|
Jasta 33
Royal Prussian Jagdstaffel 33 was a "hunting group" (i.e., fighter squadron) of the '' Luftstreitkräfte'', the air arm of the Imperial German Army during World War I. As one of the original German fighter squadrons, the unit would score a minimum of 46 verified aerial victories (the squadron's records being grossly incomplete from August 1918 onwards). In turn, their casualties for the war would amount to six pilots killed in action, seven wounded in action, and one killed in a noncombat crash. History Royal Prussian Jagdstaffel 33 was formed on 14 December 1916 at the FEA 3 training facility at Gotha, Germany. It did not get into action until March 1917, but its first aerial victory followed shortly thereafter, on 24 April 1917. As part of the changing German tactics based on concentration of air power, the squadron was incorporated into Jagdgruppe II along with Jasta 7, Jasta 29, and Jasta 35 in August 1917; the new fighter wing was commanded by Otto Schmidt. Not quite a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jasta 57
Royal Prussian Jagdstaffel 57, commonly abbreviated to Jasta 57, was a "hunting group" (i.e., fighter squadron) of the ''Luftstreitkräfte'', the air arm of the Imperial German Army during World War I. The squadron would score over 32 aerial victories during the war. The unit's victories came at the expense of four pilots killed in action, one injured in a flying accident, four wounded in action, and one taken prisoner of war. History Jasta 57 was founded at the pilots and observers training school at Königsberg on 6 January 1918. The new squadron began operations on 20 January 1918. Four days later, it was incorporated into Rudolf Berthold's ''Jagdgruppe Nord'' and tasked to support '' 6 Armee''. On 26 February 1918, the unit flew its first combat missions. On 11 March, it scored its first aerial victories. Leutnant Hans Viebig (1897–1961), who would become Oberst of the Wehrmacht with the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross, was first and shot down a Royal Aircraft Factory R.E.8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascq
Ascq (; pcd, Ask) is a former commune on the Marque river in the Nord department in northern France, at seven kilometers from Belgium. Agricultural village until the Industrial Revolution, the former independent commune merged with others to become a district of the ''new town'' planned community of Villeneuve-d'Ascq since 1970. The operatic bass Louis-Henri Obin (1820–1895) was born in Ascq. Ascq is known for the Ascq massacre of 1 April 1944, where the Nazis assaulted the inhabitants and massacred 86 innocent men. The village was decorated with the Croix de guerre 1939–1945 and the Legion of Honour. The Gare d'Ascq (railway station) is served by trains from Lille to Liège (Belgium) and to Orchies. Heraldry Architecture and points of interest Ascq main monuments are Saint-Pierre-en-Antioche Church (19th century), based on a building of 15th century, gare d'Ascq (19th century) railway station, the post office, the town hall (20th century) and the Château Cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roucourt, Nord
Roucourt () is a commune in the Nord department in northern France. German ''Jagdstaffel 11'' operated here on 13 April, 1917. Heraldry See also *Communes of the Nord department The following is a list of the 648 communes of the Nord department of the French Republic. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):Communes of Nord (French department) French Flanders {{Nord-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burscheid
Burscheid is a town in the Rheinisch-Bergischer district, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. The town is known for its sub-communities (somewhat equivalent to the American concept of neighborhoods) and the town centre with its marketplace and churches. Economy The two largest employers in Burscheid are Federal Mogul GmbH (formerly known as Goetze AG) and Johnson Controls. Government The current mayor is Stefan Caplan (CDU), first elected in 2014 and re-elected in September 2020. The current city council was elected with the following breakdown of political affiliations, as of the 2020 local election: * CDU: 14 seats * Bündnis für Burscheid: 8 seats * SPD: 7 seats * Grüne: 7 seats * FDP: 2 seats * UWG: 2 seats Transportation Burscheid is on the A1 Autobahn, and federal highway (Bundesstraße) 51 travels through the town. The Verkehrsverbund Rhein-Sieg and Verkehrsverbund Rhein-Ruhr both operate bus lines that stop in Burscheid. Neighboring communities Burscheid is within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavinchove
Bavinchove (; from Dutch; ''Bavinkhove'' in modern Dutch spelling) is a commune in the Nord department in northern France. Population Heraldry See also *Communes of the Nord department The following is a list of the 648 communes of the Nord department of the French Republic. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):Communes of Nord (French department) French Flanders {{Nord-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guise
Guise (; nl, Wieze) is a commune in the Aisne department in Hauts-de-France in northern France. The city was the birthplace of the noble family of Guise, Dukes of Guise, who later became Princes of Joinville. Population Sights The remains of the medieval castle of Guise, the seat of the Dukes of Guise, is within the commune. Economy Guise is the agricultural centre of the northern area of Aisne. Miscellaneous Guise was the birthplace of Camille Desmoulins (1760–1794), a journalist and politician who played an important part in the French Revolution, and that of Jeanne Macherez who was a heroine during the World War I. Over a period of 20 years, beginning about 1856, Jean-Baptiste Godin built the (the Social Palace), an industrial and communal residential complex that was a separate community within Guise. It expressed many of his ideas about developing social sympathy through improved housing and services for workers and their families, influenced by the ideas of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villers-au-Tertre
Villers-au-Tertre () is a commune in the Nord department in northern France. It is around 10 km south-east of Douai. Surrounding communes Neighbouring communes are Erchin to the north, Monchecourt to the east, Fressain to the south-east and Bugnicourt to the south-west. Heraldry Unwelcome fame Villers-au-Tertre hit the headlines at the end of July 2010 because the new owner of a house in the village, while trying to plant a tree, found the bones of two newly born children buried in the garden. Subsequently six more bodies were discovered at the recently acquired home of the former proprietor's daughter and son in law. The presumed mother of the deceased children has been placed under judicial investigation See also *Communes of the Nord department The following is a list of the 648 communes of the Nord department of the French Republic. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020): [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
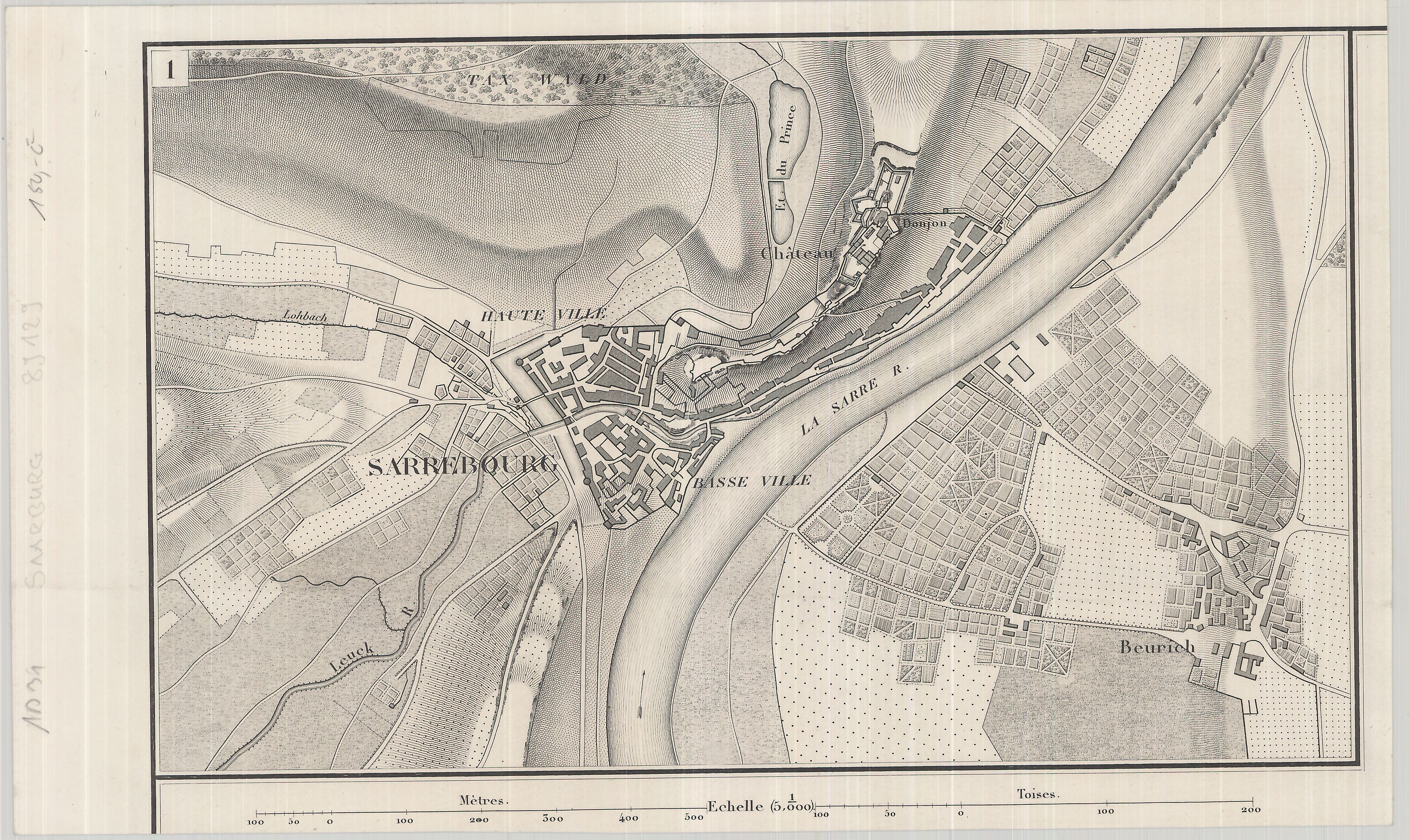
Saarburg
Saarburg (, ) is a city of the Trier-Saarburg district, in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, on the banks of the river Saar in the hilly country a few kilometers upstream from the Saar's junction with the Moselle. Now known as a tourist attraction, the river Leuk flows into the town center and makes a spectacular drop of some 60 feet before joining the larger Saar that bisects the town. The waterfall is the result of a 13th-century project to redirect the Leuk through the city center. Saarburg is the seat of the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' ("collective municipality") Saarburg-Kell. The area around Saarburg is noted for the cultivation of Riesling grapes. History The history of the city begins with the construction of the now-ruined castle by Graf Siegfried of Luxembourg in 964. It received its town charter in 1291. The city has a bell foundry, the Glockengießerei Mabilion, which has been in operation since the 1770s, and the only one in Germany that produces bronze bells. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotha
Gotha () is the fifth-largest city in Thuringia, Germany, west of Erfurt and east of Eisenach with a population of 44,000. The city is the capital of the district of Gotha and was also a residence of the Ernestine Wettins from 1640 until the end of monarchy in Germany in 1918. The House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha originating here spawned many European rulers, including the royal houses of the United Kingdom, Belgium, Portugal (until 1910) and Bulgaria (until 1946). In the Middle Ages, Gotha was a rich trading town on the trade route ''Via Regia'' and between 1650 and 1850, Gotha saw a cultural heyday as a centre of sciences and arts, fostered by the dukes of Saxe-Gotha. The first duke, Ernest the Pious, was famous for his wise rule. In the 18th century, the ''Almanach de Gotha'' was first published in the city. The publisher Justus Perthes and the encyclopedist Joseph Meyer made Gotha a leading centre of German publishing around 1800. In the early 19th century, Gotha was a bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |