Cumberland on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cumberland ( ) is a historic county in the far North West England. It covers part of the Lake District as well as the north Pennines and
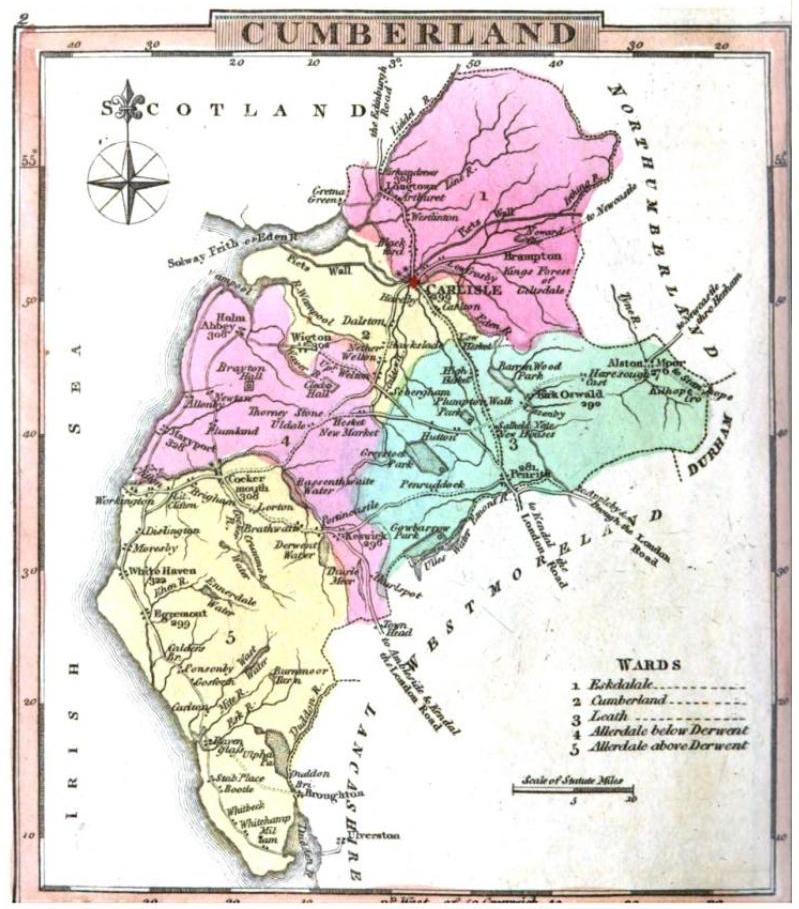 The Earldom of Carlisle was partitioned into baronies. When the County of Cumberland was created, the baronies were subdivided as
The Earldom of Carlisle was partitioned into baronies. When the County of Cumberland was created, the baronies were subdivided as
* Parts or all of these parishes and townships constituted the City of Carlisle, and were largely outside the jurisdiction of Cumberland Ward.
Cumberland, England – History and Description, 1868Map of Cumberland
on Wikishire {{Coord, 54, 45, N, 3, 00, W, display=title, region:GB_type:adm2nd_source:GNS-enwiki Cumberland, * Counties of England established in antiquity Counties of England disestablished in 1974 History of Cumbria
Solway Firth
The Solway Firth ( gd, Tràchd Romhra) is a firth that forms part of the border between England and Scotland, between Cumbria (including the Solway Plain) and Dumfries and Galloway. It stretches from St Bees Head, just south of Whitehaven ...
coast. Cumberland had an administrative function from the 12th century until 1974. From 1974 until 2023, Cumberland lay within Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in North West England, bordering Scotland. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local government, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. C ...
, a larger administrative area which also covered Westmorland
Westmorland (, formerly also spelt ''Westmoreland'';R. Wilkinson The British Isles, Sheet The British IslesVision of Britain/ref> is a historic county in North West England spanning the southern Lake District and the northern Dales. It had an ...
and parts of Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ; abbreviated Yorks), formally known as the County of York, is a historic county in northern England and by far the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its large area in comparison with other English counties, functions have ...
and Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a historic county, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly.
The non-metropolitan county of Lancash ...
. In April 2023, Cumberland will be revived as an administrative entity when Cumbria County Council is abolished and replaced by two unitary authorities
A unitary authority is a local authority responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are usually performed by a higher level of sub-national government or the national governme ...
; one of these is to be named Cumberland and will include most of the historic county, with the exception of Penrith and the surrounding area.
Cumberland is bordered by the historic counties of Northumberland
Northumberland () is a county in Northern England, one of two counties in England which border with Scotland. Notable landmarks in the county include Alnwick Castle, Bamburgh Castle, Hadrian's Wall and Hexham Abbey.
It is bordered by land ...
to the north-east, County Durham to the east, Westmorland
Westmorland (, formerly also spelt ''Westmoreland'';R. Wilkinson The British Isles, Sheet The British IslesVision of Britain/ref> is a historic county in North West England spanning the southern Lake District and the northern Dales. It had an ...
to the south-east, Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a historic county, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly.
The non-metropolitan county of Lancash ...
to the south, and the Scottish counties of Dumfriesshire
Dumfriesshire or the County of Dumfries or Shire of Dumfries (''Siorrachd Dhùn Phris'' in Gaelic) is a historic county and registration county in southern Scotland. The Dumfries lieutenancy area covers a similar area to the historic county.
I ...
and Roxburghshire to the north.
Early history
In theEarly Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
, Cumbria was part of the Kingdom of Strathclyde
Strathclyde (lit. " Strath of the River Clyde", and Strað-Clota in Old English), was a Brittonic successor state of the Roman Empire and one of the early medieval kingdoms of the Britons, located in the region the Welsh tribes referred to as ...
in the Hen Ogledd
Yr Hen Ogledd (), in English the Old North, is the historical region which is now Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands that was inhabited by the Brittonic people of sub-Roman Britain in the Early Middle Ages. Its population sp ...
, or "Old North", and its people spoke a Brittonic language
The Brittonic languages (also Brythonic or British Celtic; cy, ieithoedd Brythonaidd/Prydeinig; kw, yethow brythonek/predennek; br, yezhoù predenek) form one of the two branches of the Insular Celtic language family; the other is Goidelic. ...
now called Cumbric
Cumbric was a variety of the Common Brittonic language spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North" in what is now the counties of Westmorland, Cumberland and northern Lancashire in Northern England and the souther ...
. The first record of the term 'Cumberland' appears in AD 945, when the '' Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' recorded that the area was ceded to Malcolm I
Máel Coluim mac Domnaill ( anglicised Malcolm I; died 954) was king of Alba (before 943 – 954), becoming king when his cousin Constantine II abdicated to become a monk. He was the son of Donald II.
Biography
Malcolm was born in 897 in Au ...
, king of Alba
The monarch of Scotland was the head of state of the Kingdom of Scotland. According to tradition, the first King of Scots was Kenneth I MacAlpin (), who founded the state in 843. Historically, the Kingdom of Scotland is thought to have grown ...
(Scotland), by King Edmund I of England
Edmund I or Eadmund I (920/921 – 26 May 946) was King of the English from 27 October 939 until his death in 946. He was the elder son of King Edward the Elder and his third wife, Queen Eadgifu, and a grandson of King Alfred the Great. After ...
. As with , the native Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
name for Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
, the names 'Cumberland' and 'Cumbria' are derived from ''kombroges'' in Common Brittonic, which originally meant "compatriots".
At the time of the Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manus ...
(AD 1086) most of the future county was part of Scotland, although some villages around Millom
Millom is a town and civil parish on the north shore of the estuary of the River Duddon in southwest Cumbria, historically part of Cumberland, England. It is situated just outside the Lake District National Park, about north of Barrow-in-Furnes ...
, which were the possessions of the Earl of Northumbria
Earl of Northumbria or Ealdorman of Northumbria was a title in the late Anglo-Saxon, Anglo-Scandinavian and early Anglo-Norman period in England. The ealdordom was a successor of the Norse Kingdom of York. In the seventh century, the Anglo-Saxo ...
, had been incorporated into Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ; abbreviated Yorks), formally known as the County of York, is a historic county in northern England and by far the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its large area in comparison with other English counties, functions have ...
.
In AD 1092, King William Rufus
William II ( xno, Williame; – 2 August 1100) was King of England from 26 September 1087 until his death in 1100, with powers over Normandy and influence in Scotland. He was less successful in extending control into Wales. The third so ...
of England invaded the Carlisle district, settling it with colonists. He created an Earldom of Carlisle, and granted the territory to Ranulf le Meschin
Ranulf le Meschin, 3rd Earl of Chester (1070−1129) was a Norman magnate based in northern and central England. Originating in Bessin in Normandy, Ranulf made his career in England thanks to his kinship with Hugh d'Avranches - the Earl of Che ...
. In 1133, Carlisle was made the see
See or SEE may refer to:
* Sight - seeing
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Music:
** ''See'' (album), studio album by rock band The Rascals
*** "See", song by The Rascals, on the album ''See''
** "See" (Tycho song), song by Tycho
* Television
* ...
of a new diocese, largely identical with the area of the earldom. However, on the death of King Henry I of England in 1135, the area was regained by King David I of Scotland
David I or Dauíd mac Maíl Choluim ( Modern: ''Daibhidh I mac haoilChaluim''; – 24 May 1153) was a 12th-century ruler who was Prince of the Cumbrians from 1113 to 1124 and later King of Scotland from 1124 to 1153. The youngest son of Mal ...
. He was able to consolidate his power and made Carlisle one of his chief seats of government, while England descended into a lengthy civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
. The Cumbric language is believed to have become extinct in the 12th century.
The area returned to the English crown in 1157, when Henry II of England
Henry II (5 March 1133 – 6 July 1189), also known as Henry Curtmantle (french: link=no, Court-manteau), Henry FitzEmpress, or Henry Plantagenet, was King of England from 1154 until his death in 1189, and as such, was the first Angevin king ...
took possession of the area (from Malcolm IV of Scotland
Malcolm IV ( mga, Máel Coluim mac Eanric, label=Medieval Gaelic; gd, Maol Chaluim mac Eanraig), nicknamed Virgo, "the Maiden" (between 23 April and 24 May 11419 December 1165) was King of Scotland from 1153 until his death. He was the eldest ...
). Henry II formed two new counties from the former earldom: Westmorland
Westmorland (, formerly also spelt ''Westmoreland'';R. Wilkinson The British Isles, Sheet The British IslesVision of Britain/ref> is a historic county in North West England spanning the southern Lake District and the northern Dales. It had an ...
and Carliol – originally an abbreviation of the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
' ishopof Carlisle'. Westmorland also included areas formerly part of the Earldom of Lancaster
The title of Earl of Lancaster was created in the Peerage of England in 1267. It was succeeded by the title Duke of Lancaster in 1351, which expired in 1361. (The most recent creation of the ducal title merged with the Crown in 1413.)
King Henry ...
. The lead- and silver-mining area of Alston, previously associated with the Liberty of Tynedale was later also added to the new county of Carliol for financial reasons. By 1177, Carliol had become known as Cumberland. The border between England and Scotland was made permanent by the Treaty of York
The Treaty of York was an agreement between the kings Henry III of England and Alexander II of Scotland, signed at York on 25 September 1237, which affirmed that Northumberland (which at the time also encompassed County Durham), Cumberland, and ...
in 1237.
Geography
The boundaries formed in the 12th century were not changed substantially over the county's existence. There are four English historic counties and two Scottish counties that it borders:Northumberland
Northumberland () is a county in Northern England, one of two counties in England which border with Scotland. Notable landmarks in the county include Alnwick Castle, Bamburgh Castle, Hadrian's Wall and Hexham Abbey.
It is bordered by land ...
and County Durham to the east; Westmorland
Westmorland (, formerly also spelt ''Westmoreland'';R. Wilkinson The British Isles, Sheet The British IslesVision of Britain/ref> is a historic county in North West England spanning the southern Lake District and the northern Dales. It had an ...
to the south, the Furness
Furness ( ) is a peninsula and region of Cumbria in northwestern England. Together with the Cartmel Peninsula it forms North Lonsdale, historically an exclave of Lancashire.
The Furness Peninsula, also known as Low Furness, is an area of vill ...
part of Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a historic county, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly.
The non-metropolitan county of Lancash ...
to the southwest; Dumfriesshire
Dumfriesshire or the County of Dumfries or Shire of Dumfries (''Siorrachd Dhùn Phris'' in Gaelic) is a historic county and registration county in southern Scotland. The Dumfries lieutenancy area covers a similar area to the historic county.
I ...
to the north and Roxburghshire to the northeast.
To the west the county is bounded by the Solway Firth
The Solway Firth ( gd, Tràchd Romhra) is a firth that forms part of the border between England and Scotland, between Cumbria (including the Solway Plain) and Dumfries and Galloway. It stretches from St Bees Head, just south of Whitehaven ...
and the Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir Èireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, Môr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Ce ...
. The northern boundary was formed by the Solway Estuary and the border with Scotland running east to Scotch Knowe at Kershope Burn. The boundary runs south from Scotch Knowe along the Cheviot Hills
The Cheviot Hills (), or sometimes The Cheviots, are a range of uplands straddling the Anglo-Scottish border between Northumberland and the Scottish Borders. The English section is within the Northumberland National Park. The range includes T ...
, then followed a tributary of the River Irthing
The River Irthing is a river in Cumbria, England and a major tributary of the River Eden. The name is recorded as Ard or Arden in early references. For the first 15 miles of its course it defines the border between Northumberland and Cumbria.
...
and crossed Denton Fell to the River Tees. From Tees Head the boundary crosses the Pennines to descend Crowdundale Beck, from where it followed the rivers Eden and Eamont to the centre of Ullswater
Ullswater is the second largest lake in the English Lake District, being about long and wide, with a maximum depth a little over . It was scooped out by a glacier in the Last Ice Age.
Geography
It is a typical Lake District "ribbon lake", ...
. The line follows Glencoin Beck to the top of Helvellyn
Helvellyn (; possible meaning: ''pale yellow moorland'') is a mountain in the English Lake District, the highest point of the Helvellyn range, a north–south line of mountains to the north of Ambleside, between the lakes of Thirlmere and Ul ...
ridge at Wrynose Pass
The Wrynose Pass is a mountain pass in the Lake District National Park in Cumbria, England between the Duddon Valley and Little Langdale.
Etymology
The unusual name of the pass is taken from that of the adjacent Wrynose hill, also called W ...
and along the River Duddon
The Duddon is a river of north-west England. It rises at a point above sea level near the Three Shire Stone at the highest point of Wrynose Pass (). The river descends to the sea over a course of about before entering the Irish Sea at the Du ...
(near Millom
Millom is a town and civil parish on the north shore of the estuary of the River Duddon in southwest Cumbria, historically part of Cumberland, England. It is situated just outside the Lake District National Park, about north of Barrow-in-Furnes ...
) to the sea .
The highest point of the county is Scafell Pike
Scafell Pike () is the highest and the most prominent mountain in England, at an elevation of above sea level. It is located in the Lake District National Park, in Cumbria, and is part of the Southern Fells and the Scafell massif.
Scafell P ...
, at , the highest mountain in England. Carlisle is the county town.
Sub-divisions
 The Earldom of Carlisle was partitioned into baronies. When the County of Cumberland was created, the baronies were subdivided as
The Earldom of Carlisle was partitioned into baronies. When the County of Cumberland was created, the baronies were subdivided as ward
Ward may refer to:
Division or unit
* Hospital ward, a hospital division, floor, or room set aside for a particular class or group of patients, for example the psychiatric ward
* Prison ward, a division of a penal institution such as a pris ...
s, a county sub-division also used in Durham Durham most commonly refers to:
*Durham, England, a cathedral city and the county town of County Durham
*County Durham, an English county
* Durham County, North Carolina, a county in North Carolina, United States
*Durham, North Carolina, a city in N ...
, Northumberland
Northumberland () is a county in Northern England, one of two counties in England which border with Scotland. Notable landmarks in the county include Alnwick Castle, Bamburgh Castle, Hadrian's Wall and Hexham Abbey.
It is bordered by land ...
and Westmorland
Westmorland (, formerly also spelt ''Westmoreland'';R. Wilkinson The British Isles, Sheet The British IslesVision of Britain/ref> is a historic county in North West England spanning the southern Lake District and the northern Dales. It had an ...
. These originated as military subdivisions used to organise the male inhabitants for the county's defence from Scottish troop incursions.
Each ward was composed of a number of parishes, areas originally formed for ecclesiastical administration. In common with other northern England counties, many ancient parishes in Cumberland were very large, often consisting of a number of distinct townships and hamlets. Many of these ancient parishes eventually became civil parish
In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government below districts and counties, or their combined form, the unitary authorit ...
es and form the lowest level of local government.Allerdale above Derwent
Allerdale below Derwent
Eskdale
Leath
Cumberland Ward
Cumberland Ward included Carlisle andWigton
Wigton is a market town in the Allerdale borough of Cumbria, England. Historically in Cumberland, it lies just outside the Lake District in the borough of Allerdale. Wigton is at the centre of the Solway Plain, between the Caldbeck Fells an ...
as well as parts of Inglewood Forest
Inglewood Forest is a large tract of mainly arable and dairy farm land with a few small woodland areas between Carlisle and Penrith in the English non-metropolitan county of Cumbria or ancient county of Cumberland.
Etymology
''Inglewood'' is fi ...
. The parish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest, often termed a parish priest, who might be assisted by one o ...
of Stanwix just to the north of Carlisle was partly in both Eskdale and Cumberland wards.
Local government from the 19th century
During the 19th century a series of reforms reshaped the local government of the county, creating a system of districts with directly elected councils.Poor law and municipal reform
The first changes concerned the administration of the poor law, which was carried at parish level. ThePoor Law Amendment Act 1834
The ''Poor Law Amendment Act 1834'' (PLAA) known widely as the New Poor Law, was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom passed by the Whig government of Earl Grey. It completely replaced earlier legislation based on the ''Poor Relie ...
provided for the grouping of parishes into poor law unions, each with a central workhouse
In Britain, a workhouse () was an institution where those unable to support themselves financially were offered accommodation and employment. (In Scotland, they were usually known as poorhouses.) The earliest known use of the term ''workhouse' ...
and an elected board of guardians
Boards of guardians were ''ad hoc'' authorities that administered Poor Law in the United Kingdom from 1835 to 1930.
England and Wales
Boards of guardians were created by the Poor Law Amendment Act 1834, replacing the parish overseers of the po ...
. Cumberland was divided into nine unions: Alston with Garrigill, Bootle, Brampton, Carlisle, Cockermouth, Longtown, Penrith, Whitehaven and Wigton.
In the following year the Municipal Corporations Act 1835 was passed, reforming boroughs and cities in England and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the constituent countries England and Wales and was formed by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. The substantive law of the jurisdiction is Eng ...
as municipal borough
Municipal boroughs were a type of local government district which existed in England and Wales between 1835 and 1974, in Northern Ireland from 1840 to 1973 and in the Republic of Ireland from 1840 to 2002. Broadly similar structures existed in S ...
s with a uniform constitution. The corporation of the City of Carlisle was accordingly remodelled with a popularly elected council consisting of a mayor, aldermen and councillors.
Local boards and sanitary districts
Outside of municipal boroughs, there was no effective local government until the 1840s. In response to poor sanitary conditions and outbreaks of cholera, the Public Health Act 1848 and the Local Government Act 1858 allowed for the formation of local boards of health in populous areas. Local boards were responsible '' inter alia'' for water supply, drainage, sewerage, paving and cleansing. Eleven local boards were initially formed at Brampton, Cleator Moor, Cockermouth, Egremont, Holme Cultram, Keswick, Maryport, Millom, Penrith, Whitehaven, Wigton and Workington. Further reform under the Public Health Act 1875 saw the creation ofsanitary district
Sanitary districts were established in England and Wales in 1872 and in Ireland in 1878. The districts were of two types, based on existing structures:
*Urban sanitary districts in towns with existing local government bodies
*Rural sanitary dis ...
s throughout England and Wales. The existing municipal boroughs and local boards became "urban sanitary districts", while "rural sanitary districts" were formed from the remaining areas of the poor law unions.
Three more local boards were formed: Arlecdon and Frizington in 1882, Harrington in 1891 and Aspatria in 1892. In addition Workington and Whitehaven received charters of incorporation to become municipal boroughs in 1883 and 1894 respectively.
Local government acts of 1888 and 1894
In 1889, under theLocal Government Act 1888
Local may refer to:
Geography and transportation
* Local (train), a train serving local traffic demand
* Local, Missouri, a community in the United States
* Local government, a form of public administration, usually the lowest tier of administrat ...
, the Cumberland County Council was created as the county council
A county council is the elected administrative body governing an area known as a county. This term has slightly different meanings in different countries.
Ireland
The county councils created under British rule in 1899 continue to exist in Irel ...
for Cumberland, taking over administrative functions from the Court of Quarter Sessions
The courts of quarter sessions or quarter sessions were local courts traditionally held at four set times each year in the Kingdom of England from 1388 (extending also to Wales following the Laws in Wales Act 1535). They were also established in ...
. The Local Government Act 1894
The Local Government Act 1894 (56 & 57 Vict. c. 73) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales outside the County of London. The Act followed the reforms carried out at county level un ...
reconstituted the existing sanitary districts as urban districts and rural districts, each with an elected council.
The Act of 1888 also allowed any municipal borough with a population of 50,000 people or more to become a "county borough
County borough is a term introduced in 1889 in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, to refer to a borough or a city independent of county council control, similar to the unitary authorities created since the 1990s. An equivalent te ...
", independent of county council control. In 1914, Carlisle successfully applied for this status, ceasing to form part of the administrative county
An administrative county was a first-level administrative division in England and Wales from 1888 to 1974, and in Ireland from 1899 until either 1973 (in Northern Ireland) or 2002 (in the Republic of Ireland). They are now abolished, although mos ...
, although remaining within Cumberland for the purposes such as Lieutenancy and shrievalty
A sheriff is a government official, with varying duties, existing in some countries with historical ties to England where the office originated. There is an analogous, although independently developed, office in Iceland that is commonly transla ...
.
Reform in 1934
TheLocal Government Act 1929
The Local Government Act 1929 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that made changes to the Poor Law and local government in England and Wales.
The Act abolished the system of poor law unions in England and Wales and their board ...
imposed the duty on county councils of reviewing the districts within their administrative county so as to form more efficient units of local government. In general, this meant the merging of small or lightly populated areas into larger units. A review was carried in Cumberland in 1934. The following table lists the urban and rural districts before and after the changes.
The distribution of population in 1971 was as follows:1971 Census; Small Area Statistics
In 1974, under the Local Government Act 1972, the administrative county and county borough were abolished and their former area was combined with Westmorland
Westmorland (, formerly also spelt ''Westmoreland'';R. Wilkinson The British Isles, Sheet The British IslesVision of Britain/ref> is a historic county in North West England spanning the southern Lake District and the northern Dales. It had an ...
and parts of Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a historic county, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly.
The non-metropolitan county of Lancash ...
and the West Riding of Yorkshire
The West Riding of Yorkshire is one of three historic subdivisions of Yorkshire, England. From 1889 to 1974 the administrative county County of York, West Riding (the area under the control of West Riding County Council), abbreviated County ...
to form the new county of Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in North West England, bordering Scotland. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local government, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. C ...
. The area from Cumberland went on to form the districts of Carlisle, Allerdale, Copeland and part of Eden.
Legacy
The name continues in use as a geographical and cultural term, and it survives inCumberland sausage
Cumberland sausage is a pork sausage that originated in the ancient county of Cumberland, England, now part of Cumbria. It is traditionally very long, up to , and sold rolled in a flat, circular coil, but within western Cumbria, it is more often s ...
s; HMS ''Cumberland''; the Cumberland Fell Runners Club; the Cumberland Athletics Club; and various organisations and companies, such as the local newspapers ''The Cumberland News'', and ''The West Cumberland Times and Star'', and the Cumberland Building Society. It is also mentioned in '' Macbeth'' as the kingdom given to Prince Malcolm.
In June 1994, during the 1990s UK local government reform
The structure of local government in the United Kingdom underwent large changes in the 1990s. The system of two-tier local government introduced in the 1970s by the Local Government Act 1972 and the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973 was abol ...
, the Local Government Commission published draft recommendations, suggesting as one option a North Cumbria unitary authority
A unitary authority is a local authority responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are usually performed by a higher level of sub-national government or the national governmen ...
(also including Appleby, the historic county town of Westmorland). It also suggested that Cumberland could be reinstated as an independent ceremonial county. The final recommendations, published in October 1994, did not include such recommendations, apparently due to lack of expression of support for the proposal to the commission.
The Grass-of-Parnassus was the county flower
In a number of countries, plants have been chosen as symbols to represent specific geographic areas. Some countries have a country-wide floral emblem; others in addition have symbols representing subdivisions. Different processes have been used to ...
. It had been associated with the county since 1951, when it was included in the coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic achievement, which in its ...
granted to the Cumberland County Council. It subsequently featured in the arms granted to Cumbria County Council and Copeland Borough Council, in both cases to represent Cumberland. The flower was also attributed to Cumbria in 2002 as part of a national County flowers of the United Kingdom In 2002 Plantlife ran a "County Flowers" campaign to assign flowers to each of the counties of the United Kingdom and the Isle of Man. The results of this campaign designated a single plant species to a "county or metropolitan area" in the UK and Is ...
campaign by the charity Plantlife
Plantlife is the international conservation membership charity working to secure a world rich in wild plants and fungi. It is the only UK membership charity dedicated to conserving wild plants and fungi in their natural habitats and helping peo ...
.
In 2012, a flag based on the arms of the former Cumberland County Council was registered as the flag of Cumberland with the Flag Institute.
In 2013, the Secretary of State for Communities and Local Government, Eric Pickles, formally recognised and acknowledged the continued existence of England's 39 historic counties, including Cumberland.
In 2021, it was announced that in April 2023 local government in Cumbria will be reorganised into two unitary authorities
A unitary authority is a local authority responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are usually performed by a higher level of sub-national government or the national governme ...
, one of which is to be named Cumberland and would include most of the historic county, with the exception of Penrith and the surrounding area.
See also
* Lord Lieutenant of Cumberland, List of Lord Lieutenants for Cumberland * High Sheriff of Cumberland, List of High Sheriffs for Cumberland * Custos Rotulorum of Cumberland - Keepers of the Rolls * Cumberland (UK Parliament constituency), List of MPs for Cumberland constituency * Broughan (Cumberland surname)References
Further reading
* ''Cumberland Heritage'' by Molly Lefebure (Chapters include Camden, Briathwaite, Millbeck, Fellwalkers, Carlisle Canal, Armboth, John Peel (farmer) and the Blencathra), with endpaper maps of old Cumberland.Detail taken from a copy of ''Cumberland Heritage'' published by Victor Gollancz, London in 1970,External links
Cumberland, England – History and Description, 1868
on Wikishire {{Coord, 54, 45, N, 3, 00, W, display=title, region:GB_type:adm2nd_source:GNS-enwiki Cumberland, * Counties of England established in antiquity Counties of England disestablished in 1974 History of Cumbria