|
James S. Hyde
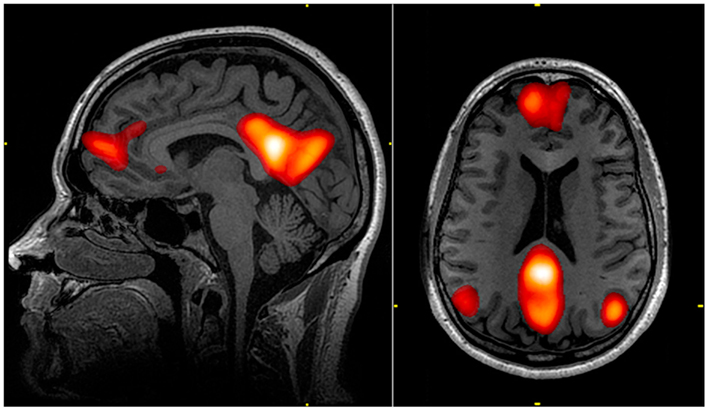
James S. Hyde (May 20, 1932 - August 13, 2022) was an American biophysicist. He held the James S. Hyde chair in Biophysics at the Medical College of Wisconsin (MCW) where he specialized in magnetic resonance instrumentation and methodology development in two distinct areas: electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). He is senior author of the widely cited 1995 paper by B.B. Biswal ''et al.'' reporting the discovery of resting state functional connectivity (fcMRI) in the human brain.Biswal, B. B., Yetkin, F. Z., Haughton, V. M., Hyde, J. S.: Functional Connectivity in the Motor Cortex of Resting Human Brain Using Echo-Planar MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 34:537-541, 1995 He also served as Director of the National Biomedical EPR Center, a Research Resource supported by the National Institutes of Health. He was author of more than 400 peer-reviewed papers and review articles and held 35 U.S. Patents. He was recognized by Festschrifts in both EPR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biophysics
Biophysics is an interdisciplinary science that applies approaches and methods traditionally used in physics to study biological phenomena. Biophysics covers all scales of biological organization, from molecular to organismic and populations. Biophysical research shares significant overlap with biochemistry, molecular biology, physical chemistry, physiology, nanotechnology, bioengineering, computational biology, biomechanics, developmental biology and systems biology. The term ''biophysics'' was originally introduced by Karl Pearson in 1892. Roland Glaser. Biophysics: An Introduction'. Springer; 23 April 2012. . The term ''biophysics'' is also regularly used in academia to indicate the study of the physical quantities (e.g. electric current, temperature, stress, entropy) in biological systems. Other biological sciences also perform research on the biophysical properties of living organisms including molecular biology, cell biology, chemical biology, and biochemistry. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loop-gap Resonator
A loop-gap resonator (LGR) is an electromagnetic resonator that operates in the radio and microwave frequency ranges. The simplest LGRs are made from a conducting tube with a narrow slit cut along its length. The LGR dimensions are typically much smaller than the free-space wavelength of the electromagnetic fields at the resonant frequency. Therefore, relatively compact LGRs can be designed to operate at frequencies that are too low to be accessed using, for example, cavity resonators. These structures can have very sharp resonances (high quality factors) making them useful for electron spin resonance (ESR) experiments, and precision measurements of electromagnetic material properties (permittivity and permeability). Background Loop-gap resonators (LGRs) can be modelled as lumped-element circuits. The slit along the length of the resonator has an effective capacitance C and the bore of the resonator has effective inductance L. At, or near, the resonance frequency, a circumfe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical College Of Wisconsin Faculty
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since prehistoric times, and for most of this time it was an art (an area of skill and knowledge), frequently having connections to the religious and philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for healing, or an anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Mitchell, South Dakota
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Biophysicists
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams Soccer * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1932 Births
Year 193 ( CXCIII) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sosius and Ericius (or, less frequently, year 946 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 193 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * January 1 – Year of the Five Emperors: The Roman Senate chooses Publius Helvius Pertinax, against his will, to succeed the late Commodus as Emperor. Pertinax is forced to reorganize the handling of finances, which were wrecked under Commodus, to reestablish discipline in the Roman army, and to suspend the food programs established by Trajan, provoking the ire of the Praetorian Guard. * March 28 – Pertinax is assassinated by members of the Praetorian Guard, who storm the imperial palace. The Empire is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tesla (unit)
The tesla (symbol: T) is the unit of magnetic flux density (also called magnetic B-field strength) in the International System of Units (SI). One tesla is equal to one weber per square metre. The unit was announced during the General Conference on Weights and Measures in 1960 and is named in honour of Serbian-American electrical and mechanical engineer Nikola Tesla, upon the proposal of the Slovenian electrical engineer France Avčin. Definition A particle, carrying a charge of one coulomb (C), and moving perpendicularly through a magnetic field of one tesla, at a speed of one metre per second (m/s), experiences a force with magnitude one newton (N), according to the Lorentz force law. That is, : \text = \dfrac. As an SI derived unit, the tesla can also be expressed in terms of other units. For example, a magnetic flux of 1 weber (Wb) through a surface of one square meter is equal to a magnetic flux density of 1 tesla.''The International System of Units (SI), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Connectome Project
The Human Connectome Project (HCP) is a five-year project sponsored by sixteen components of the National Institutes of Health, split between two consortia of research institutions. The project was launched in July 2009 as the first of three Grand Challenges of the NIH's Blueprint for Neuroscience Research. On September 15, 2010, the NIH announced that it would award two grants: $30 million over five years to a consortium led by Washington University in St. Louis and the University of Minnesota, with strong contributions from Oxford University (FMRIB) and $8.5 million over three years to a consortium led by Harvard University, Massachusetts General Hospital and the University of California Los Angeles. The goal of the Human Connectome Project is to build a "network map" (connectome) that will shed light on the anatomical and functional connectivity within the healthy human brain, as well as to produce a body of data that will facilitate research into brain disorders such as dyslex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute Of Mental Health
The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) is one of 27 institutes and centers that make up the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The NIH, in turn, is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services and is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and health-related research. NIMH is the largest research organization in the world specializing in mental illness. Joshua A. Gordon is the current director of NIMH. The institute was first authorized by the U.S. government in 1946, when then President Harry Truman signed into law the National Mental Health Act, although the institute was not formally established until 1949. NIMH is a $1.5 billion enterprise, supporting research on mental health through grants to investigators at institutions and organizations throughout the United States and through its own internal (intramural) research effort. The mission of NIMH is "to transform the understanding and treatment of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Functional Connectivity
Dynamic functional connectivity (DFC) refers to the observed phenomenon that functional connectivity changes over a short time. Dynamic functional connectivity is a recent expansion on traditional functional connectivity analysis which typically assumes that functional networks are static in time. DFC is related to a variety of different neurological disorders, and has been suggested to be a more accurate representation of functional brain networks. The primary tool for analyzing DFC is fMRI, but DFC has also been observed with several other mediums. DFC is a recent development within the field of functional neuroimaging whose discovery was motivated by the observation of temporal variability in the rising field of steady state connectivity research. Overview and history Static connectivity Functional connectivity refers to the functionally integrated relationship between spatially separated brain regions. Unlike structural connectivity which looks for physical connections in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiofrequency Coil
Radiofrequency coils (RF coils) are the receivers, and sometimes also the transmitters, of radiofrequency (RF) signals in equipment used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The MR signal in MRI is produced by the process of resonance, which is the result of radiofrequency pulses. They consist of two electromagnetic coils, the transmitter and receiver, which generate the field and receive the resulting signal. Atomic nuclei of interest in MRI studies have their own resonant frequencies, in the radiofrequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Although the electromagnetic fields produced by the transmitting coil are in the RF range of tens of megahertz (often in the shortwave radio portion of the electromagnetic spectrum) at powers usually exceeding the highest powers used by amateur radio, there is very little RF interference produced by the MRI machine. The reason for this is that the MRI is a very poor radio transmitter, and is without an antenna. The RF frequency electrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_1938.jpg)