|
Jan Van Boendale
Jan van Boendale (c.1280 – c.1351), formerly sometimes known as Jan De Klerk ("Jan the Clerk") was a 14th-century secretary of the city of Antwerp and author of narrative and didactic verse.Ph. Blommaert, "Boendale (Jean)", ''Biographie Nationale de Belgique''vol. 2(Brussels, 1868), 587-591. Two of his works, '' Brabantsche yeesten'' and '' Der leken spieghel'', are listed in the Canon of Dutch Literature compiled by the Digital Library for Dutch Literature. Life Jan was born in Boendale, near Tervuren, around 1280. He moved to Antwerp, where he became secretary to the city council, and lived there until his death around 1351. He undertook a number of diplomatic missions on behalf of the city of Antwerp or of the States of Brabant, and in 1332 was present in the entourage of John III, Duke of Brabant, at Heylissem. Works *''Brabantsche yeesten'' (a history of the duchy of Brabant) *''Der leken spieghel'' (a history of salvation) *''Jans Testeye'' (a dialogue on controverted q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godfried Lutgarde
Godfried is the Dutch form of Geoffrey and Gottfried. It may refer to: *Carel Godfried Willem Hendrik baron van Boetzelaer van Oosterhout (1892–1986), Dutch diplomat and politician * Eugène Godfried (1952–2009), Curaçao-born political activist and broadcaster * Godfried Aduobe (born 1975), former Ghanaian football midfielder *Godfried Bomans (1913–1971), popular Dutch author and television personality and a prominent Dutch catholic *Godfried Danneels (1933–2019), Belgian cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church * Godfried Dejonckheere (born 1952), retired Belgian race walker *Godfried Donkor (born 1964), Ghanaian artist, living and working in London *Godfried Schalcken (1643–1706), Dutch genre and portrait painter *Godfried Toussaint, Research Professor of Computer Science at New York University Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) *Godfried van Mierlo (1518–1587), bishop of Haarlem and abbot of Egmond Abbey from 1570 to 1578 *Godfried-Willem Raes, Belgian composer, performer and instrument ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th-century Births
The 13th century was the century which lasted from January 1, 1201 ( MCCI) through December 31, 1300 ( MCCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan, which stretched from Eastern Asia to Eastern Europe. The conquests of Hulagu Khan and other Mongol invasions changed the course of the Muslim world, most notably the Siege of Baghdad (1258), the destruction of the House of Wisdom and the weakening of the Mamluks and Rums which, according to historians, caused the decline of the Islamic Golden Age. Other Muslim powers such as the Mali Empire and Delhi Sultanate conquered large parts of West Africa and the Indian subcontinent, while Buddhism witnessed a decline through the conquest led by Bakhtiyar Khilji. The Southern Song dynasty would begin the century as a prosperous kingdom but would eventually be invaded and annexed into the Yuan dynasty of the Mongols. The Kamakura Shogunate of Japan would be invaded by the Mongols. Goryeo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgundian Netherlands Poets
Burgundian can refer to any of the following: *Someone or something from Burgundy. *Burgundians, an East Germanic tribe, who first appear in history in South East Europe. Later Burgundians colonised the area of Gaul that is now known as Burgundy (French Bourgogne) *The Old Burgundian language (Germanic), an East Germanic language spoken by the Burgundians *The Modern Burgundian language (Oïl), an Oïl language also known as spoken in the region of Burgundy, France. * Frainc-Comtou dialect, sometimes regarded as part of the Burgundian group of languages *Burgundian (party) The Burgundian party was a political allegiance against France that formed during the latter half of the Hundred Years' War. The term "Burgundians" refers to the supporters of the Duke of Burgundy, John the Fearless, that formed after the assa ..., a political faction in early 15th century during the Hundred Years' War See also * Burgundian War (other) {{disambiguation Language and nationality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tournaisis Campaign Of 1340
The Tournaisis campaign of 1340, also known as the Tournai Campaign was a military campaign of King Edward III of England during the Hundred Years War. The English army was supported by Flemish, Hainault, Brabant and Holy Roman Empire forces. The campaign resulted in the defeat of an Anglo-Flemish force, carrying out a small scale chevauchée in the County of Artois, at the Battle of Saint-Omer, an unsuccessful siege of Tournai and ended with meeting of the English and French armies at Bouvines without battle. The campaign ended with the Truce of Espléchin and the withdrawal of the English led forces. The English army was led by King Edward III, and the French by King Philip VI of France. Aftermath The truce was broken in 1341, when conflict erupted between English and French forces over the succession to the Duchy of Brittany. Edward III, backed John de Montfort, and Philip VI, backed Charles of Blois Charles of Blois-Châtillon (131929 September 1364), nicknamed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward III Of England
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring royal authority after the disastrous and unorthodox reign of his father, Edward II. EdwardIII transformed the Kingdom of England into one of the most formidable military powers in Europe. His fifty-year reign was one of the longest in English history, and saw vital developments in legislation and government, in particular the evolution of the English Parliament, as well as the ravages of the Black Death. He outlived his eldest son, Edward the Black Prince, and the throne passed to his grandson, Richard II. Edward was crowned at age fourteen after his father was deposed by his mother, Isabella of France, and her lover Roger Mortimer. At age seventeen he led a successful coup d'état against Mortimer, the ''de facto'' ruler of the coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
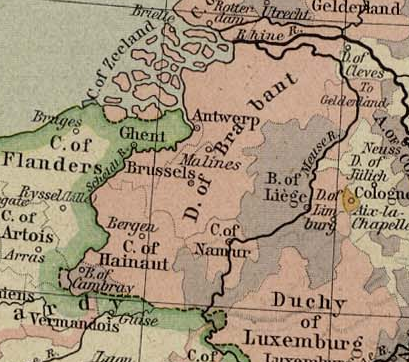
Duchy Of Brabant
The Duchy of Brabant was a State of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1183. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries, part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1430 and of the Habsburg Netherlands from 1482, until it was partitioned after the Dutch revolt. Present-day North Brabant (''Noord-Brabant'') was ceded to the Generality Lands of the Dutch Republic according to the 1648 Peace of Westphalia, while the reduced duchy remained part of the Habsburg Netherlands until it was conquered by French Revolutionary forces in 1794, which was recognized by treaty in 1797. Today all the duchy's former territories, apart from exclaves, are in Belgium except for the Dutch province of North Brabant. Geography The Duchy of Brabant (adjective: ''Brabantian'' or '' Brabantine'') was historically divided into four parts, each with its own capital. The four capitals were Leuven, Brussels, Antwerp and 's-Hertogenbosch. Before 's-Hertogenb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John III, Duke Of Brabant
John III ( nl, Jan; 1300 – 5 December 1355) was Duke of Brabant, Duke of Lothier, Lothier (1312–1355) and List of rulers of Limburg, Limburg (1312–1347 then 1349–1355). He was the son of John II, Duke of Brabant, and Margaret of England, Duchess of Brabant, Margaret of England. John and the towns of Brabant The early fourteenth century, an economic boom time for Brabant, marks the rise of the duchy's towns, which depended on English wool for their essential cloth industry. During John's minority, the major towns of Brabant had the authority to appoint councillors to direct a regency, under terms of the Charter of Kortenberg granted by his father in the year of his death (1312). By 1356 his daughter and son-in-law were forced to accept the Joyous Entry of 1356, famous Joyous Entry as a condition for their recognition, so powerful had the states of Brabant become. The marital alignment with France was tested and failed as early as 1316, when Louis X of France, Louis X reque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,Statistics Belgium; ''Loop van de bevolking per gemeente'' (Excel file) Population of all municipalities in Belgium, . Retrieved 1 November 2017. it is the most populous municipality in Belgium, and with a metropolitan population of around 1,200,000 people, it is the second-largest metrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States Of Brabant
The States of Brabant were the representation of the three estates (nobility, clergy and commons) to the court of the Duke of Brabant. The three estates were also called the States. Supported by the economic strength of the cities Antwerp, Brussels and Leuven, the States always were an important power before the rulers of the country, as was reflected by the charter of the duchy. After the duchy of Brabant and all Seventeen Provinces of the Netherlands came under the rule of the dukes of Burgundy, the States of Brabant became the host of the States-General of the Netherlands, who used to assemble in Brussels. In 1579 and 1580, during the Eighty Years' War, most cities and States of Brabant joined Dutch independence declaration (Union of Utrecht and Act of Abjuration), but Spanish troops reconquered most of the territory of the duchy and restored Spanish Catholic rule (except for North Brabant. See also Siege of Antwerp (1584-1585)). By the end of 1789, the States of Brabant aga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tervuren
Tervuren () is a municipality in the province of Flemish Brabant, in Flanders, Belgium. The municipality comprises the villages of Duisburg, Tervuren, Vossem and Moorsel. On January 1, 2006, Tervuren had a total population of 20,636. The total area is 32.92 km², which gives it a population density of 627 inhabitants per km². The official language of Tervuren is Dutch. Local minorities consist primarily of French speakers and nationals of many countries of the European Union, the USA, and Canada. The reason for this diverse mix of nationalities is the presence of expatriate workers and their families working in and around Brussels, usually either for the European Union, NATO or for multinational corporations. The British School of Brussels has been located in Tervuren since 1970. Tervuren is also home of the English speaking St. Paul's Church, part of the Anglican Church Tervuren is one of the richest municipalities in Belgium. It is linked to Brussels by a large processi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |