|
Izanagi Shrine
is a Shinto shrine in the Taga neighborhood of the city of Awaji in Hy┼Źgo Prefecture, Japan. It is the ''ichinomiya'' of former Awaji Province. The main festival of the shrine is held annually on April 22. Enshrined ''kami'' The ''kami'' enshrined at Izanagi Jing┼½ are: * * History Per Japanese mythology as outlined in the ''Kojiki'' and '' Nihon Shoki'', the Japanese archipelago (starting with Awaji Island), the ''kami'', and all living things were created by the progenitor gods Izanagi and Izanami. After this work was completed, Izanagi retired into seclusion on Awaji Island where his tomb was located on the site of his palace. The documentary history, mention of a shrine to Izanagi in Awaji is made in an entry in the ''Nihon Shoki'' under the reigns of Emperor Richu and Emperor Ingy┼Ź and the shrine appears in the ''Nihon Sandai Jitsuroku'' in an entry dated 859. In the 927 ''Engishiki'', it is listed a ''My┼Źjin Taisha'', and as the ''ichinomiya'' of the province. Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinto
Shinto () is a religion from Japan. Classified as an East Asian religion by scholars of religion, its practitioners often regard it as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion. Scholars sometimes call its practitioners ''Shintoists'', although adherents rarely use that term themselves. There is no central authority in control of Shinto, with much diversity of belief and practice evident among practitioners. A polytheistic and animistic religion, Shinto revolves around supernatural entities called the . The are believed to inhabit all things, including forces of nature and prominent landscape locations. The are worshiped at household shrines, family shrines, and ''jinja'' public shrines. The latter are staffed by priests, known as , who oversee offerings of food and drink to the specific enshrined at that location. This is done to cultivate harmony between humans and and to solicit the latter's blessing. Other common rituals include the dances, rites of pass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Ingy┼Ź
was the 19th legendary Emperor of Japan,Imperial Household Agency (''Kunaich┼Ź'') ÕģüµüŁÕż®ńÜć (19) retrieved 2013-8-28. according to the traditional order of succession. No firm dates can be assigned to this Emperor's life or reign, but he is conventionally considered to have reigned from 410 to 453. Legendary narrative Ingy┼Ź is regarded by historians as a "legendary Emperor" of the 5th century. The reign of Emperor Kinmei ( ŌĆō 571 AD), the 29th Emperor,Titsinghpp. 34ŌĆō36 Brown pp. 261ŌĆō262 Varley, pp. 123ŌĆō124. is the first for which contemporary historiography is able to assign verifiable dates; however, the conventionally accepted names and dates of the early Emperors were not to be confirmed as "traditional" until the reign of Emperor Kanmu (737ŌĆō806), the 50th sovereign of the Yamato dynasty. According to ''Kojiki'' and '' Nihon Shoki'', he was the fourth son of Emperor Nintoku and his consort Princess Iwa, and therefore a younger brother of his predecessor Em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Shinto
was Imperial Japan's ideological use of the Japanese folk religion and traditions of Shinto. The state exercised control of shrine finances and training regimes for priests to strongly encourage Shinto practices that emphasized the Emperor as a divine being. The State Shinto ideology emerged at the start of the Meiji era, after government officials defined freedom of religion within the Meiji Constitution. Imperial scholars believed Shinto reflected the historical fact of the Emperor's divine origins rather than a religious belief, and argued that it should enjoy a privileged relationship with the Japanese state. The government argued that Shinto was a non-religious moral tradition and patriotic practice, to give the impression that they supported religious freedom. Though early Meiji-era attempts to unite Shinto and the state failed, this non-religious concept of ideological Shinto was incorporated into state bureaucracy. Shrines were defined as patriotic, not religious, ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiji Period
The is an era of Japanese history that extended from October 23, 1868 to July 30, 1912. The Meiji era was the first half of the Empire of Japan, when the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonization by Western powers to the new paradigm of a modern, industrialized nation state and emergent great power, influenced by Western scientific, technological, philosophical, political, legal, and aesthetic ideas. As a result of such wholesale adoption of radically different ideas, the changes to Japan were profound, and affected its social structure, internal politics, economy, military, and foreign relations. The period corresponded to the reign of Emperor Meiji. It was preceded by the Kei┼Ź era and was succeeded by the Taish┼Ź era, upon the accession of Emperor Taish┼Ź. The rapid modernization during the Meiji era was not without its opponents, as the rapid changes to society caused many disaffected traditionalists from the former samurai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokushima Domain
was a feudal domain under the Tokugawa shogunate of Edo period Japan, controlling all of Awa Province and Awaji Province in what is now Tokushima Prefecture and Awaji Island of modern-day Hy┼Źgo Prefecture. It was centered around Tokushima Castle, and was ruled throughout its history by the ''tozama daimy┼Ź'' Hachisuka clan. History Hachisuka Masakatsu was a vassal of Toyotomi Hideyoshi and dominated Tatsuno in Harima Province. He was awarded territories in Awa Province after Hideyoshi's conquest of Shikoku in 1585; however, due to his advanced age, he turned the clan chieftainship over to his son Hachisuka Iemasa. At the time, his territory was only a portion of Awa Province, with a ''kokudaka'' of 175,000 ''koku''. He constructed Tokushima Castle, which would remain the clan's seat for the next 300 years. The clan had always been on bad terms with Ishida Mitsunari and at the time of the Battle of Sekigahara, Mitsunari forced Hachisuka Iemasa to take the tonsure and forc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daimy┼Ź
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji era, Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast, hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and nominally to the Emperor of Japan, emperor and the ''kuge''. In the term, means 'large', and stands for , meaning 'private land'. From the ''shugo'' of the Muromachi period through the Sengoku period, Sengoku to the ''daimyo'' of the Edo period, the rank had a long and varied history. The backgrounds of ''daimyo'' also varied considerably; while some ''daimyo'' clans, notably the M┼Źri clan, M┼Źri, Shimazu clan, Shimazu and Hosokawa clan, Hosokawa, were cadet branches of the Imperial family or were descended from the ''kuge'', other ''daimyo'' were promoted from the ranks of the samurai, notably during the Edo period. ''Daimyo'' often hired samurai to guard their land, and they paid the samurai in land or food as relatively few could aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hachitsuka Clan
The are descendants of Emperor Seiwa (850-880) of Japan and are a branch of the Ashikaga clan through the Shiba clan (Seiwa Genji). History Ashikaga Ieuji (13th century), son of Ashikaga Yasuuji, was the first to adopt the name Shiba. The Shiba were ''Shugo'' (Governors) of Echizen, Owari, and other provinces, and during the Ashikaga shogunate were one of three families (Shiba, Hosokawa and Hatakeyama) from which the ''Kyoto-kanryo'' (Prime Minister of the Sh┼Źgun) could be chosen. Shiba Masaaki, the descendant of Shiba Takatsune (1305ŌĆō1367), established himself in Hachisuka, near the Kiso River at the border of Owari and Mino provinces, whence he took the name Hachisuka. In the 16th century, the Hachisuka clan came to prominence thanks to its head, Hachisuka Koroku. His uncle held Hachisuka Castle and he lived first in Miyaushiro Castle, which was his mother's family home. Koroku served the Oda clan, being instrumental in several of the early victories of Oda Nobunaga. He la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edo Period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional '' daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characterized by economic growth, strict social order, isolationist foreign policies, a stable population, perpetual peace, and popular enjoyment of arts and culture. The period derives its name from Edo (now Tokyo), where on March 24, 1603, the shogunate was officially established by Tokugawa Ieyasu. The period came to an end with the Meiji Restoration and the Boshin War, which restored imperial rule to Japan. Consolidation of the shogunate The Edo period or Tokugawa period is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's regional '' daimyo''. A revolution took place from the time of the Kamakura shogunate, which existed with the Tenn┼Ź's court, to the Tok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Takeda Katsuyori
was a Japanese ''daimy┼Ź'' of the Sengoku period, who was famed as the head of the Takeda clan and the successor to the legendary warlord Takeda Shingen. He was son in law of Hojo Ujiyasu. Early life He was the son of Shingen by the daughter of Suwa Yorishige (posthumous name:). Katsuyori's children included Takeda Nobukatsu and Katsuchika.http://www2.harimaya.com/sengoku/html/takeda.html Katsuyori, first known as , succeeded to his mother's Suwa clan and gained Takat┼Ź Castle as the seat of his domain. After his elder brother Takeda Yoshinobu died, Katsuyori's son Nobukatsu became heir to the Takeda clan, making Katsuyori the true ruler of the Takeda clan. Takeda Katsuyori built Shinpu Castle, a new and larger castle at Nirasaki and transferred his residence there in 1581. Military life In 1569, Katsuyori defeated Hojo Ujinobu at Siege of Kanbara In 1572, Katsuyori successfully took a Tokugawa clan possession in the Siege of Futamata, and participated in the Battle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
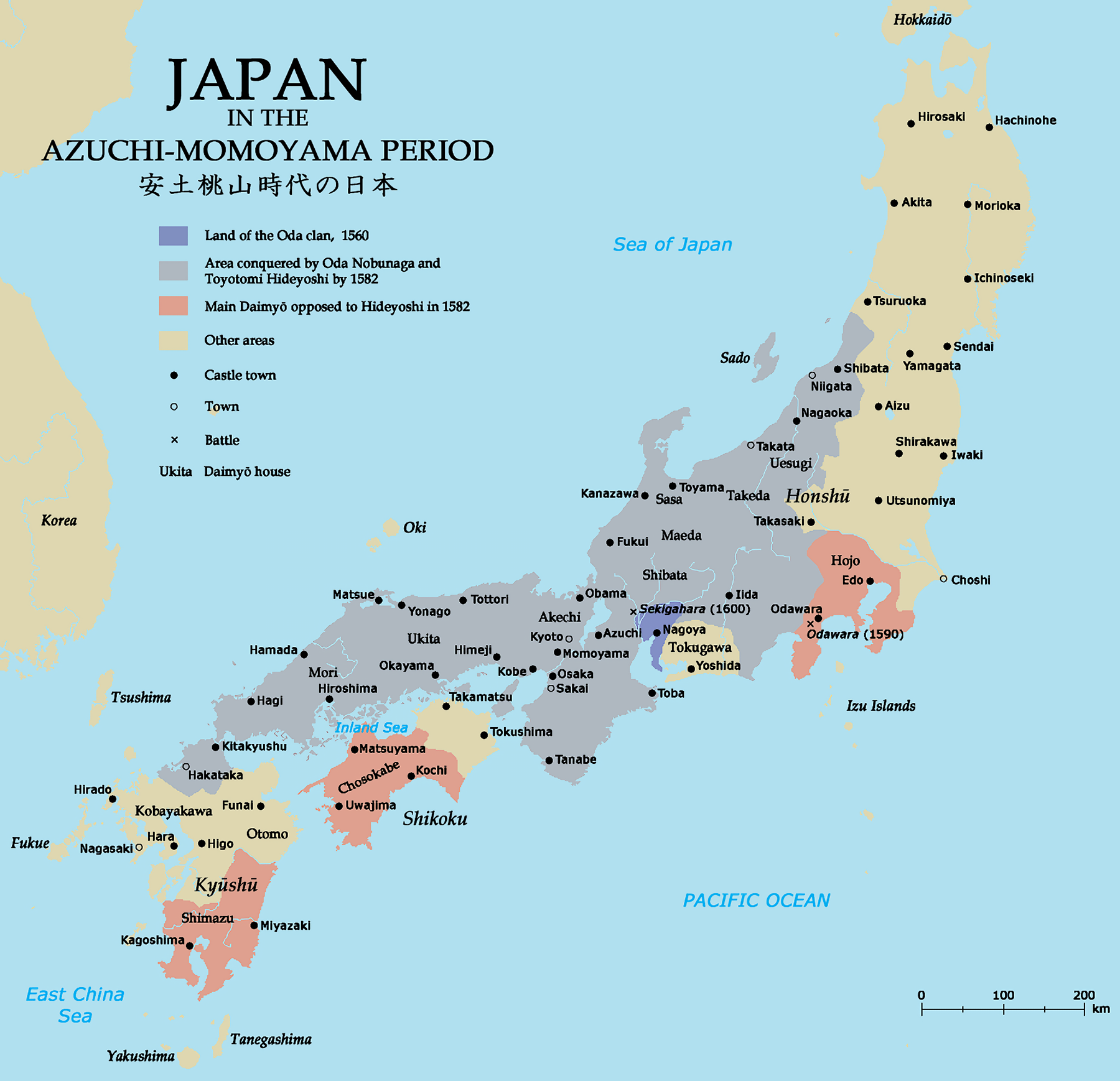
Oda Nobunaga
was a Japanese ''daimy┼Ź'' and one of the leading figures of the Sengoku period. He is regarded as the first "Great Unifier" of Japan. Nobunaga was head of the very powerful Oda clan, and launched a war against other ''daimy┼Ź'' to unify Japan in the 1560s. Nobunaga emerged as the most powerful ''daimy┼Ź'', overthrowing the nominally ruling shogun Ashikaga Yoshiaki and dissolving the Ashikaga Shogunate in 1573. He conquered most of Honshu island by 1580, and defeated the ''Ikk┼Ź-ikki'' rebels in the 1580s. Nobunaga's rule was noted for innovative military tactics, fostering of free trade, reforms of Japan's civil government, and the start of the Momoyama historical art period, but also for the brutal suppression of those who refused to cooperate or yield to his demands. Nobunaga was killed in the Honn┼Ź-ji Incident in 1582, when his retainer Akechi Mitsuhide ambushed him in Kyoto and forced him to commit . Nobunaga was succeeded by Toyotomi Hideyoshi, who along with Toku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sengoku Period
The was a period in History of Japan, Japanese history of near-constant civil war and social upheaval from 1467 to 1615. The Sengoku period was initiated by the ┼īnin War in 1467 which collapsed the Feudalism, feudal system of Japan under the Ashikaga shogunate. Various samurai warlords and Japanese clans, clans fought for control over Japan in the power vacuum, while the emerged to fight against samurai rule. The Nanban trade, arrival of Europeans in 1543 introduced the arquebus into Japanese warfare, and Japan ended its status as a Tributary system of China, tributary state of China in 1549. Oda Nobunaga dissolved the Ashikaga shogunate in 1573 and launched a war of political unification by force, including the Ishiyama Hongan-ji War, until his death in the Honn┼Ź-ji Incident in 1582. Nobunaga's successor Toyotomi Hideyoshi completed his campaign to unify Japan and consolidated his rule with numerous influential reforms. Hideyoshi launched the Japanese invasions of Korea (159 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannushi
A , also called , is a person responsible for the maintenance of a as well as for leading worship of a given .* ''Kannushi'' (in Japanese), Iwanami Japanese dictionary, 6th Edition (2008), DVD version The characters for are sometimes also read as with the same meaning. History Originally, the were intermediaries between and people and could transmit their will to common humans. A was a man capable of miracles or a holy man who, because of his practice of purificatory rites, was able to work as a medium for a . Later the term evolved to being synonymous with - a man who works at a shrine and holds religious ceremonies there. In ancient times, because of the overlap of political and religious power within a clan, it was the head of the clan who led the clansmen during religious functions, or else it could be another official. Later, the role evolved into a separate and more specialized form. The term appears in both the (680 AD) and (720 AD), where the Empress Jing┼ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |