|
Iwai Rebellion
The was a rebellion against the Yamato court that took place in Tsukushi Province, Japan (now nearby Ogōri city in Fukuoka Prefecture) in 527 AD. The rebellion was named after its leader, Iwai, who is believed by historians to have been a powerful governor of Tsukushi. The rebellion was quelled by the Yamato court, and played an important part in the consolidation of early Japan. The main record of the rebellion can be found in the '' Nihon Shoki'', although it is also mentioned in ''Kojiki'' and other historical sources. Background The Yamato Kingdom was formed in the central areas of Honshu in the late 3rd or early 4th century, and by 350 this state had extended its rule to the western part of Honshu and the northern part of Kyushu. In 366, Yamato invaded the Korean peninsula, which at the time was divided into three kingdoms: Goguryeo, Paekje, and Silla. In this campaign the kingdom of Yamato subdued the kingdom of Pаekje, and forced it to pay an annual tribute. The Japa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kofun Period
The is an era in the history of Japan from about 300 to 538 AD (the date of the introduction of Buddhism), following the Yayoi period. The Kofun and the subsequent Asuka periods are sometimes collectively called the Yamato period. This period is the earliest era of recorded history in Japan, but studies depend heavily on archaeology since the chronology of historical sources tends to be distorted. The word '' kofun'' is Japanese for the type of burial mound dating from this era. It was a period of cultural import. Continuing from the Yayoi period, the Kofun period is characterized by influence from China and the Korean Peninsula; archaeologists consider it a shared culture across the southern Korean Peninsula, Kyūshū and Honshū. On the other hand, the most prosperous keyhole-shaped burial mounds in Japan during this period were approximately 5,000 in Japan from the middle of the 3rd century in the Yayoi period to the 7th century in the Asuka period, and many of them had huge t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
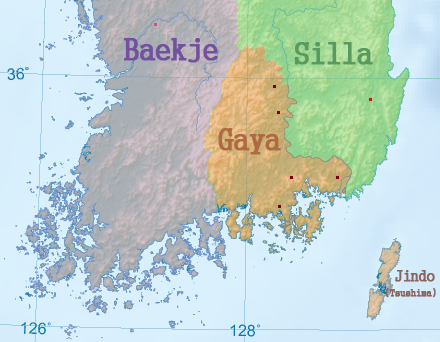
Three Kingdoms Of Korea
Samhan or the Three Kingdoms of Korea () refers to the three kingdoms of Goguryeo (고구려, 高句麗), Baekje (백제, 百濟), and Silla (신라, 新羅). Goguryeo was later known as Goryeo (고려, 高麗), from which the modern name ''Korea'' is derived. The Three Kingdoms period is defined as being from 57 BC to 668 AD (but there existed Gaya confederacy in the southern region of the Korean Peninsula and relatively large states like Okjeo, Buyeo, and Dongye in its northern part and Manchuria of modern China). The "Korean Three Kingdoms" (Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla) contributed to what would become Korea; and the Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla peoples became what we know as the Korean people. The Book of Sui (Volume 81) recorded: "The customs, laws and clothes of Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla are generally identical." The three kingdoms occupied the entire peninsula of Korea and roughly half of Manchuria, located mostly in present-day China, along with smaller parts from present- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
520s Conflicts
5 (five) is a number, numeral (linguistics), numeral and numerical digit, digit. It is the natural number, and cardinal number, following 4 and preceding 6, and is a prime number. It has attained significance throughout history in part because typical humans have five Digit (anatomy), digits on each hand. In mathematics 5 is the third smallest prime number, and the second super-prime. It is the first safe prime, the first good prime, the first balanced prime, and the first of three known Wilson primes. Five is the second Fermat prime and the third Mersenne prime exponent, as well as the third Catalan number, and the third Sophie Germain prime. Notably, 5 is equal to the sum of the ''only'' consecutive primes, 2 + 3, and is the only number that is part of more than one pair of twin primes, (3, 5) and (5, 7). It is also a sexy prime with the fifth prime number and first Repunit#Decimal repunit primes, prime repunit, 11 (number), 11. Five is the third factorial prime, an alternat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rebellions In Japan
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority. A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and then manifests itself by the refusal to submit or to obey the authority responsible for this situation. Rebellion can be individual or collective, peaceful ( civil disobedience, civil resistance, and nonviolent resistance) or violent (terrorism, sabotage and guerrilla warfare). In political terms, rebellion and revolt are often distinguished by their different aims. While rebellion generally seeks to evade and/or gain concessions from an oppressive power, a revolt seeks to overthrow and destroy that power, as well as its accompanying laws. The goal of rebellion is resistance while a revolt seeks a revolution. As power shifts relative to the external adversary, or power shifts within a mixed coalition, or positions harden or soften on eit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th-century Rebellions
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire. In its second Golden Age, the Sassanid Empire reached the peak of its power under Khosrau I in the 6th century.Roberts, J: "History of the World.". Penguin, 1994. The classical Gupta Empire of Northern India, largely overrun by the Huna, ended in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial House Of Japan
The , also referred to as the Imperial Family or the House of Yamato, comprises those members of the extended family of the reigning Emperor of Japan who undertake official and public duties. Under the present Constitution of Japan, the Emperor is "the symbol of the State and of the unity of the people". Other members of the Imperial Family perform ceremonial and social duties, but have no role in the affairs of government. The duties as an Emperor are passed down the line to their male children. This Japanese monarchy is the oldest continuous hereditary monarchy in the world. The Imperial House recognizes 126 monarchs, beginning with Emperor Jimmu (traditionally dated to 11 February 660 BC), and continuing up to the current emperor, Naruhito. However, scholars have agreed that there is no evidence of Jimmu's existence, that the traditional narrative of Japan’s founding is mythical, and that Jimmu is a mythical figure. Historical evidence for the first 25 emperors is mythical, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kumaso
The were a mythical people of ancient Japan mentioned in the '' Kojiki'', believed to have lived in the south of Kyūshū until at least the Nara period. The last leader of the Kumaso, Torishi-Kaya was killed by Yamato Takeru in 397. The name of Kumamoto Prefecture originates from the Kumaso people. Origins Scholars such as Kakubayashi Fumio, ''"although information is extremely limited"'', concluded that they were of Austronesian origin based on some linguistic and cultural evidence, theorising that the word ''kaya'', present in personal names or titles, such as Torishi-Kaya, has the same root as Tagalog ''"kaya"'', meaning "ability; capability; competence; resources; wealth" and Malay and Indonesian ''"kaya"'', meaning "rich, wealthy, having wealth". The ''So'' present in Kumaso was also theorised to have the same origins as ''tsuo, tsau, thau, sau, tau, tao'' supposedly meaning "people" in Austronesian languages. Overview William George Aston, in his translation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaya Confederacy
Gaya (, ) was a Korean confederacy of territorial polities in the Nakdong River basin of southern Korea, growing out of the Byeonhan confederacy of the Samhan period. The traditional period used by historians for Gaya chronology is AD 42–532. According to archaeological evidence in the third and fourth centuries some of the city-states of Byeonhan evolved into the Gaya confederacy, which was later annexed by Silla, one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. The individual polities that made up the Gaya confederacy have been characterized as small city-states. The material culture remains of Gaya culture mainly consist of burials and their contents of mortuary goods that have been excavated by archaeologists. Archaeologists interpret mounded burial cemeteries of the late third and early fourth centuries such as Daeseong-dong in Gimhae and Bokcheon-dong in Busan as the royal burial grounds of Gaya polities. Names Although most commonly referred to as Gaya (가야; 加耶, 伽耶, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimana
Mimana (), also transliterated as Imna according to the Korean pronunciation, is the name used primarily in the 8th-century Japanese text '' Nihon Shoki'', likely referring to one of the Korean states of the time of the Gaya confederacy (c. 1st–5th centuries). As Atkins notes, "The location, expanse, and Japaneseness of Imna/Mimana remain among the most disputed issues in East Asian historiography." Seth notes that the very existence of Mimana is still disputed. Usage of term The name (pronounced Mimana in Japanese, Imna in Korean, and Renna in Mandarin Chinese) is used over 200 times in the 8th-century Japanese text '' Nihongi''. Much earlier, it is mentioned in a 5th-century Chinese history text, the ''Book of Song'', in the chapter on the State of Wa. It is also used in two Korean epigraphic relics, as well as in several Korean texts, including ''Samguk Sagi''. Hypotheses on meaning The first serious hypothesis on the meaning of Mimana comes from Japanese scholars. Bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Busan
Busan (), officially known as is South Korea's most populous city after Seoul, with a population of over 3.4 million inhabitants. Formerly romanized as Pusan, it is the economic, cultural and educational center of southeastern South Korea, with its port being Korea's busiest and the sixth-busiest in the world. The surrounding "Southeastern Maritime Industrial Region" (including Ulsan, South Gyeongsang, Daegu, and some of North Gyeongsang and South Jeolla) is South Korea's largest industrial area. The large volumes of port traffic and urban population in excess of 1 million make Busan a Large-Port metropolis using the Southampton System of Port-City classification . Busan is divided into 15 major administrative districts and a single county, together housing a population of approximately 3.6 million. The full metropolitan area, the Southeastern Maritime Industrial Region, has a population of approximately 8 million. The most densely built-up areas of the city are situated in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baekje
Baekje or Paekche (, ) was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BC to 660 AD. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla. Baekje was founded by Onjo, the third son of Goguryeo's founder Jumong and So Seo-no, at Wiryeseong (present-day southern Seoul). Baekje, like Goguryeo, claimed to succeed Buyeo, a state established in present-day Manchuria around the time of Gojoseon's fall. Baekje alternately battled and allied with Goguryeo and Silla as the three kingdoms expanded control over the peninsula. At its peak in the 4th century, Baekje controlled most of the western Korean peninsula, as far north as Pyongyang, and may have even held territories in China, such as in Liaoxi, though this view is controversial. It became a significant regional sea power, with political and trade relations with China and Japan. Baekje was a great maritime power; its nautical skill, which made it the Phoenicia of East Asia, was instrumental i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |