|
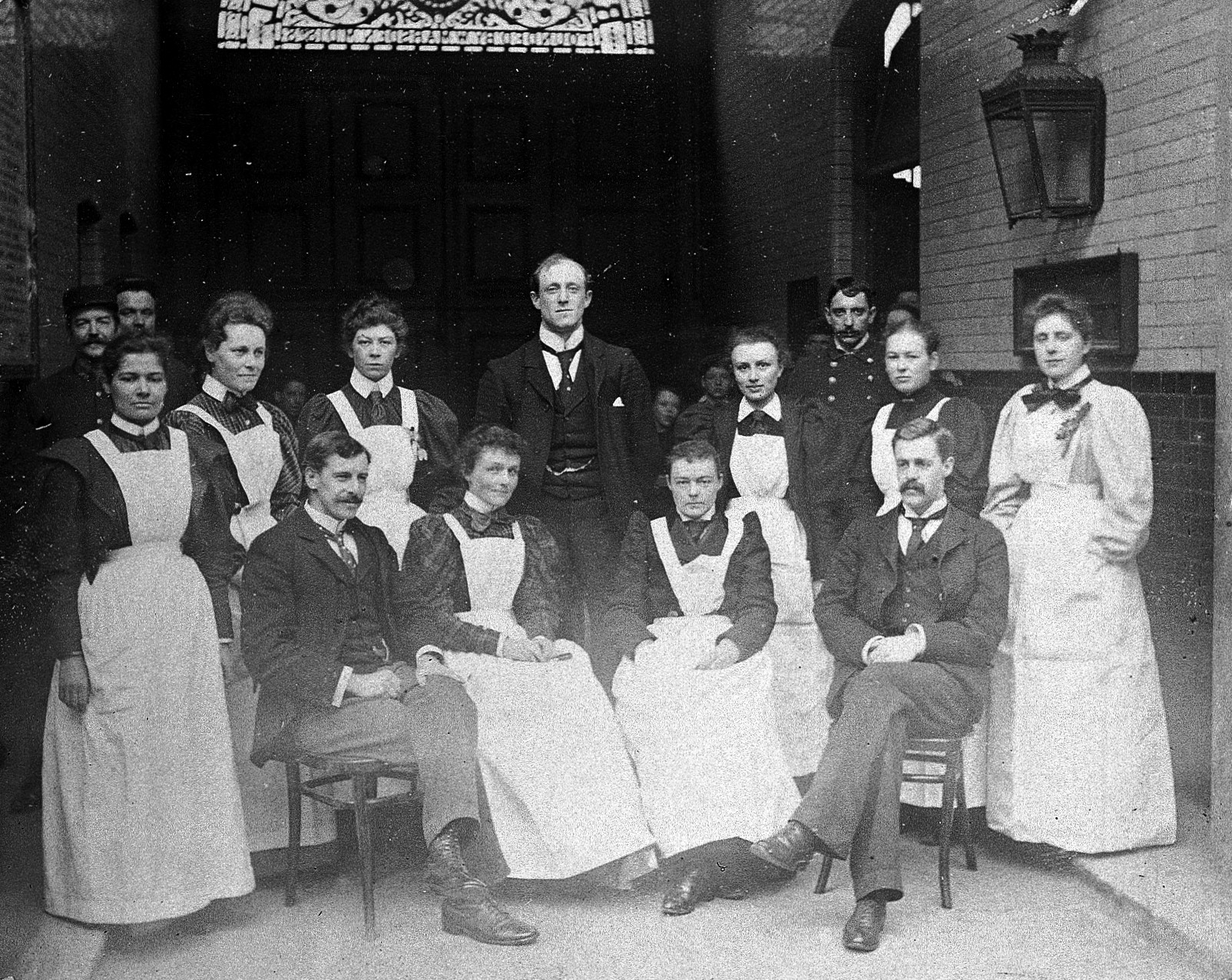
Jane Harriett Walker
Jane Harriett Walker CH (24 October 1859 – 7 November 1938) was an English medical doctor who first implemented the open-air method of treating tuberculosis in England. She was appointed a Companion of Honour in 1931. Life Walker was born at Dewsbury in Yorkshire, one of eight children of a wool merchant. She was educated in Southport and at the Yorkshire College of Science. Determined to become a doctor, she studied at the London School of Medicine for Women in 1880 and qualified as a Licentiate of the Royal College of Physicians of Ireland in 1884.Susan L. Cohen, ‘Walker, Jane Harriett (1859–1938)’, Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford University Press, 2004; online edn, September 201accessed 14 April 2017/ref> She was the 45th woman to be included on the General Medical Register: the first was Elizabeth Blackwell in 1859. She established a private medical practice on Harley Street in London. She was interested in treating women and children. She became a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dewsbury
Dewsbury is a minster and market town in the Metropolitan Borough of Kirklees in West Yorkshire, England. It lies on the River Calder and on an arm of the Calder and Hebble Navigation waterway. It is to the west of Wakefield, east of Huddersfield and south of Leeds. Historically a part of the West Riding of Yorkshire, after undergoing a period of major growth in the 19th century as a mill town, Dewsbury went through a period of decline. Dewsbury forms part of the Heavy Woollen District of which it is the largest town. According to the 2011 census, Dewsbury had a population of 62,945. History Toponymy The ''Domesday Book'' of 1086 records the name as ''Deusberie'', ''Deusberia'', ''Deusbereia'', or ''Deubire'', literally "Dewi's fort", Dewi being an old Welsh name (equivalent to David) and "bury" coming from the old English word "burh", meaning fort. Other, less supported, theories exist as to the name's origin. For example, that it means "dew hill", from Old English ''d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denver, Norfolk
Denver is a village and civil parish in the English county of Norfolk. The village is situated on the River Great Ouse, approximately 1 mile (2 km) south of the small town of Downham Market, 14 miles (22 km) south of the larger town of King's Lynn, and 37 miles (60 km) west of the city of Norwich. History Denver's name is of Anglo-Saxon origin and derives from the Old English for a passage or crossing used by the Danes. Denver acted as the terminus for the Roman Fen Causeway which began in Peterborough. In the Domesday Book, Denver is listed as a settlement of 43 households in the hundred of Clackclose. In 1086, the village was part of the estates of William de Warenne. In 1651, the first sluice to help with the drainage of The Fens was built by the Dutch architect Cornelius Vermuyden. The sluice was rebuilt after bursting in 1713. Today, the West Norfolk Rowing Club are based at Denver Sluice. Denver Windmill was built in the mid-Nineteenth Century and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiston, Suffolk
Wissington or Wiston is a small village and former civil parish In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government below districts and counties, or their combined form, the unitary authorit ..., now in the parish of Nayland-with-Wissington in the Babergh district, in south Suffolk, England. In 1881 the civil parish had a population of 191. On the 1 April 1844 it was merged to create Nayland-with-Wissington. References External links Villages in Suffolk Babergh District Former civil parishes in Suffolk {{suffolk-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
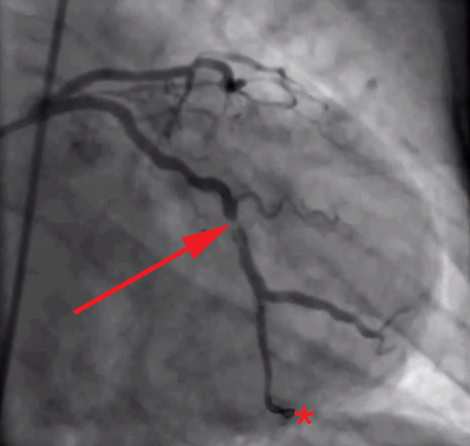
Coronary Thrombosis
Coronary thrombosis is defined as the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel of the heart. This blood clot may then restrict blood flow within the heart, leading to heart tissue damage, or a myocardial infarction, also known as a heart attack. Coronary thrombosis is most commonly caused as a downstream effect of atherosclerosis, a buildup of cholesterol and fats in the artery walls. The smaller vessel diameter allows less blood to flow and facilitates progression to a myocardial infarction. Leading risk factors for coronary thrombosis are high LDL cholesterol, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, and hypertension. Signs and symptoms A coronary thrombus is asymptomatic until it causes significant obstruction, leading to various forms of angina or eventually a myocardial infarction. Common warning symptoms are crushing chest pain, shortness of breath, and upper body discomfort. Pathogenesis Coronary thrombosis and myocardial infarction are sometimes used as synonyms, althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Leeds
, mottoeng = And knowledge will be increased , established = 1831 – Leeds School of Medicine1874 – Yorkshire College of Science1884 - Yorkshire College1887 – affiliated to the federal Victoria University1904 – University of Leeds , type = Public , endowment = £90.5 million , budget = £751.7 million , chancellor = Jane Francis , vice_chancellor = Simone Buitendijk , students = () , undergrad = () , postgrad = () , city = Leeds , province = West Yorkshire , country = England , campus = Urban, suburban , free_label = Newspaper , free = The Gryphon , colours = , website www.leeds.ac.uk, logo = Leeds University logo.svg , logo_size = 250 , administrative_staff = 9,200 , coor = , affiliations = The University of Leeds is a public research university in Leeds, West Yorkshire, England. It was established in 1874 as the Yorkshire College of Science. In 1884 it merged with the Leeds School of Medicine (established 1831) and was renam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magistrate
The term magistrate is used in a variety of systems of governments and laws to refer to a civilian officer who administers the law. In ancient Rome, a '' magistratus'' was one of the highest ranking government officers, and possessed both judicial and executive powers. In other parts of the world, such as China, a magistrate was responsible for administration over a particular geographic area. Today, in some jurisdictions, a magistrate is a judicial officer who hears cases in a lower court, and typically deals with more minor or preliminary matters. In other jurisdictions (e.g., England and Wales), magistrates are typically trained volunteers appointed to deal with criminal and civil matters in their local areas. Original meaning In ancient Rome, the word '' magistratus'' referred to one of the highest offices of state. Analogous offices in the local authorities, such as ''municipium'', were subordinate only to the legislature of which they generally were members, '' ex officio'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Wycombe
High Wycombe, often referred to as Wycombe ( ), is a market town in Buckinghamshire, England. Lying in the valley of the River Wye surrounded by the Chiltern Hills, it is west-northwest of Charing Cross in London, south-southeast of Aylesbury, southeast of Oxford, northeast of Reading and north of Maidenhead. According to the 2021 United Kingdom census, High Wycombe's built up area has a population of 127,856, making it the second largest town in the ceremonial county of Buckinghamshire after Milton Keynes. The High Wycombe Urban Area, the conurbation of which the town is the largest component, has a population of 140,684. High Wycombe is mostly an unparished area. Part of the urban area constitutes the civil parish of Chepping Wycombe, which had a population of 14,455 according to the 2001 census – this parish represents that part of the ancient parish of Chepping Wycombe which was outside the former municipal borough of Wycombe. There has been a market he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preparatory School (United Kingdom)
A preparatory school (or, shortened: prep school) in the United Kingdom is a fee-charging independent primary school that caters for children up to approximately the age of 13. The term "preparatory school" is used as it ''prepares'' the children for the Common Entrance Examination in order to secure a place at an independent secondary school, typically one of the English public schools. They are also preferred by some parents in the hope of getting their child into a state selective grammar school. Most prep schools are inspected by the Independent Schools Inspectorate, which is overseen by Ofsted on behalf of the Department for Education. Overview Boys' prep schools are generally for 8-13 year-olds, who are prepared for the Common Entrance Examination, the key to entry into many secondary independent schools. Before the age of 7 or 8, the term "pre-prep school" is used. Girls' independent schools in England tend to follow the age ranges of state schools more closely than th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Medicine
The Royal Society of Medicine (RSM) is a medical society in the United Kingdom, headquartered in London. History The Society was established in 1805 as Medical and Chirurgical Society of London, meeting in two rooms in barristers’ chambers at Gray's Inn and then moving to Lincoln's Inn Fields where it stayed for 25 years. In 1834 the Society moved to Berners Street and was granted a Royal Charter by King William IV. In 1889 under the leadership of Sir John MacAlister, a Building Committee chaired by Timothy Holmes supervised the move of the quarters of the Society from Berners Street to 20 Hanover Square. In 1905 an eleven-member committee headed by Sir Richard Douglas Powell organised the celebration of the Society's centenary. Two years later the Royal Medical and Chirurgical Society of London came together with seventeen specialist medical societies and, with a supplementary Royal Charter granted by Edward VII, became the Royal Society of Medicine. In 1910 the Society ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Women's Federation
The Medical Women's Federation is the largest UK body of women doctors. The organisation is dedicated to the advancement of the personal and professional development of women in medicine and to improving the health of women and their families in society. It was founded in 1917, and its headquarters are located in Tavistock Square, London. Origins The Medical Women's Foundation built upon the Association of Registered Medical Women, which had been founded in London in 1879 with the intention that it would 'speak on behalf of all medical women and represent their interests.' Nine members comprised the original association, though other provincial associations and members rapidly followed as more women became qualified in medicine. Representatives of these associations came together in 1916 to discuss the benefits of establishing a Federation. This meeting was in part stimulated by the Government's dismissive attitude towards women doctors who wished to serve in the First World Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleanor Soltau
Eleanor Soltau (1877–1962) was an English doctor who led the first unit of the Scottish Women's Hospitals for Foreign Service in Serbia. Early life Soltau was born in Romford, Essex, in late 1877. Her parents were George Soltau (d. c.1896), a nonconformist minister of Barnstaple, and his wife, Grace Elizabeth Soltau, suffragist and first president of the Tasmanian Woman's Christian Temperance Union, daughter of A. J. Tapson MB, London. There were nine children in all, born between 1876 and 1890. In the 1880s the family moved to Launceston, Tasmania, where Eleanor's father took charge of a mission church and in 1887 her mother set up the pioneering Hope Cottage, a refuge and lying-in home for single mothers. Soltau attended Launceston Ladies' College and was successful in the matriculation examination for Melbourne University in 1893. Medical career Soltau qualified as a doctor at the London School of Medicine for Women. Then at Ilford, she passed her final examination i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |