|
Jacobus De Kerle
Jacobus de Kerle (Ypres 1531/1532 - Prague 7 January 1591) was a Flemish composer and organist of the late Renaissance. Life De Kerle was trained at the monastery of St. Martin in Ypres, and held positions as a singer in Cambrai and choirmaster in Orvieto, where he also became organist and carillonneur. After entering the priesthood, he began having his music printed, including a 1561 collection of psalms and ''Magnificat'' settings in Venice. He was commissioned to write ''Preces Speciales'' set to texts by the Dominican Pedro de Soto for the Council of Trent, which he completed by 1562, and visited the city during the time of the Council in his travels with Otto Truchsess von Waldburg, cardinal of Augsburg. Although he did not take part in their discussions, the performance of the ''Preces Speciales'' reportedly influenced the deliberations of the Council Fathers on sacred music.Patrick Bergin Jr. (2009)Preces speciales: Prototype of Tridentine Musical Reform OSOM Volume 2. In 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, language, politics, and history, and sometimes involving neighbouring countries. The demonym associated with Flanders is Fleming, while the corresponding adjective is Flemish. The official capital of Flanders is the City of Brussels, although the Brussels-Capital Region that includes it has an independent regional government. The powers of the government of Flanders consist, among others, of economic affairs in the Flemish Region and the community aspects of Flanders life in Brussels, such as Flemish culture and education. Geographically, Flanders is mainly flat, and has a small section of coast on the North Sea. It borders the French department of Nord to the south-west near the coast, the Dutch provinces of Zeeland, North Brabant an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vienna
en, Viennese , iso_code = AT-9 , registration_plate = W , postal_code_type = Postal code , postal_code = , timezone = CET , utc_offset = +1 , timezone_DST = CEST , utc_offset_DST = +2 , blank_name = Vehicle registration , blank_info = W , blank1_name = GDP , blank1_info = € 96.5 billion (2020) , blank2_name = GDP per capita , blank2_info = € 50,400 (2020) , blank_name_sec1 = HDI (2019) , blank_info_sec1 = 0.947 · 1st of 9 , blank3_name = Seats in the Federal Council , blank3_info = , blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD , blank_info_sec2 = .wien , website = , footnotes = , image_blank_emblem = Wien logo.svg , blank_emblem_size = Vienna ( ; german: Wien ; ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
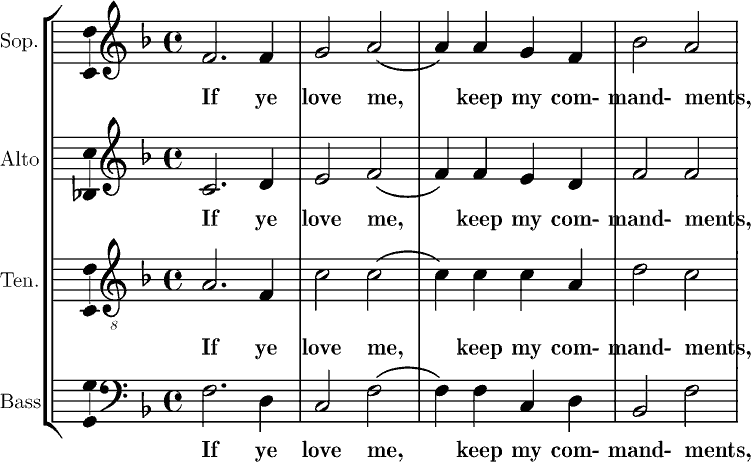
Hymn
A hymn is a type of song, and partially synonymous with devotional song, specifically written for the purpose of adoration or prayer, and typically addressed to a deity or deities, or to a prominent figure or personification. The word ''hymn'' derives from Greek (''hymnos''), which means "a song of praise". A writer of hymns is known as a hymnist. The singing or composition of hymns is called hymnody. Collections of hymns are known as hymnals or hymn books. Hymns may or may not include instrumental accompaniment. Although most familiar to speakers of English in the context of Christianity, hymns are also a fixture of other world religions, especially on the Indian subcontinent (''stotras''). Hymns also survive from antiquity, especially from Egyptian and Greek cultures. Some of the oldest surviving examples of notated music are hymns with Greek texts. Origins Ancient Eastern hymns include the Egyptian ''Great Hymn to the Aten'', composed by Pharaoh Akhenaten; the Hurrian ''Hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motet
In Western classical music, a motet is mainly a vocal musical composition, of highly diverse form and style, from high medieval music to the present. The motet was one of the pre-eminent polyphonic forms of Renaissance music. According to Margaret Bent, "a piece of music in several parts with words" is as precise a definition of the motet as will serve from the 13th to the late 16th century and beyond.Margaret Bent,The Late-Medieval Motet in ''Companion to Medieval & Renaissance Music'', edited by Tess Knighton and David Fallows, 114–19 (Berkeley, California: University of California Press, 1992): 114. . The late 13th-century theorist Johannes de Grocheo believed that the motet was "not to be celebrated in the presence of common people, because they do not notice its subtlety, nor are they delighted in hearing it, but in the presence of the educated and of those who are seeking out subtleties in the arts". Etymology In the early 20th century, it was generally believed the name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass (music)
The Mass ( la, missa) is a form of sacred musical composition that sets the invariable portions of the Christian Eucharistic liturgy (principally that of the Catholic Church, the Anglican Communion, and Lutheranism), known as the Mass. Most Masses are settings of the liturgy in Latin, the sacred language of the Catholic Church's Roman Rite, but there are a significant number written in the languages of non-Catholic countries where vernacular worship has long been the norm. For example, there have been many Masses written in English for a United States context since the Second Vatican Council, and others (often called "communion services") for the Church of England. Masses can be ''a cappella'', that is, without an independent accompaniment, or they can be accompanied by instrumental ''obbligatos'' up to and including a full orchestra. Many masses, especially later ones, were never intended to be performed during the celebration of an actual mass. History Middle Ages The earli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counterpoint
In music, counterpoint is the relationship between two or more musical lines (or voices) which are harmonically interdependent yet independent in rhythm and melodic contour. It has been most commonly identified in the European classical tradition, strongly developing during the Renaissance and in much of the common practice period, especially in the Baroque period. The term originates from the Latin ''punctus contra punctum'' meaning "point against point", i.e. "note against note". In Western pedagogy, counterpoint is taught through a system of species (see below). There are several different forms of counterpoint, including imitative counterpoint and free counterpoint. Imitative counterpoint involves the repetition of a main melodic idea across different vocal parts, with or without variation. Compositions written in free counterpoint often incorporate non-traditional harmonies and chords, chromaticism and dissonance. General principles The term "counterpoint" has been us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madrigal (music)
A madrigal is a form of secular vocal music most typical of the Renaissance music, Renaissance (15th–16th c.) and early Baroque music, Baroque (1600–1750) periods, although revisited by some later European composers. The Polyphony, polyphonic madrigal is Accompaniment, unaccompanied, and the number of voices varies from two to eight, but usually features three to six voices, whilst the Metre (music), metre of the madrigal varies between two or three tercets, followed by one or two couplets. Unlike the verse-repeating strophic forms sung to the same music, most madrigals are through-composed, featuring different music for each stanza of lyrics, whereby the composer expresses the emotions contained in each line and in single words of the poem being sung. As written by Italianized Franco–Flemish composers in the 1520s in music, 1520s, the madrigal partly originated from the three-to-four voice frottola (1470–1530); partly from composers' renewed interest in poetry written in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vincenzo Ruffo
Vincenzo Ruffo (c. 1508 – 9 February 1587) was an Italian composer of the Renaissance. He was one of the composers most responsive to the musical reforms suggested by the Council of Trent, especially in his composition of masses, and as such was an influential member of the Counter-Reformation. Vincenzo Ruffo was born at Verona, and became a priest there in 1531. Most likely he studied with Biagio Rossetti, the organist at the cathedral in Verona. Ruffo published his first book of music in 1542. Also in 1542 he became ''maestro di cappella'' at the cathedral in Savona, but he only held this position for a year; the cathedral was destroyed in 1543 by the Genoese, and Ruffo fled. In either 1543 or 1544 he went to Milan to work for Alfonso d'Avalos, who was the governor of Milan at this time. When d'Avalos was called back to Madrid in 1546, Ruffo went back to in Verona, where he was the music director at the Accademia Filarmonica in 1551-1552, superseding Jan Nasco; in 155 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homophony
In music, homophony (;, Greek: ὁμόφωνος, ''homóphōnos'', from ὁμός, ''homós'', "same" and φωνή, ''phōnē'', "sound, tone") is a texture in which a primary part is supported by one or more additional strands that flesh out the harmony. One melody predominates while the other parts play either single notes or an elaborate accompaniment. This differentiation of roles contrasts with equal-voice polyphony (in which similar lines move with rhythmic and melodic independence to form an even texture) and monophony (in which all parts move in unison or octaves). Historically, homophony and its differentiated roles for parts emerged in tandem with tonality, which gave distinct harmonic functions to the soprano, bass and inner voices. A homophonic texture may be homorhythmic, which means that all parts have the same rhythm. Chorale texture is another variant of homophony. The most common type of homophony is melody-dominated homophony, in which one voice, often the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Pierluigi Da Palestrina
Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina ( – 2 February 1594) was an Italian composer of late Renaissance music. The central representative of the Roman School, with Orlande de Lassus and Tomás Luis de Victoria, Palestrina is considered the leading composer of late 16th-century Europe. Primarily known for his masses and motets, which number over 105 and 250 respectively, Palestrina had a long-lasting influence on the development of church and secular music in Europe, especially on the development of counterpoint. According to '' Grove Music Online'', Palestrina's "success in reconciling the functional and aesthetic aims of Catholic church music in the post-Tridentine period earned him an enduring reputation as the ideal Catholic composer, as well as giving his style (or, more precisely, later generations’ selective view of it) an iconic stature as a model of perfect achievement." Biography Palestrina was born in the town of Palestrina, near Rome, then part of the Papal States to N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolas Gombert
Nicolas Gombert (c. 1495 – c. 1560)Atlas, p. 396 was a Franco-Flemish composer of the Renaissance. He was one of the most famous and influential composers between Josquin des Prez and Palestrina, and best represents the fully developed, complex polyphonic style of this period in music history. Life Details of his early life are sketchy, but he was probably born around 1495 in southern Flanders, probably between Lille and Saint-Omer, possibly in the town of La Gorgue. German writer and music theorist Hermann Finck wrote that Gombert studied with Josquin; this would have been during the renowned composer's retirement in Condé-sur-l'Escaut, sometime between 1515 and 1521.Nugent/Jas, Grove online Gombert was employed by the emperor Charles V as a singer in his court chapel in 1526 and possibly as a composer as well. Most likely he was taken on while Charles was passing through Flanders, for the emperor traveled often, bringing his retinue with him, and picking up new members as h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrian Willaert
Adrian Willaert ( – 7 December 1562) was a Flemish composer of High Renaissance music. Mainly active in Italy, he was the founder of the Venetian School. He was one of the most representative members of the generation of northern composers who moved to Italy and transplanted the polyphonic Franco-Flemish style there. Life He was born at Rumbeke near Roeselare. According to his student, the renowned 16th century music theorist Gioseffo Zarlino, Willaert went to Paris first to study law, but instead decided to study music. In Paris he met Jean Mouton, the principal composer of the French royal chapel and stylistic compatriot of Josquin des Prez, and studied with him. Sometime around 1515 Willaert first went to Rome. An anecdote survives that indicates the musical ability of the young composer: Willaert was surprised to discover the choir of the papal chapel singing one of his own compositions, most likely the six-part motet ''Verbum bonum et suave'', and even more sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |