|
Jarkko Kari
Jarkko J. Kari is a Finland, Finnish mathematician and computer scientist, known for his contributions to the theory of Wang tiles and cellular automata. Kari is currently a professor at the Department of Mathematics, University of Turku. Biography Kari received his Ph.D. in 1990 from the University of Turku; his dissertation, supervised by Arto Salomaa. He married Lila Kari, a later mathematics student at Turku; they divorced, and afterwards Lila Kari became a professor of computer science at the University of Western Ontario in Canada. Research Wang tiles are unit squares with colored markings on each side; they may be used to Tessellation, tesselate the plane, but only with tiles that have matching colors on adjoining edges. The problem of determining whether a set of Wang tiles forms a valid tessellation is undecidable problem, undecidable, and its undecidability rests on finding sets of Wang tiles that can only tesselate the plane aperiodic tiling, aperiodically, in such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jarkko Kari A N Kirillov And Tero Laihonen At University Of Turku 20190404
Jarkko is a given name. Notable people with the given name include: *Jarkko Ahola (born 1977), Finnish performing artist, composer and singer *Jarkko Ala-Huikku (born 1980), Finnish Greco-Roman wrestler *Jarkko Hattunen (born 1987), Finnish ice hockey player *Jarkko Hentula (born 1970), Finnish film and television producer *Jarkko Huovila (born 1975), Finnish orienteering competitor *Jarkko Hurme (born 1986), Finnish footballer *Jarkko Immonen (born 1982), Finnish ice hockey player *Jarkko Immonen (ice hockey, born 1984) (born 1984), Finnish ice hockey player *Jarkko Kari, Finnish mathematician and computer scientist *Jarkko Kauppinen (born 1982), Finnish biathlete *Jarkko Kauvosaari (born 1983), Finnish ice hockey player *Jarkko Kinnunen (born 1984), Finnish race walker *Jarkko Komula (born 1976), Finnish darts player *Jarkko Lahdenmäki (born 1991), Finnish footballer *Jarkko Lahti (born 1978), Finnish actor *Jarkko Laine (1947–2006), Finnish poet and writer *Jarkko Laukia, Finni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Undecidable Problem
In computability theory and computational complexity theory, an undecidable problem is a decision problem for which it is proved to be impossible to construct an algorithm that always leads to a correct yes-or-no answer. The halting problem is an example: it can be proven that there is no algorithm that correctly determines whether arbitrary programs eventually halt when run. Background A decision problem is any arbitrary yes-or-no question on an infinite set of inputs. Because of this, it is traditional to define the decision problem equivalently as the set of inputs for which the problem returns ''yes''. These inputs can be natural numbers, but also other values of some other kind, such as strings of a formal language. Using some encoding, such as a Gödel numbering, the strings can be encoded as natural numbers. Thus, a decision problem informally phrased in terms of a formal language is also equivalent to a set of natural numbers. To keep the formal definition simple, it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Mathematicians
Finnish may refer to: * Something or someone from, or related to Finland * Culture of Finland * Finnish people or Finns, the primary ethnic group in Finland * Finnish language, the national language of the Finnish people * Finnish cuisine See also * Finish (other) * Finland (other) * Suomi (other) Suomi means ''Finland'' in Finnish. It may also refer to: *Finnish language * Suomi (surname) * Suomi, Minnesota, an unincorporated community * Suomi College, in Hancock, Michigan, now referred to as Finlandia University * Suomi Island, Western ... * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Computer Scientists
Finnish may refer to: * Something or someone from, or related to Finland * Culture of Finland * Finnish people or Finns, the primary ethnic group in Finland * Finnish language Finnish ( endonym: or ) is a Uralic language of the Finnic branch, spoken by the majority of the population in Finland and by ethnic Finns outside of Finland. Finnish is one of the two official languages of Finland (the other being Swedis ..., the national language of the Finnish people * Finnish cuisine See also * Finish (other) * Finland (other) * Suomi (other) * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Automatists
Cellular may refer to: *Cellular automaton, a model in discrete mathematics *Cell biology, the evaluation of cells work and more * ''Cellular'' (film), a 2004 movie *Cellular frequencies, assigned to networks operating in cellular RF bands *Cellular manufacturing *Cellular network, cellular radio networks *U.S. Cellular Field, also known as "The Cell", a baseball stadium in Chicago *U.S. Cellular Arena, an arena in Milwaukee, Wisconsin Terms such as cellular organization, cellular structure, cellular system, and so on may refer to: *Cell biology, the evaluation of how cells work and more *Cellular communication networks, systems for allowing communication through mobile phones and other mobile devices *Cellular organizational structures, methods of human organization in social groups *Clandestine cell organizations, entities organized to commit crimes, acts of terror, or other malicious activities See also *Cell (other) Cell most often refers to: * Cell (biology), th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theoretical Computer Science (journal)
''Theoretical Computer Science'' (TCS) is a computer science journal published by Elsevier, started in 1975 and covering theoretical computer science. The journal publishes 52 issues a year. It is abstracted and indexed by Scopus and the Science Citation Index. According to the Journal Citation Reports, its 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... is 0.827. References Computer science journals Elsevier academic journals Publications established in 1975 {{comp-sci-theory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear Phenomena
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathematicians, and many other scientists because most systems are inherently nonlinear in nature. Nonlinear dynamical systems, describing changes in variables over time, may appear chaotic, unpredictable, or counterintuitive, contrasting with much simpler linear systems. Typically, the behavior of a nonlinear system is described in mathematics by a nonlinear system of equations, which is a set of simultaneous equations in which the unknowns (or the unknown functions in the case of differential equations) appear as variables of a polynomial of degree higher than one or in the argument of a function which is not a polynomial of degree one. In other words, in a nonlinear system of equations, the equation(s) to be solved cannot be written as a linear combination of the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reversible Cellular Automaton
A reversible cellular automaton is a cellular automaton in which every configuration has a unique predecessor. That is, it is a regular grid of cells, each containing a state drawn from a finite set of states, with a rule for updating all cells simultaneously based on the states of their neighbors, such that the previous state of any cell before an update can be determined uniquely from the updated states of all the cells. The time-reversed dynamics of a reversible cellular automaton can always be described by another cellular automaton rule, possibly on a much larger neighborhood. Several methods are known for defining cellular automata rules that are reversible; these include the block cellular automaton method, in which each update partitions the cells into blocks and applies an invertible function separately to each block, and the second-order cellular automaton method, in which the update rule combines states from two previous steps of the automaton. When an automaton is not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Geometry
In mathematics, hyperbolic geometry (also called Lobachevskian geometry or Bolyai– Lobachevskian geometry) is a non-Euclidean geometry. The parallel postulate of Euclidean geometry is replaced with: :For any given line ''R'' and point ''P'' not on ''R'', in the plane containing both line ''R'' and point ''P'' there are at least two distinct lines through ''P'' that do not intersect ''R''. (Compare the above with Playfair's axiom, the modern version of Euclid's parallel postulate.) Hyperbolic plane geometry is also the geometry of pseudospherical surfaces, surfaces with a constant negative Gaussian curvature. Saddle surfaces have negative Gaussian curvature in at least some regions, where they locally resemble the hyperbolic plane. A modern use of hyperbolic geometry is in the theory of special relativity, particularly the Minkowski model. When geometers first realised they were working with something other than the standard Euclidean geometry, they described their geomet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lecture Notes In Computer Science
''Lecture Notes in Computer Science'' is a series of computer science books published by Springer Science+Business Media since 1973. Overview The series contains proceedings, post-proceedings, monographs, and Festschrifts. In addition, tutorials, state-of-the-art surveys, and "hot topics" are increasingly being included. The series is indexed by DBLP. See also *''Monographiae Biologicae'', another monograph series published by Springer Science+Business Media *''Lecture Notes in Physics'' *''Lecture Notes in Mathematics'' *''Electronic Workshops in Computing ''Electronic Workshops in Computing'' (eWiC) is a publication series by the British Computer Society. The series provides free online access for conferences and workshops in the area of computing. For example, the EVA London Conference proceeding ...'', published by the British Computer Society References External links * Publications established in 1973 Computer science books Series of non-fiction books Springer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
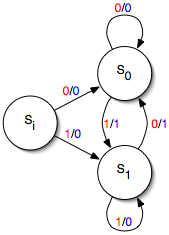
Mealy Machine
In the theory of computation, a Mealy machine is a finite-state machine whose output values are determined both by its current state and the current inputs. This is in contrast to a Moore machine, whose output values are determined solely by its current state. A Mealy machine is a deterministic finite-state transducer: for each state and input, at most one transition is possible. History The Mealy machine is named after George H. Mealy, who presented the concept in a 1955 paper, "A Method for Synthesizing Sequential Circuits". Formal definition A Mealy machine is a 6-tuple (S, S_0, \Sigma, \Lambda, T, G) consisting of the following: * a finite set of states S * a start state (also called initial state) S_0 which is an element of S * a finite set called the input alphabet \Sigma * a finite set called the output alphabet \Lambda * a transition function T : S \times \Sigma \rightarrow S mapping pairs of a state and an input symbol to the corresponding next state. * an output functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |