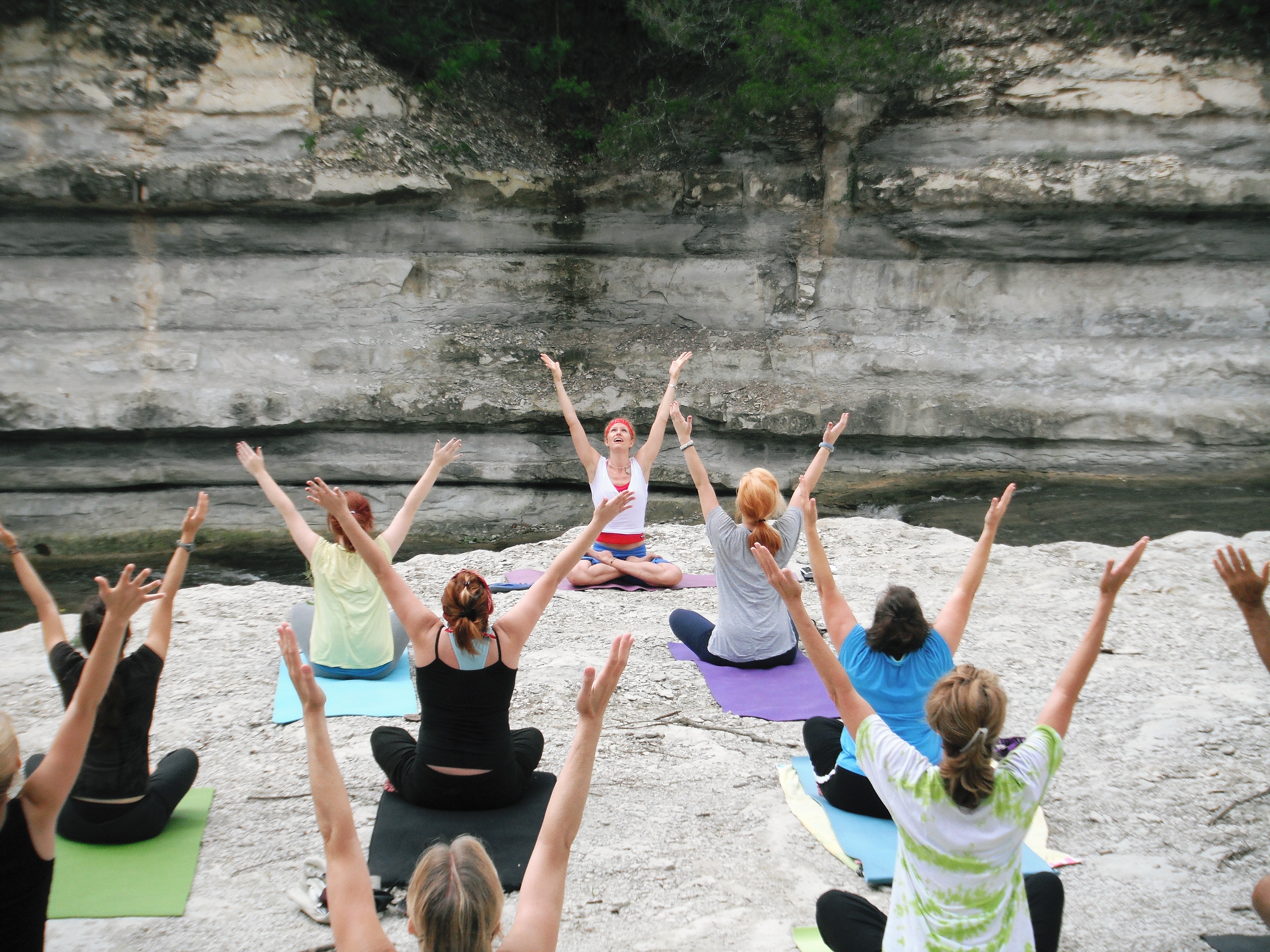
Yoga As Exercise
Yoga as exercise is a physical activity consisting mainly of postures, often connected by flowing sequences, sometimes accompanied by breathing exercises, and frequently ending with relaxation lying down or meditation. Yoga in this form has become familiar across the world, especially in America and Europe. It is derived from medieval Haṭha yoga, which made use of similar postures, but it is generally simply called "yoga". Academics have given yoga as exercise a variety of names, including modern postural yoga and transnational anglophone yoga. Posture is described in the ''Yoga Sutras'' II.29 as the third of the eight limbs, the ashtanga, of yoga. Sutra II.46 defines it as that which is ''steady and comfortable'', but no further elaboration or list of postures is given. Postures were not central in any of the older traditions of yoga; posture practice was revived in the 1920s by yoga gurus including Yogendra and Kuvalayananda, who emphasised its health benefits. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoga Journal
''Yoga Journal'' is a website and digital journal, formerly a print magazine, on yoga as exercise founded in California in 1975 with the goal of combining the essence of traditional yoga with scientific understanding. It has produced live events and materials such as DVDs on yoga and related subjects. The magazine grew from the California Yoga Teachers Association's newsletter, which was called ''The Word''. ''Yoga Journal'' has repeatedly won Western Publications Association's Maggie Awards for "Best Health and Fitness Magazine". It has however been criticized for representing yoga as being intended for affluent white women; in 2019 it attempted to remedy this by choosing a wider variety of yoga models. Beginnings ''Yoga Journal'' was started in May 1975 by the California Yoga Teachers Association (CYTA), with Rama Jyoti Vernon as President, William Staniger as the founding editor, and Judith Lasater on the board and serving as copy editor. Their goal was to combine "the ess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatha Yoga
Haṭha yoga is a branch of yoga which uses physical techniques to try to preserve and channel the vital force or energy. The Sanskrit word हठ ''haṭha'' literally means "force", alluding to a system of physical techniques. Some haṭha yoga style techniques can be traced back at least to the 1st-century CE, in texts such as the Hindu Sanskrit epics and Buddhism's Pali canon. The oldest dated text so far found to describe haṭha yoga, the 11th-century ''Amṛtasiddhi'', comes from a tantric Buddhist milieu. The oldest texts to use the terminology of ''hatha'' are also Vajrayana Buddhist. Hindu hatha yoga texts appear from the 11th century onwards. Some of the early haṭha yoga texts (11th-13th c.) describe methods to raise and conserve bindu (vital force, that is, semen, and in women ''rajas –'' menstrual fluid). This was seen as the physical essence of life that was constantly dripping down from the head and being lost. Two early Haṭha yoga techniques sought to e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light On Yoga
''Light on Yoga: Yoga Dipika'' (Sanskrit: योग दीपिका, "Yoga Dīpikā") is a 1966 book on the Iyengar Yoga style of modern yoga as exercise by B. K. S. Iyengar, first published in English. It describes more than 200 yoga postures or asanas, and is illustrated with some 600 monochrome photographs of Iyengar demonstrating these. The book has been described as the 'bible of modern yoga', and its presentation of the asanas has been called "unprecedented" and "encyclopedic". It has been translated into at least 23 languages and has sold over three million copies. Context Yoga is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices from ancient India, forming one of the six orthodox schools of Hindu philosophical traditions. In the Western world, however, yoga is often taken to mean a modern form of medieval Hatha yoga, practised mainly for exercise, consisting largely of the postures called asanas. B. K. S. Iyengar (1918-2014) was born in a poor family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supta Matsyendrasana
Matsyendrasana ( sa, मत्स्येन्द्रासन; IAST: ''Matsyendrāsana''), Matsyendra's Pose or Lord of the Fishes Pose, is a seated twisting asana in hatha yoga and modern yoga as exercise. The full form is the difficult Paripurna Matsyendrasana. A common and easier variant is Ardha Matsyendrasana. The asana has many variations, and in its half form is one of the twelve basic asanas in many systems of hatha yoga. Etymology and origins The name comes from the Sanskrit words परिपूर्ण ''Paripurna'', perfected; मत्स्येन्द् ''Matsyendra'', one of the founders of hatha yoga, whose name in turn means "lord of the fishes"; and आसन ''asana'', posture or seat; अर्ध ''ardha'' means half. The asana is medieval, described in the 15th century ''Haṭha Yoga Pradīpikā'' 1.26-7, which states that it destroys many diseases, and the 17th century ''Gheraṇḍa Saṃhitā'' 2.22-23. Yogi Ghamande chose the asana for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |