|
Jagdgeschwader 50
''Jagdgeschwader'' 50 (JG 50), sometimes erroneously referred to as ''Jagdgruppe'' 50, was formed at Wiesbaden-Erbenheim Airfield in the in early June 1943 as ''Jagdgruppe Süd''. It only controlled two augmented '' Staffeln'' (squadrons). It was a specialized unit with the primary objective to combat the United States Army Air Forces' heavy bomber formations as well as intercepting the Royal Air Force's de Havilland Mosquito light bombers during World War II. The Geschwader was equipped with the Messerschmitt Bf 109, some of them equipped with the under-wing WGr 21 rocket-propelled mortar, as well as a special high-altitude variant. History On 21 July 1943, ''Jagdgruppe Süd der ObdL'' was formed as a high-altitude fighter unit to combat the RAF's Mosquito twin-engine bomber and reconnaissance aircraft. On 15 August 1943 the unit was redesignated ''Jagdgeschwader'' 50 and was commanded by ''Major'' Hermann Graf, the first pilot in history to achieve 200 aerial victories. It wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fighter Aircraft
Fighter aircraft are fixed-wing military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat. In military conflict, the role of fighter aircraft is to establish air superiority of the battlespace. Domination of the airspace above a battlefield permits bombers and attack aircraft to engage in tactical and strategic bombing of enemy targets. The key performance features of a fighter include not only its firepower but also its high speed and maneuverability relative to the target aircraft. The success or failure of a combatant's efforts to gain air superiority hinges on several factors including the skill of its pilots, the tactical soundness of its doctrine for deploying its fighters, and the numbers and performance of those fighters. Many modern fighter aircraft also have secondary capabilities such as ground attack and some types, such as fighter-bombers, are designed from the outset for dual roles. Other fighter designs are highly specialized while still filling the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrous Oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or nos, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula . At room temperature, it is a colourless non-flammable gas, and has a slightly sweet scent and taste. At elevated temperatures, nitrous oxide is a powerful oxidiser similar to molecular oxygen. Nitrous oxide has significant medical uses, especially in surgery and dentistry, for its anaesthetic and pain-reducing effects. Its colloquial name, "laughing gas", coined by Humphry Davy, is due to the euphoric effects upon inhaling it, a property that has led to its recreational use as a dissociative anaesthetic. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is also used as an oxidiser in rocket propellants, and in motor racing to increase the power output of engines. Nitrous oxide's atmospheric concentration reached 333 parts per billion (ppb) in 2020, increasing at a rate of abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
I Gruppe
I, or i, is the ninth letter and the third vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''i'' (pronounced ), plural '' ies''. History In the Phoenician alphabet, the letter may have originated in a hieroglyph for an arm that represented a voiced pharyngeal fricative () in Egyptian, but was reassigned to (as in English "yes") by Semites, because their word for "arm" began with that sound. This letter could also be used to represent , the close front unrounded vowel, mainly in foreign words. The Greeks adopted a form of this Phoenician ''yodh'' as their letter ''iota'' () to represent , the same as in the Old Italic alphabet. In Latin (as in Modern Greek), it was also used to represent and this use persists in the languages that descended from Latin. The modern letter ' j' originated as a variation of 'i', and both were used interchangeably for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stuttgart
Stuttgart (; Swabian: ; ) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is located on the Neckar river in a fertile valley known as the ''Stuttgarter Kessel'' (Stuttgart Cauldron) and lies an hour from the Swabian Jura and the Black Forest. Stuttgart has a population of 635,911, making it the sixth largest city in Germany. 2.8 million people live in the city's administrative region and 5.3 million people in its metropolitan area, making it the fourth largest metropolitan area in Germany. The city and metropolitan area are consistently ranked among the top 20 European metropolitan areas by GDP; Mercer listed Stuttgart as 21st on its 2015 list of cities by quality of living; innovation agency 2thinknow ranked the city 24th globally out of 442 cities in its Innovation Cities Index; and the Globalization and World Cities Research Network ranked the city as a Beta-status global city in their 2020 survey. Stuttgart was one of the host cities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
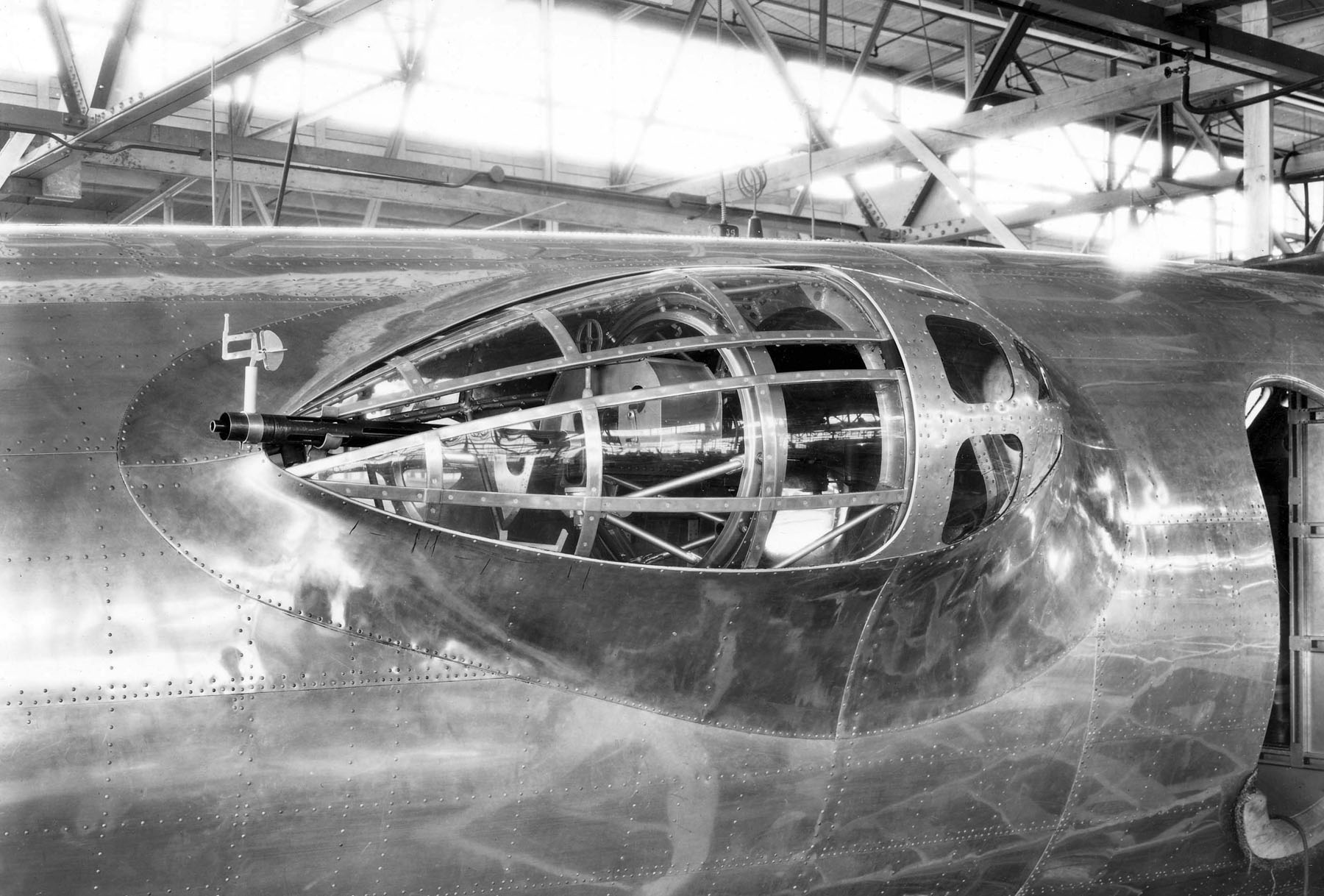
Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress
The Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress is a four-engined heavy bomber developed in the 1930s for the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC). Relatively fast and high-flying for a bomber of its era, the B-17 was used primarily in the European Theater of Operations and dropped more bombs than any other aircraft during World War II. It is the third-most produced bomber of all time, behind the four-engined Consolidated B-24 Liberator and the multirole, twin-engined Junkers Ju 88. It was also employed as a transport, antisubmarine aircraft, drone controller, and search-and-rescue aircraft. In a USAAC competition, Boeing's prototype Model 299/XB-17 outperformed two other entries but crashed, losing the initial 200-bomber contract to the Douglas B-18 Bolo. Still, the Air Corps ordered 13 more B-17s for further evaluation, then introduced it into service in 1938. The B-17 evolved through numerous design advances but from its inception, the USAAC (later, the USAAF) promoted the aircraft a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schweinfurt–Regensburg Mission
The Schweinfurt–Regensburg mission was a strategic bombing mission during World War II carried out by Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress heavy bombers of the U.S. Army Air Forces on August 17, 1943. The mission was an ambitious plan to cripple the German aircraft industry; it was also known as the "double-strike mission" because it entailed two large forces of bombers attacking separate targets in order to disperse fighter reaction by the Luftwaffe. It was also the first American "shuttle" mission, in which all or part of a mission landed at a different field and later bombed another target before returning to its base. After being postponed several times by unfavorable weather, the operation, known within the Eighth Air Force as "Mission No. 84", was flown on the anniversary of the first daylight raid by the Eighth Air Force. Mission No. 84 was a strike by 376 bombers of 16 bomb groups against German heavy industry well beyond the range of escorting fighters. The mission inflicte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
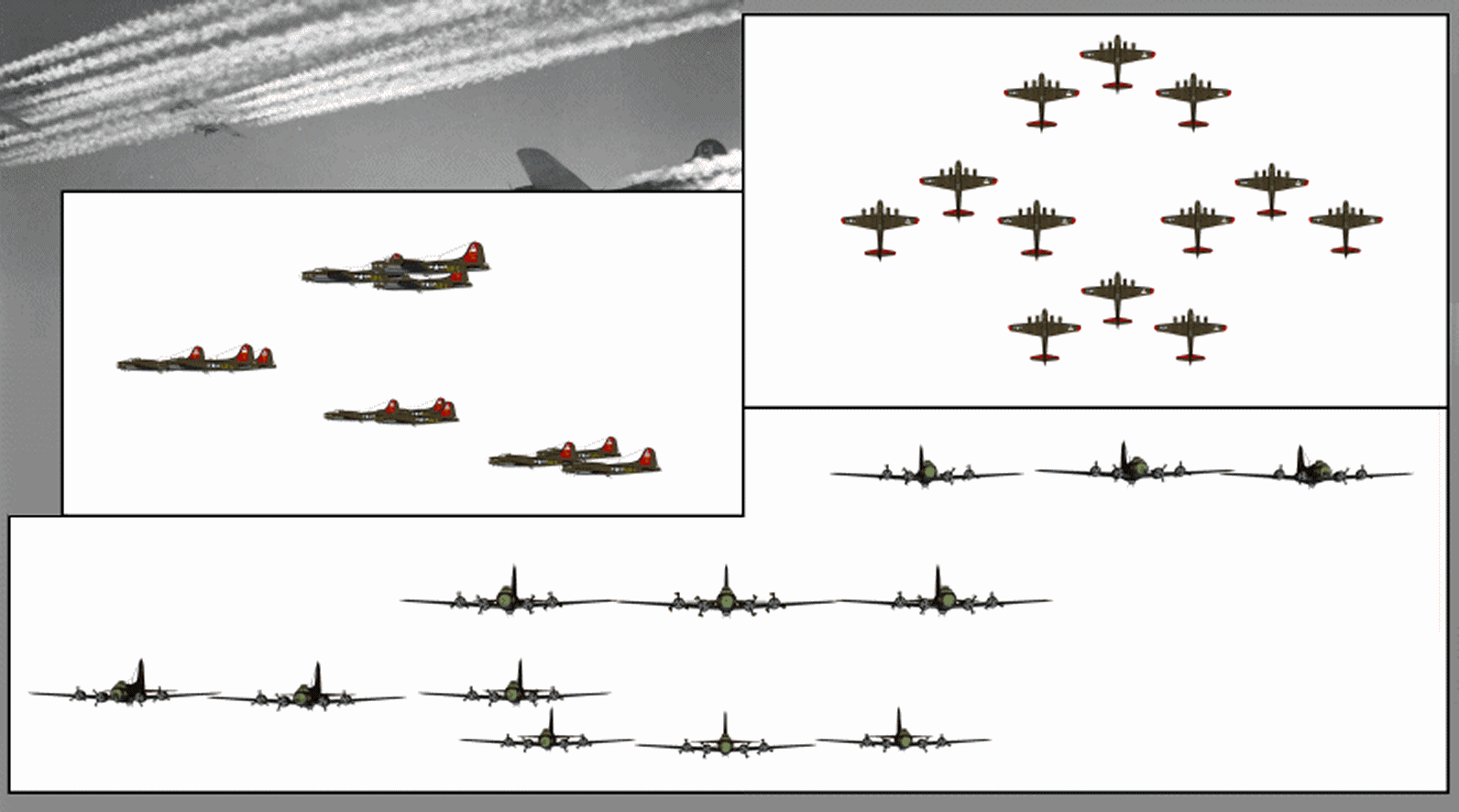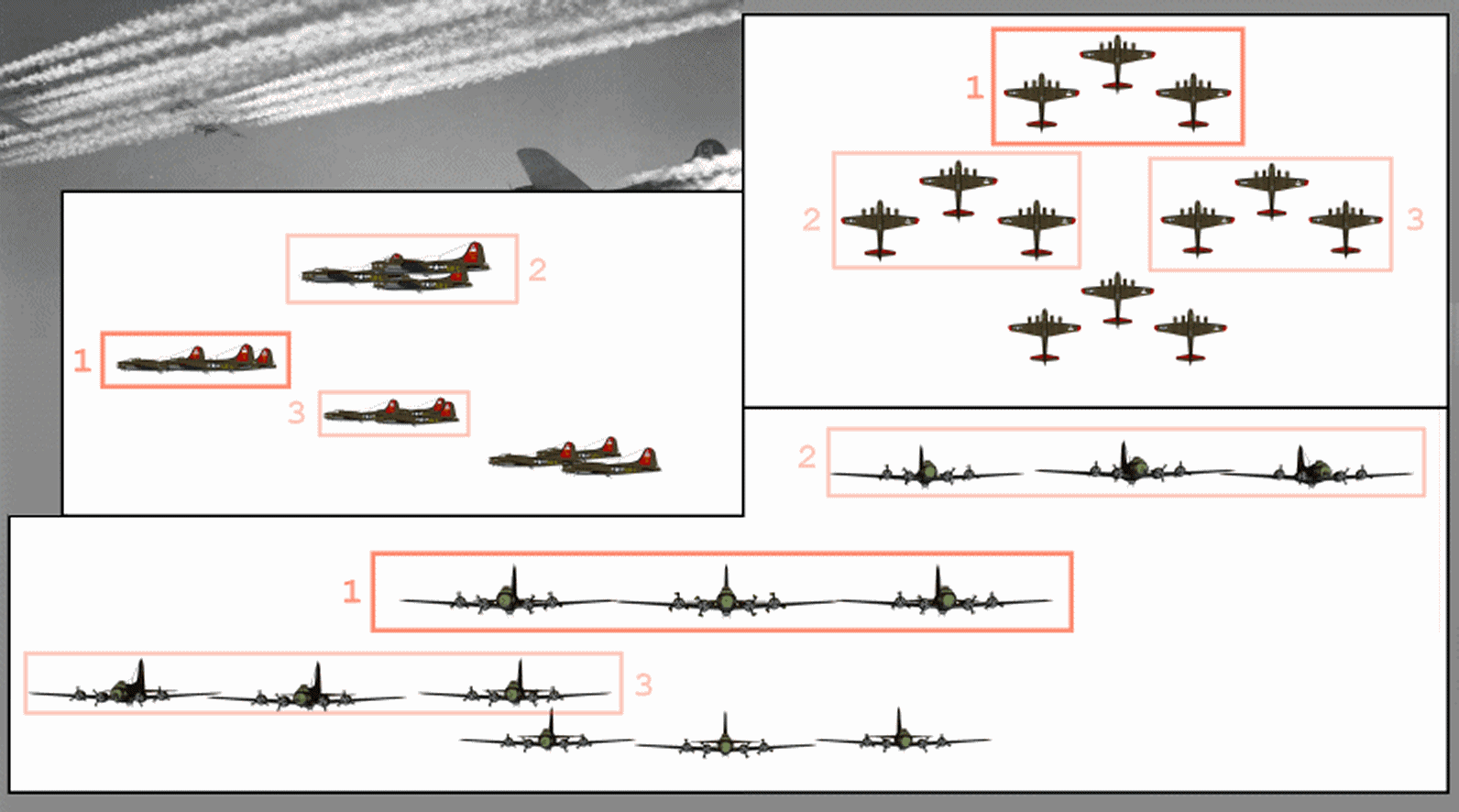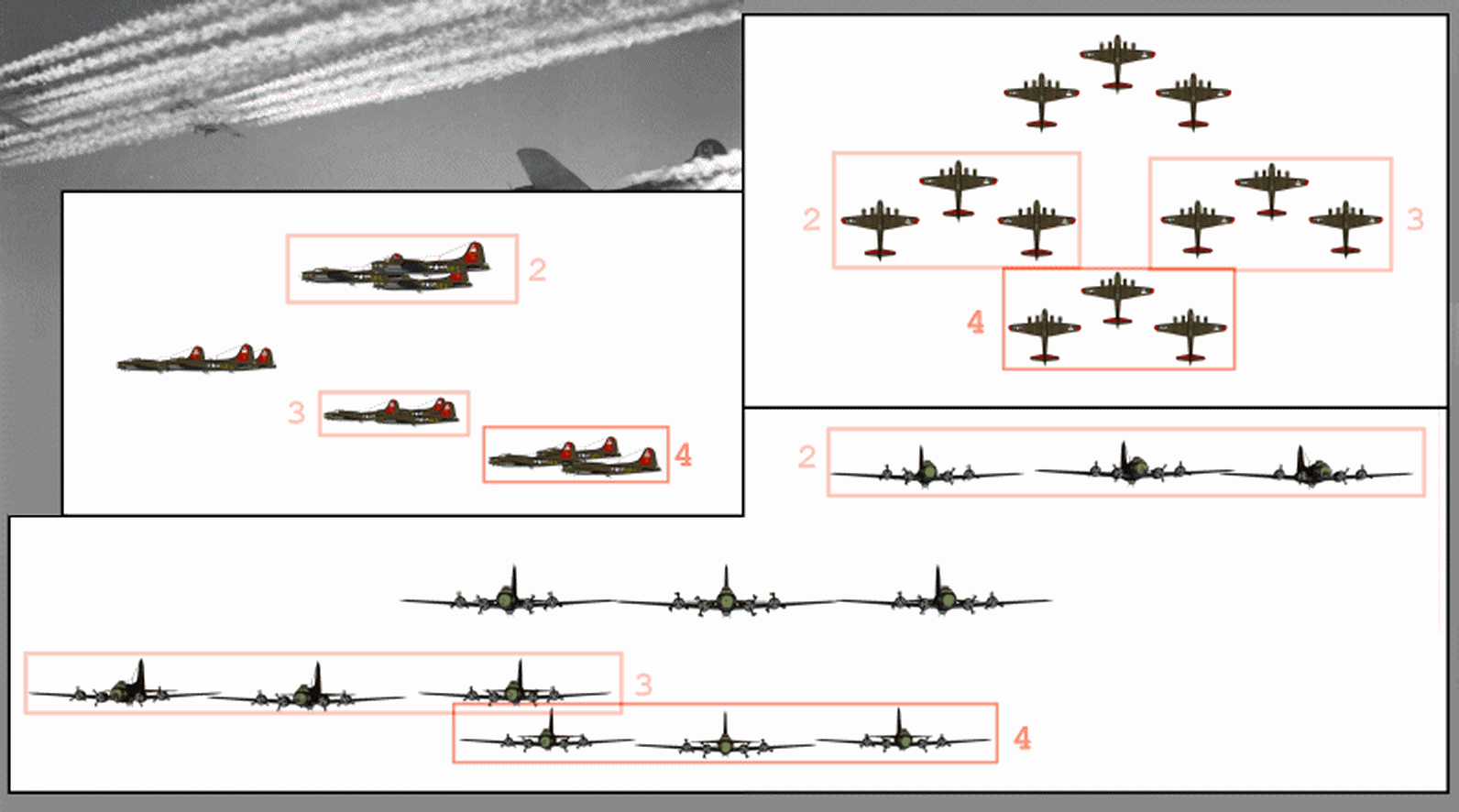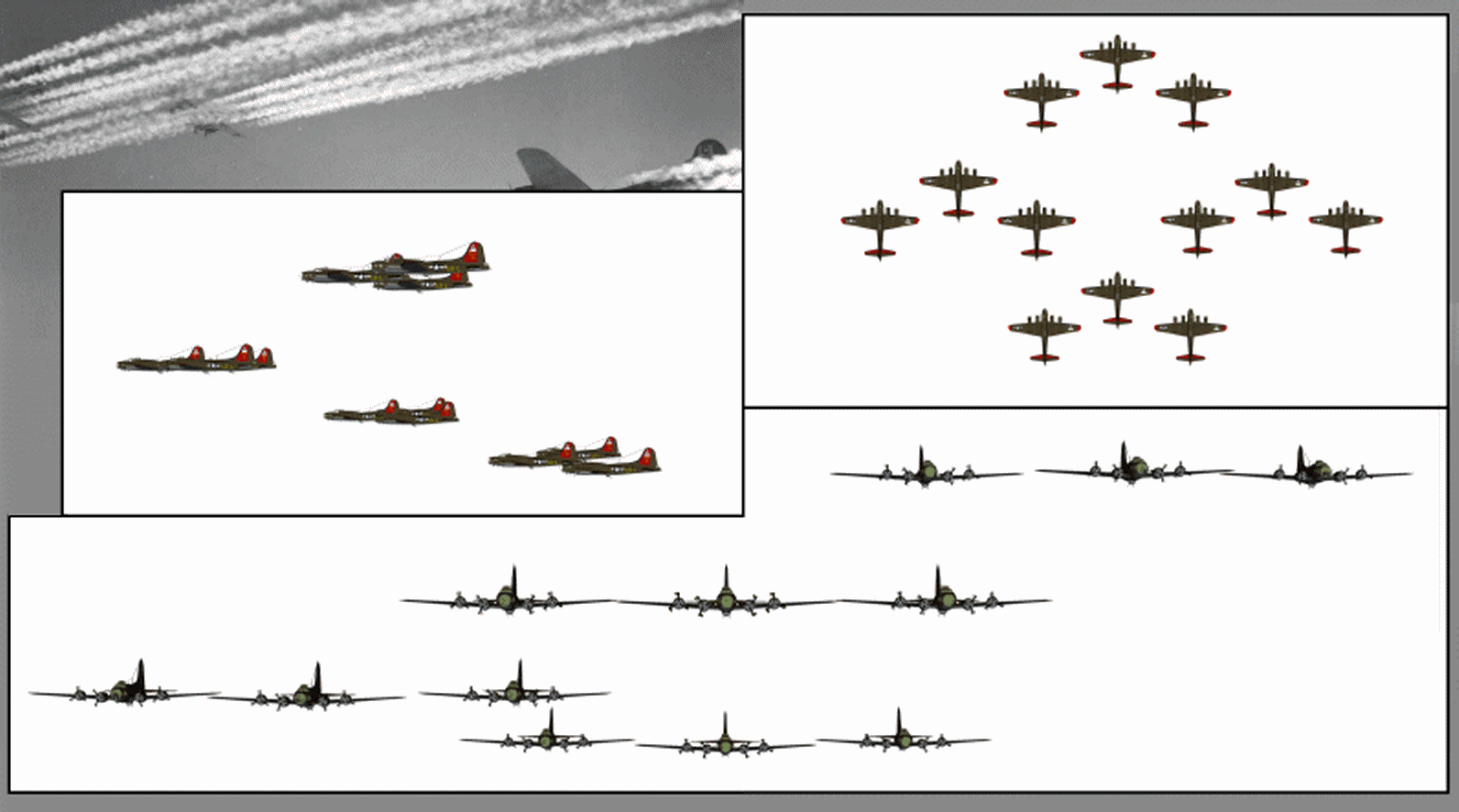
Combat Box
The combat box was a tactical formation used by heavy (strategic) bombers of the U.S. Army Air Forces during World War II. The combat box was also referred to as a "staggered formation". Its defensive purpose was in massing the firepower of the bombers' guns, while offensively it concentrated the release of bombs on a target. Initially formations were created in keeping with the pre-war Air Corps doctrine that massed bombers could attack and destroy targets in daylight without fighter escort, relying on interlocking fire from their defensive machine guns, almost exclusively the "light barrel" Browning AN/M2 .50 calibre (12.7 mm) gun. However the use of high altitudes by USAAF bombers resulted in factors that demanded a tighter bomb pattern and the combat box continued in use even after the advent of fighter escort – and especially starting in the spring of 1944 over Europe, with USAAF fighters flying far ahead of the combat boxes in air supremacy mode instead against the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Werfer-Granate 21
The ''Werfer-Granate 21'' rocket launcher, also known as the BR 21 (the "BR" standing for ''Bordrakete'') in official Luftwaffe manuals, was a weapon used by the German Luftwaffe during World War II and was the first on-board rocket placed into service by the Luftwaffe, first introduced in mid 1943. Based on the 21 cm Nebelwerfer 42 infantry barrage rocket system's hardware, the weapon was developed by Rheinmetall-Borsig under the leadership of Dipl.-Ing. Rudolf Nebel, who had pioneered German use of wing-mounted offensive rocketry in World War I with the ''Luftstreitkräfte''. History The tight formations flown by USAAF heavy bombers allowed their defensive heavy machine guns to provide mutual cover to one another, and such a combat box was an extremely dangerous environment for a fighter aircraft to fly through, with dozens of heavy machine guns aimed at attacking Luftwaffe fighters from almost every conceivable direction. This led to numerous efforts to develop weapons that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JG 52
''Jagdgeschwader'' 52 (JG 52) was a German World War II fighter ''Geschwader'' (wing) that exclusively used the Messerschmitt Bf 109 throughout the war. The unit originally formed near Munich in November 1938, then moved to a base near Stuttgart. JG 52 became the most successful fighter-''Geschwader'' of the war, with a claimed total of more than 10,000 victories over enemy aircraft during World War II. It was the unit of the top three scoring flying aces of all time, Erich Hartmann, Gerhard Barkhorn and Günther Rall. Formation In 1935, the Ministry of Aviation designed an air force (''Luftwaffe'') of 2,370 active planes by April 1938, which would require the production of about 18,000 planes to cover attrition. When 1938 came, the Luftwaffe split its fighter groups into light "Jagdgeschwader" flying the Messerschmitt Bf 109, for home defense, and heavy fighter wings called ''Zerstörergeschwader'' flying the Messerschmitt Bf 110, for offensive operations, based on doctrine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Füllgrabe
Heinrich Füllgrabe (26 July 1916 – 30 January 1945) was a Luftwaffe ace and recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross during World War II. The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross was awarded to recognise extreme battlefield bravery or successful military leadership. After joining the Luftwaffe in the late 1930s, after his training as a fighter pilot, Füllgrabe was appointed to serve as the Unteroffizier 9./JG 52 in spring 1941. Füllgrabe became a member of one of the most efficient units of the Luftwaffe, Karaya Quartet, where he flew alongside Hermann Graf (212 kills), Alfred Grislawski (133) and Ernst Süß (68). Füllgrabe was killed on 30 January 1945 by Soviet anti-aircraft fire near Brieg in Silesia. During his career he was credited with 67 aerial victories, all of them on the Eastern Front, including five Il-2 Sturmoviks. Early life and career Füllgrabe was born on 26 July 1916 in Witzenhausen in Hesse-Nassau, a province of the Kingdom of Prussia within th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Süß
Ernst Süß (31 August 1912 – 20 December 1943) was a Luftwaffe fighter ace and recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross during World War II. During his career he was credited with 68 aerial victories. Career Süß was born on 31 August 1912 in Pozezdrze, Possessern, at the time in East Prussia, Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia within the German Empire, present-day Pozezdrze in northern Poland. As a reserve pilot, he was appointed to join 9./Jagdgeschwader 52 (JG 52—52nd Fighter Wing) as an ''Unteroffizier''. With this unit he participated in the Battle of France and the Battle of Britain, without achieving any victory confirmed in this period. The rise of General Ion Antonescu in Romania in 1940 led to a reorganization of his country's armed forces. In this, he was supported by a military mission from Germany, the ''Luftwaffenmission Rumänien'' (''Luftwaffe'' Mission Romania) under the command of ''Generalleutnant'' (equivalent to major gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Grislawski
Alfred Grislawski (2 November 191919 September 2003) was a German Luftwaffe fighter ace and recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves during World War II. He was credited with 133 victories claimed in over 800 combat missions. He recorded 24 victories over the Western Front, including 18 United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) four–engine bombers. Of his 109 claims recorded over the Eastern Front, 16 were Il-2 Sturmoviks. Early life and career Grislawski was born 2 November 1919 at Wanne-Eickel in the Ruhrgebiet, the son of Gustav Grislawski, a coal miner and member of the Communist Party of Germany (KPD), and his wife Henriette. He was the second of four children, with an older brother, Walter, a younger sister, Herta, and the youngest brother Horst. His first years of his life were characterized by hardship and starvation caused by the hyperinflation in the Weimar Republic in aftermaths of World War I. On leaving school in July 1934, Grislawski left his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |