|
J. Richard McIntosh
J. Richard McIntosh is a Distinguished Professor Emeritus in Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology at the University of Colorado Boulder. McIntosh first graduated from Harvard with a BA in Physics in 1961, and again with a Ph.D. in Biophysics in 1968. He began his teaching career at Harvard but has spent most of his career at the University of Colorado Boulder. At the University of Colorado Boulder, McIntosh taught biology courses at both the undergraduate and graduate levels. Additionally, he created an undergraduate course in the biology of cancer towards the last several years of his teaching career. McIntosh's research career looks at a variety of things, including different parts of mitosis, microtubules, and motor proteins. Research interests Mitosis Most of McIntosh’s work focuses on the process of mitosis in the cell. Mitosis is the process of cell division that includes distinct movements of chromosomes in the cell and formation of Spindle apparatus, mitotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Colorado Boulder
The University of Colorado Boulder (CU Boulder, CU, or Colorado) is a public research university in Boulder, Colorado. Founded in 1876, five months before Colorado became a state, it is the flagship university of the University of Colorado system. CU Boulder is a member of the Association of American Universities, a selective group of major research universities in North America, and is classified among R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity. In 2021, the university attracted support of over $634 million for research and spent $536 million on research and development according to the National Science Foundation, ranking it 50th in the nation. The university consists of nine colleges and schools and offers over 150 academic programs, enrolling more than 35,000 students as of January 2022. To date, 5 Nobel Prize laureates, 10 Pulitzer Prize winners, 11 MacArthur "Genius Grant" recipients, 1 Turing Award laureate, and 20 astronauts have been affiliated with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal Body
A basal body (synonymous with basal granule, kinetosome, and in older cytological literature with blepharoplast) is a protein structure found at the base of a eukaryotic undulipodium (cilium or flagellum). The basal body was named by Theodor Wilhelm Engelmann in 1880 It is formed from a centriole and several additional protein structures, and is, essentially, a modified centriole. The basal body serves as a nucleation site for the growth of the axoneme microtubules. Centrioles, from which basal bodies are derived, act as anchoring sites for proteins that in turn anchor microtubules, and are known as the microtubule organizing center (MTOC). These microtubules provide structure and facilitate movement of vesicles and organelles within many eukaryotic cells. Assembly, structure Cilia and basal bodies form during quiescence or the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Before the cell enters G1 phase, i.e. before the formation of the cilium, the mother centriole serves as a component of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clathrin
Clathrin is a protein that plays a major role in the formation of coated vesicles. Clathrin was first isolated and named by Barbara Pearse in 1976. It forms a triskelion shape composed of three clathrin heavy chains and three light chains. When the triskelia interact they form a polyhedral lattice that surrounds the vesicle, hence the protein's name, which is derived from the Latin ''clathrum'' meaning lattice. Coat-proteins, like clathrin, are used to build small vesicles in order to transport molecules within cells. The endocytosis and exocytosis of vesicles allows cells to communicate, to transfer nutrients, to import signaling receptors, to mediate an immune response after sampling the extracellular world, and to clean up the cell debris left by tissue inflammation. The endocytic pathway can be hijacked by viruses and other pathogens in order to gain entry to the cell during infection. Structure The clathrin triskelion is composed of three clathrin heavy chains inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesicle (biology And Chemistry)
In cell biology, a vesicle is a structure within or outside a cell, consisting of liquid or cytoplasm enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Vesicles form naturally during the processes of secretion (exocytosis), uptake ( endocytosis) and transport of materials within the plasma membrane. Alternatively, they may be prepared artificially, in which case they are called liposomes (not to be confused with lysosomes). If there is only one phospholipid bilayer, the vesicles are called ''unilamellar liposomes''; otherwise they are called ''multilamellar liposomes''. The membrane enclosing the vesicle is also a lamellar phase, similar to that of the plasma membrane, and intracellular vesicles can fuse with the plasma membrane to release their contents outside the cell. Vesicles can also fuse with other organelles within the cell. A vesicle released from the cell is known as an extracellular vesicle. Vesicles perform a variety of functions. Because it is separated from the cytosol, the inside of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles inside the cell before the vesicles are sent to their destination. It resides at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. It is of particular importance in processing proteins for secretion, containing a set of glycosylation enzymes that attach various sugar monomers to proteins as the proteins move through the apparatus. It was identified in 1897 by the Italian scientist Camillo Golgi and was named after him in 1898. Discovery Owing to its large size and distinctive structure, the Golgi apparatus was one of the first organelles to be discovered and observed in detail. It was discovered in 1898 by Italian physician Camillo Golgi during an investigation of the nervous system. After first observing it under his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryofixation
Cryofixation is a technique for fixation or stabilisation of biological materials as the first step in specimen preparation for electron microscopy and cryo-electron microscopy. Typical specimens for cryofixation include small samples of plant or animal tissue, cell suspensions of microorganisms or cultured cells, suspensions of viruses or virus capsids and samples of purified macromolecules, especially proteins. Cryo fixation Types 1.Freezing-drying 2.Freezing-substitution 3.freezing-etching Plunge freezing The method involves ultra-rapid cooling of small tissue or cell samples to the temperature of liquid nitrogen (−196 °C) or below, stopping all motion and metabolic activity and preserving the internal structure by freezing all fluid phases solid. Typically, a sample is plunged into liquid nitrogen or into liquid ethane or liquid propane in a container cooled by liquid nitrogen. The ultimate objective is to freeze the specimen so rapidly (at 104 to 106 K per secon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IMOD (software)
IMOD is an open-source, cross-platform suite of modeling, display and image processing programs used for 3D reconstruction and modeling of microscopy images with a special emphasis on electron microscopy data. IMOD has been used across a range of scales from macromolecule structures to organelles to whole cells and can also be used for optical sections. Included in IMOD are tools for image reconstruction, image segmentation, 3D mesh modeling and analysis of 2D and 3D data. IMOD was developed at thBoulder Laboratory for 3-D Electron Microscopy of Cells IMOD was first released in 1995, is free tand use for any purpose. Main programs IMOD includes over 180 command line programand three main GUI programs: * 3dmod - IMOD's main GUI used to view and segment images and 3D vector models. * Midas - A program used to align images over the top of each other, typically to apply fine adjustments after automatic cross-correlation. * eTomo - A program used to reconstruct 3D volumes by joining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell's internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance or cytoplasmic matrix which remains after exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, the plant plastids, lipid droplets, and vacuoles. Most cellular activities take place within the cytoplasm, such as many metabolic pathways including glycolysis, and proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
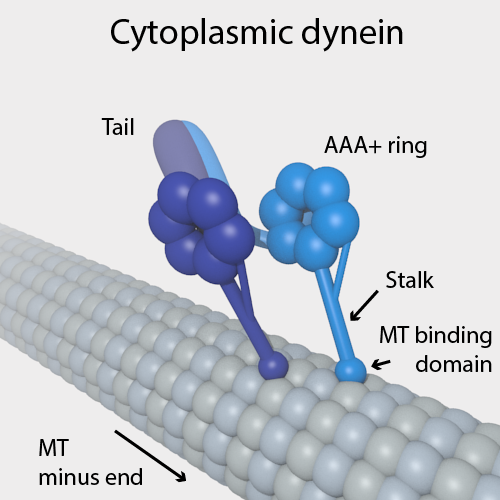
Dynein
Dyneins are a family of cytoskeletal motor proteins that move along microtubules in cells. They convert the chemical energy stored in ATP to mechanical work. Dynein transports various cellular cargos, provides forces and displacements important in mitosis, and drives the beat of eukaryotic cilia and flagella. All of these functions rely on dynein's ability to move towards the minus-end of the microtubules, known as retrograde transport; thus, they are called "minus-end directed motors". In contrast, most kinesin motor proteins move toward the microtubules' plus-end, in what is called anterograde transport. Classification Dyneins can be divided into two groups: cytoplasmic dyneins and axonemal dyneins, which are also called ciliary or flagellar dyneins. * cytoplasmic ** heavy chain: DYNC1H1, DYNC2H1 ** intermediate chain: DYNC1I1, DYNC1I2 ** light intermediate chain: DYNC1LI1, DYNC1LI2, DYNC2LI1 ** light chain: DYNLL1, DYNLL2, DYNLRB1, DYNLRB2, DYNLT1, DYNLT3 * axo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinesin
A kinesin is a protein belonging to a class of motor proteins found in eukaryotic cells. Kinesins move along microtubule (MT) filaments and are powered by the hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) (thus kinesins are ATPases, a type of enzyme). The active movement of kinesins supports several cellular functions including mitosis, meiosis and transport of cellular cargo, such as in axonal transport, and intraflagellar transport. Most kinesins walk towards the plus end of a microtubule, which, in most cells, entails transporting cargo such as protein and membrane components from the center of the cell towards the periphery. This form of transport is known as anterograde transport. In contrast, dyneins are motor proteins that move toward the minus end of a microtubule in retrograde transport. Discovery Kinesins were discovered in 1985, based on their motility in cytoplasm extruded from the giant axon of the squid. They turned out as MT-based anterograde intracellular trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching
Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) is a method for determining the kinetics of diffusion through tissue or cells. It is capable of quantifying the two dimensional lateral diffusion of a molecularly thin film containing fluorescently labeled probes, or to examine single cells. This technique is very useful in biological studies of cell membrane diffusion and protein binding. In addition, surface deposition of a fluorescing phospholipid bilayer (or monolayer) allows the characterization of hydrophilic (or hydrophobic) surfaces in terms of surface structure and free energy. Similar, though less well known, techniques have been developed to investigate the 3-dimensional diffusion and binding of molecules inside the cell; they are also referred to as FRAP. Experimental setup The basic apparatus comprises an optical microscope, a light source and some fluorescent probe. Fluorescent emission is contingent upon absorption of a specific optical wavelength or color which re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interphase
Interphase is the portion of the cell cycle that is not accompanied by visible changes under the microscope, and includes the G1, S and G2 phases. During interphase, the cell grows (G1), replicates its DNA (S) and prepares for mitosis (G2). A cell in interphase is not simply quiescent. The term quiescent (i.e. dormant) would be misleading since a cell in interphase is very busy synthesizing proteins, copying DNA into RNA, engulfing extracellular material, processing signals, to name just a few activities. The cell is quiescent only in the sense of cell division (i.e. the cell is out of the cell cycle, G0). Interphase is the phase of the cell cycle in which a typical cell spends most of its life. Interphase is the 'daily living' or metabolic phase of the cell, in which the cell obtains nutrients and metabolizes them, grows, replicates its DNA in preparation for mitosis, and conducts other "normal" cell functions. Interphase was formerly called the resting phase. However, interp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |