|
James I'Anson Cudworth
James I'Anson Cudworth (12 January 1817 – 22 October 1899) was an English railway engineer, and was Locomotive Superintendent of the South Eastern Railway (SER). He served in this capacity from 1845 to 1876. He is notable for designing a successful method for burning coal in steam locomotives without significant emission of smoke, and for introducing the 0-4-4T wheel arrangement to English railways. Early life Cudworth was born in Darlington, County Durham on 12 January 1817, the second of three children born to William Cudworth and Mary I'Anson (born 18 November 1785, Darlington). His parents were Quakers, and had married in 1810; William Cudworth was a grocer and druggist, whilst Mary I'Anson's family name was of Scandinavian origin. James Cudworth's elder brother William was a civil engineer, and worked for the Stockton & Darlington Railway; William's son William John, also a civil engineer, worked for the North Eastern Railway. Career Cudworth was apprenticed to Rober ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darlington
Darlington is a market town in the Borough of Darlington, County Durham, England. The River Skerne flows through the town; it is a tributary of the River Tees. The Tees itself flows south of the town. In the 19th century, Darlington underwent substantial industrial development, spurred by the establishment there of the world's first permanent steam-locomotive-powered passenger railway: the Stockton and Darlington Railway. Much of the vision (and financing) behind the railway's creation was provided by local Quaker families in the Georgian and Victorian eras. In the 2011 Census, the town had a population of 92,363 (the county's largest settlement by population) which had increased by the 2020 estimate population to 93,417. The borough's population was 105,564 in the census, It is a unitary authority and is a constituent member of the Tees Valley Combined Authority therefore part of the Tees Valley mayoralty. History Darnton Darlington started as an Anglo-Saxon settlem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniflow Steam Engine
The uniflow type of steam engine uses steam that flows in one direction only in each half of the cylinder. Thermal efficiency is increased by having a temperature gradient along the cylinder. Steam always enters at the hot ends of the cylinder and exhausts through ports at the cooler centre. By this means, the relative heating and cooling of the cylinder walls is reduced. Design details Steam entry is usually controlled by poppet valves (which act similarly to those used in internal combustion engines) that are operated by a camshaft. The inlet valves open to admit steam when minimum expansion volume has been reached at the start of the stroke. For a period of the crank cycle, steam is admitted, and the poppet inlet is then closed, allowing continued expansion of the steam during the stroke, driving the piston. Near the end of the stroke, the piston will uncover a ring of exhaust ports mounted radially around the centre of the cylinder. These ports are connected by a manifold an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folkestone
Folkestone ( ) is a port town on the English Channel, in Kent, south-east England. The town lies on the southern edge of the North Downs at a valley between two cliffs. It was an important harbour and shipping port for most of the 19th and 20th centuries. There has been a settlement in this location since the Mesolithic era. A nunnery was founded by Eanswith, granddaughter of Æthelberht of Kent in the 7th century, who is still commemorated as part of the town's culture. During the 13th century it subsequently developed into a seaport and the harbour developed during the early 19th century to provide defence against a French invasion. Folkestone expanded further west after the arrival of the railway in 1843 as an elegant coastal resort, thanks to the investment of the Earl of Radnor under the urban plan of Decimus Burton. In its heyday - during the Edwardian era - Folkestone was considered the most fashionable resort of the time, visited by royalties - amongst them Queen Vic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Eastern Main Line
The South Eastern Main Line is a major long-distance railway route in South East England, UK, one of the three main routes crossing the county of Kent, going via Sevenoaks, Tonbridge, Ashford and Folkestone to Dover. The other routes are the Chatham Main Line which runs along the north Kent coast to Ramsgate or Dover via Chatham and High Speed 1 which runs through the centre of Kent to the coast at Folkestone where it joins the Channel Tunnel. History Construction The line was built by the South Eastern Railway (SER), which was in competition with the London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR), hence the duplication of routes in Kent. The original main line was given sanction by Act of Parliament in 1836. The route first authorised was from via Oxted, Tunbridge, Maidstone, Ashford and Folkestone. The route was to make use of the existing London and Croydon Railway and London and Greenwich Railway companies' tracks. The SER did not have much spare capital. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Stirling (1835–1917)
James Stirling (1835–1917) was a Scottish mechanical engineer. He was Locomotive Superintendent of the Glasgow and South Western Railway and later the South Eastern Railway. Stirling was born on 2 October 1835, a son of Robert Stirling, rector of Galston, East Ayrshire. Career Glasgow and South Western Railway After working for a village millwright he joined the Glasgow and South Western Railway (GSWR) where he was apprenticed to his brother Patrick, who had been Locomotive Superintendent of that railway since 1853. On completion of his apprenticeship, he spent a year as a fitter at Sharp Stewart in Manchester, before returning to the GSWR drawing office at Kilmarnock; he later became works manager. On 1 March 1866, his brother Patrick left the GSWR for the Great Northern Railway (GNR), where he became Works Manager at Doncaster, and James was appointed Locomotive Superintendent of the GSWR in his place. Patrick became the Locomotive Superintendent of the GNR from 1 Oct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
0-6-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and no trailing wheels. This was the most common wheel arrangement used on both tender and tank locomotives in versions with both inside and outside cylinders. In the United Kingdom, the Whyte notation of wheel arrangement was also often used for the classification of electric and diesel-electric locomotives with side-rod coupled driving wheels. Under the UIC classification, popular in Europe, this wheel arrangement is written as C if the wheels are coupled with rods or gears, or Co if they are independently driven, the latter usually being electric and diesel-electric locomotives. Overview History The 0-6-0 configuration was the most widely used wheel arrangement for both tender and tank steam locomotives. The type was also widely used for diesel switchers (shunters). Because they lack lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumberland
Cumberland ( ) is a historic counties of England, historic county in the far North West England. It covers part of the Lake District as well as the north Pennines and Solway Firth coast. Cumberland had an administrative function from the 12th century until 1974. From 1974 until 2023, Cumberland lay within Cumbria, a larger administrative area which also covered Westmorland and parts of Yorkshire and Lancashire. In April 2023, Cumberland will be revived as an administrative entity when Cumbria County Council is abolished and replaced by two Unitary authorities of England, unitary authorities; one of these is to be named Cumberland (unitary authority), Cumberland and will include most of the historic county, with the exception of Penrith, Cumbria, Penrith and the surrounding area. Cumberland is bordered by the historic counties of Northumberland to the north-east, County Durham to the east, Westmorland to the south-east, Lancashire to the south, and the Scotland, Scottish counties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitehaven
Whitehaven is a town and port on the English north west coast and near to the Lake District National Park in Cumbria, England. Historically in Cumberland, it lies by road south-west of Carlisle and to the north of Barrow-in-Furness. It is the administrative seat of the Borough of Copeland, and has a town council for the parish of Whitehaven. The population of the town was 23,986 at the 2011 census. The town's growth was largely due to the exploitation of the extensive coal measures by the Lowther family, driving a growing export of coal through the harbour from the 17th century onwards. It was also a major port for trading with the American colonies, and was, after London, the second busiest port of England by tonnage from 1750 to 1772. This prosperity led to the creation of a Georgian planned town in the 18th century which has left an architectural legacy of over 170 listed buildings. Whitehaven has been designated a "gem town" by the Council for British Archaeology d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulk And Ley
Tulk and Ley was a 19th-century iron mining company in west Cumberland which also ran an engineering works at Lowca near Whitehaven. Overview Established on the Lowca site in 1800 as "Heslops, Milward, Johnston & Co."- the engineering and ironfounding expertise coming from the brothers Adam, Thomas & Crosby Heslop, formerly associated with the Seaton ironworks- the firm was taken over by iron-mining firm Tulk, Ley & Co. about 1837. Ley was an absentee investor, the driving force behind the enterprise being engineer John Augustus Tulk. His decision to concentrate on finished goods rather than simple foundry products swiftly paid off, with orders for locomotives from the new Maryport and Carlisle Railway. The first two were a 2-2-2 and an 0-6-0, with a further 2-2-2 in 1843. They then built a number of 0-4-2 locos for various Northern railways. They also attempted to move into the shipbuilding business in 1842-3, producing ''Lowca'', the first iron ship ever launched in Cumberland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
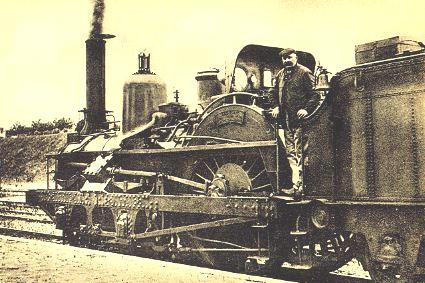
Crampton Locomotive
A Crampton locomotive is a type of steam locomotive designed by Thomas Russell Crampton and built by various firms from 1846. The main British builders were Tulk and Ley and Robert Stephenson and Company. Notable features were a low boiler and large driving wheels. The crux of the Crampton patent was that the single driving axle was placed behind the firebox, so that the driving wheels could be very large. This helped to give this design a low centre of gravity, so that it did not require a very broad-gauge track to travel safely at high speeds. Its wheel arrangement was usually or . Design variations Because the single driving axle was behind the firebox, Crampton locomotives usually had outside cylinders. However, some inside cylinder versions were built using indirect drive, then known as a ''jackshaft''. The inside cylinders drove a crankshaft located in front of the firebox and the crankshaft was connected to the driving wheels by outside rods. Some long-wheelbase s we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-2-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, two powered driving wheels on one axle and no trailing wheels. This type of locomotive is often called a Jervis type, the name of the original designer. Overview The wheel arrangement type was common on United States railroads from the 1830s through the 1850s. The first to be built was the ''Experiment'', later named ''Brother Jonathan'', for the Mohawk and Hudson Railroad in 1832. It was built by the West Point Foundry based on a design by John B. Jervis. Having little else to reference, the manufacturers patterned the boiler and valve gear after locomotives built by Robert Stephenson of England. A few examples of Stephenson locomotives were already in operation in America, so engineers did not have to travel too far to get their initial ideas. In England, the was developed around 1840 from the 2-2-2 design of Stephenson's first Long B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SER 59 Class
Ser or SER may refer to: Places * Ser, a village in Bogdand Commune, Satu Mare County, Romania * Serpens (Ser), an astronomical constellation of the northern hemisphere * Serres, known as Ser in Serbian, a city in Macedonia, Greece Organizations * Social-Economic Council (''Sociaal-Economische Raad'', SER) of the Dutch government * Society for Ecological Restoration (SER) * Society for Epidemiologic Research, North America Science and technology * Ser (unit), an obsolete unit of volume in India * Sequence of events recorder * Serine (Ser), an ɑ-amino acid in biochemistry * Single-ended recuperative burner, a type of gas burner * SIP Express Router * Smooth endoplasmic reticulum, in cell biology * Soft error rate, in computing * ''Ser.'', taxonomic author abbreviation of Nicolas Charles Seringe (1776–1858), French physician and botanist Transport * SER, IATA code for Freeman Municipal Airport, Seymour, Indiana, U.S. * SER, MRT station abbreviation for Serangoon MRT station, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)