|
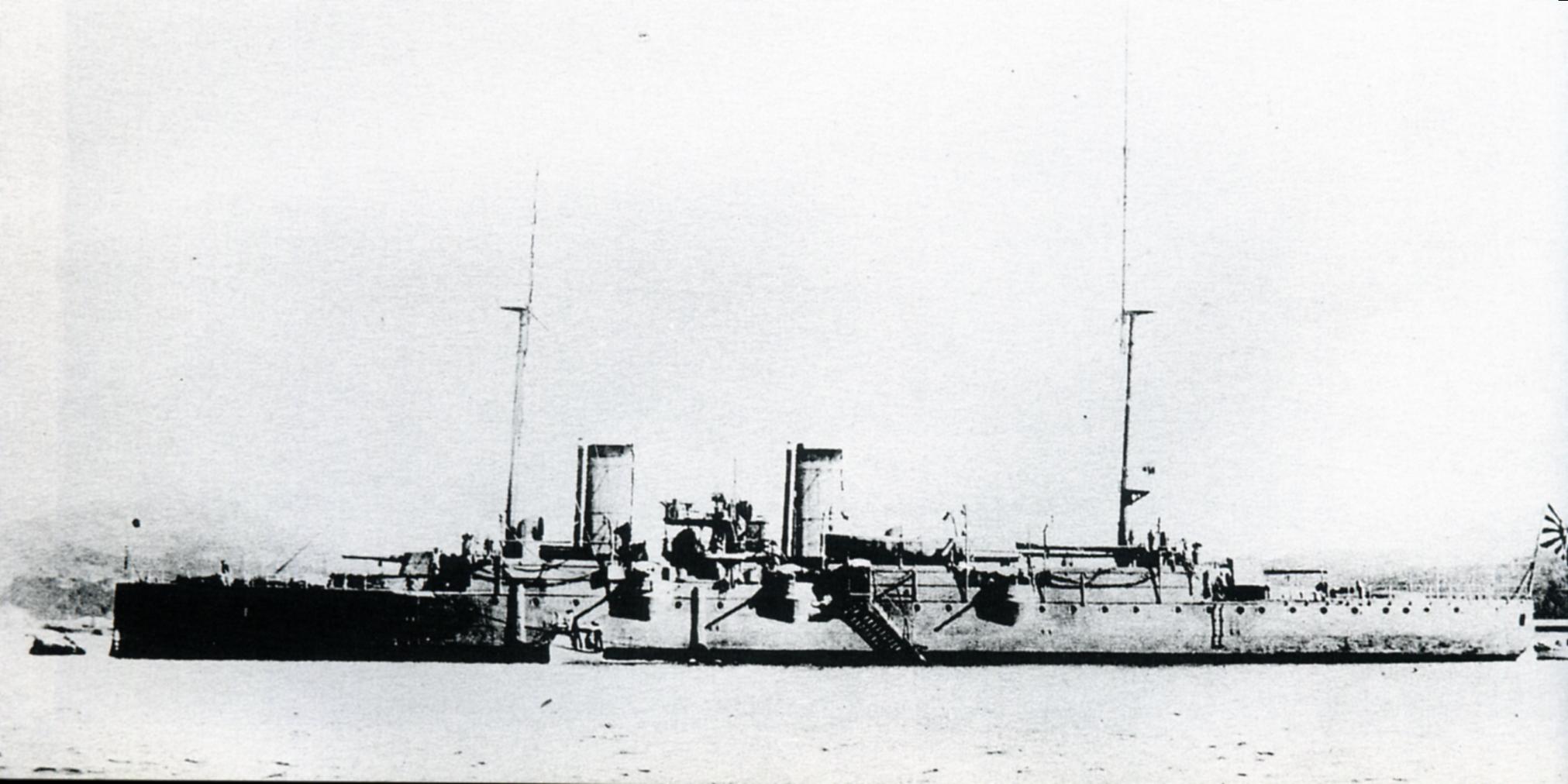
Izumrud-class Cruiser
The ''Izumrud'' class were a group of two protected cruisers built for the Imperial Russian Navy. The two ships ''Izumrud'' ("emerald") and ''Zhemchug'' ("pearl"), were copies of newly designed cruiser, , that was built at the Schichau yard in Danzig, German Empire The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary .... With the prototype purchased copies were soon underway at the Nyevsky Shipyard in St. Petersburg between 1901-1904. Specifications The two Russian-built cruisers were 111m x 12.2m x 4.88m in size with a standard weight of 3,050 tons. They were armed with six 120 mm 45 caliber guns, six 47mm Hotchkiss 3-pounder guns, two 37mm Hotchkiss 1-pounder guns and five 356mm torpedo tubes. For propulsion the ships would carry 5/600 tons of coal to fuel their 16 coal-fired Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Cruiser
Protected cruisers, a type of naval cruiser of the late-19th century, gained their description because an armoured deck offered protection for vital machine-spaces from fragments caused by shells exploding above them. Protected cruisers resembled armored cruisers, which had in addition a belt of armour along the sides. Evolution From the late 1850s, navies began to replace their fleets of wooden ships-of-the-line with armoured ironclad warships. However, the frigates and sloops which performed the missions of scouting, commerce raiding and trade protection remained unarmoured. For several decades, it proved difficult to design a ship which had a meaningful amount of protective armour but at the same time maintained the speed and range required of a "cruising warship". The first attempts to do so, armored cruisers like , proved unsatisfactory, generally lacking enough speed for their cruiser role. During the 1870s the increasing power of armour-piercing shells made armou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be transformed, by a connecting rod and crank, into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is generally applied only to reciprocating engines as just described, not to the steam turbine. Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separated from the combustion products. The ideal thermodynamic cycle used to analyze this process is called the Rankine cycle. In general usage, the term ''steam engine'' can refer to either complete steam plants (including boilers etc.), such as railway steam locomotives and portable engines, or may refer to the piston or turbine machinery alone, as in the beam engine and stationary steam engine. Although steam-driven devices were known as early as the aeolipile in the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarrow Boiler
Yarrow boilers are an important class of high-pressure water-tube boilers. They were developed by Yarrow & Co. (London), Shipbuilders and Engineers and were widely used on ships, particularly warships. The Yarrow boiler design is characteristic of the three-drum boiler: two banks of straight water-tubes are arranged in a triangular row with a single furnace between them. A single steam drum is mounted at the top between them, with smaller water drums at the base of each bank. Circulation, both upwards and downwards, occurs within this same tube bank. The Yarrow's distinctive features were the use of straight tubes and also circulation in both directions taking place within the tube bank, rather than using external downcomers. Early watertube boilers Early use of the water-tube boiler within the Royal Navy was controversial at times, giving rise to the '' ' Battle of the Boilers' '' around 1900. These first boilers, such as the Belleville and Niclausse, were large-tube desig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
120mm 45 Caliber Pattern 1892
The 120mm 45 caliber Pattern 1892 was a Russian naval gun developed in the years before the Russo-Japanese War that armed a variety of warships of the Imperial Russian Navy during the Russo-Japanese War and World War I. Guns salvaged from scrapped ships found a second life on river gunboats of the Soviet Navy during the Russian Civil War and as coastal artillery and railway artillery during World War II. It was estimated that in 1941 there were 35 still in service. History In 1891 a Russian naval delegation was shown three guns designed by the French designer Canet. One was a 75/50 gun, one was a 120/45 gun, and the last was a 152/45 gun. All three guns used fixed QF ammunition which produced a rate of fire of 15 rpm for the 75/50 gun, 12 rpm for the 120/45 gun and 10 rpm for the 152/45 gun. The Russians were impressed and in 1892 they negotiated a production license for all three guns. Construction There were two main series of the 120/45 guns produced. The first serie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QF 3-pounder Hotchkiss
The QF 3-pounder Hotchkiss or in French use Canon Hotchkiss à tir rapide de 47 mm were a family of long-lived light naval guns introduced in 1886 to defend against new, small and fast vessels such as torpedo boats and later submarines. There were many variants produced, often under license which ranged in length from 32 to 50 calibers but 40 caliber was the most common version. They were widely used by the navies of a number of nations and often used by both sides in a conflict. They were also used ashore as coastal defense guns and later as an anti-aircraft gun, whether on improvised or specialized HA/LA mounts. Operational history French service The French Navy used two versions of the Hotchkiss 3-pounder: the short-barreled M1885 and the long-barreled M1902, which had a larger muzzle velocity than its predecessor. The French L/40 M1885 and the British QF 3-pounder were largely the same gun. Like the British who paired their 3-pounders with the larger QF 6-poun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Cruiser
Protected cruisers, a type of naval cruiser of the late-19th century, gained their description because an armoured deck offered protection for vital machine-spaces from fragments caused by shells exploding above them. Protected cruisers resembled armored cruisers, which had in addition a belt of armour along the sides. Evolution From the late 1850s, navies began to replace their fleets of wooden ships-of-the-line with armoured ironclad warships. However, the frigates and sloops which performed the missions of scouting, commerce raiding and trade protection remained unarmoured. For several decades, it proved difficult to design a ship which had a meaningful amount of protective armour but at the same time maintained the speed and range required of a "cruising warship". The first attempts to do so, armored cruisers like , proved unsatisfactory, generally lacking enough speed for their cruiser role. During the 1870s the increasing power of armour-piercing shells made armou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Russian Navy
The Imperial Russian Navy () operated as the navy of the Russian Tsardom and later the Russian Empire from 1696 to 1917. Formally established in 1696, it lasted until dissolved in the wake of the February Revolution of 1917. It developed from a smaller force that had existed prior to Tsar Peter the Great's founding of the modern Russian navy during the Second Azov campaign in 1696. It expanded in the second half of the 18th century and reached its peak strength by the early part of the 19th century, behind only the British and French fleets in terms of size. The Imperial Navy drew its officers from the aristocracy of the Empire, who belonged to the state Russian Orthodox Church. Young aristocrats began to be trained for leadership at a national naval school. From 1818 on, only officers of the Imperial Russian Navy were appointed to the position of Chief Manager of the Russian-American Company, based in Russian America (present-day Alaska) for colonization and fur-trade developme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary empire led by an emperor, although has been used in German to denote the Roman Empire because it had a weak hereditary tradition. In the case of the German Empire, the official name was , which is properly translated as "German Empire" because the official position of head of state in the constitution of the German Empire was officially a "presidency" of a confederation of German states led by the King of Prussia who would assume "the title of German Emperor" as referring to the German people, but was not emperor of Germany as in an emperor of a state. –The German Empire" ''Harper's New Monthly Magazine''. vol. 63, issue 376, pp. 591–603; here p. 593. also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Second Reich, as well as simply Germany, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsushima Battle Map-de
Tsushima may refer to: Places * Tsushima Island, part of Nagasaki Prefecture ** Tsushima, Nagasaki, a city in Nagasaki Prefecture (coterminous with Tsushima Island) ** Tsushima Province, a historical province, coterminous with modern Tsushima Subprefecture ** Tsushima Subprefecture, an administrative subdivision of Nagasaki prefecture (coterminous with Tsushima Island) ** Tsushima Fuchū Domain, a feudal domain of the early modern period, largely if not entirely contiguous with the Province * Tsushima Basin, also known as Ulleung Basin, located at the juncture of the Sea of Japan and the Korea Strait * Tsushima Strait, the eastern channel of the Korea Strait * Tsushima, Aichi, a city in Aichi Prefecture * Tsushima, Ehime, a town dissolved in August 2005, formerly located in Ehime Prefecture * Tsushima Shrine, Aichi Prefecture * Tsushima Shrine, located in the city of Mitoyo, Kagawa Prefecture and only accessible one day a year in early August Events * Battle of Tsushima (1905), als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |