|
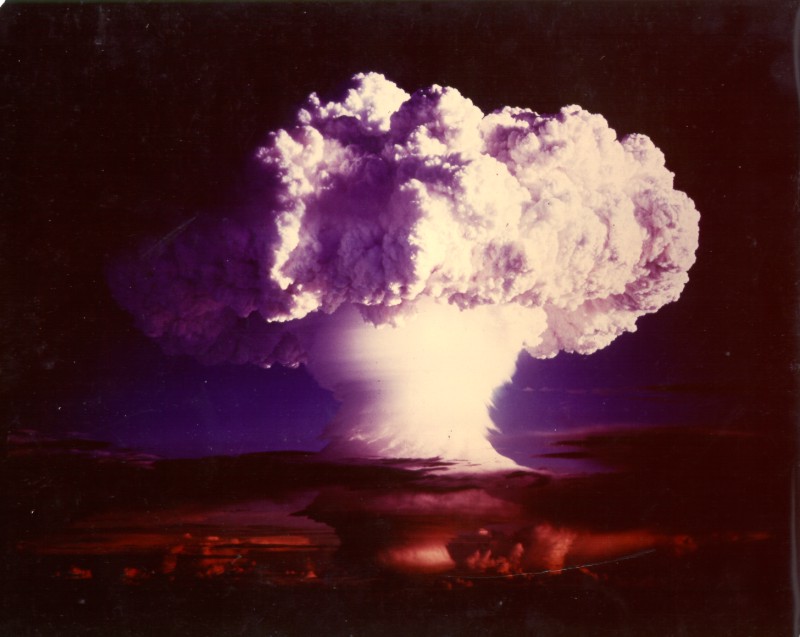
Ivy Mike
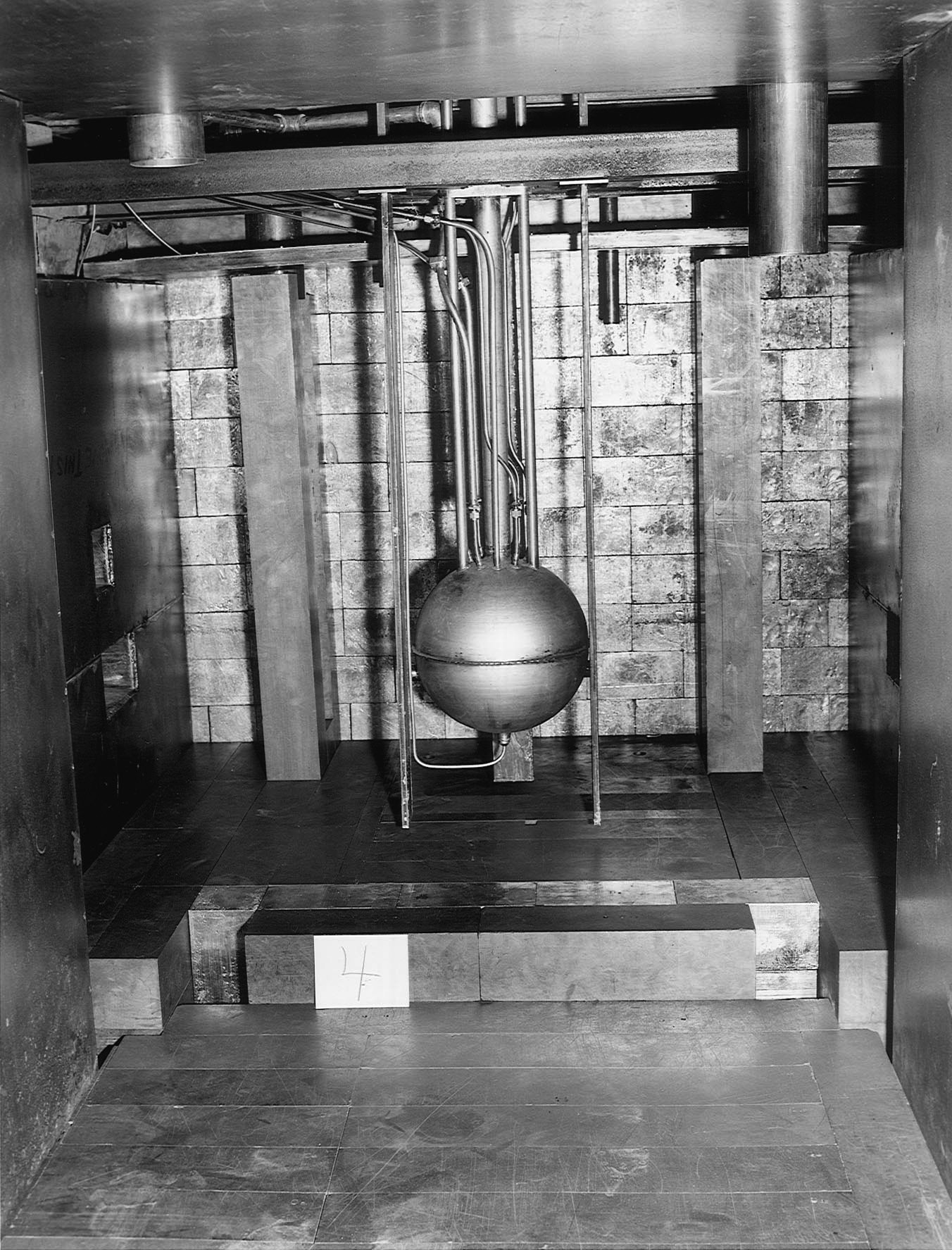
Ivy Mike was the codename given to the first full-scale test of a thermonuclear device, in which part of the explosive yield comes from nuclear fusion. Ivy Mike was detonated on November 1, 1952, by the United States on the island of Elugelab in Enewetak Atoll, in the now independent island nation of the Marshall Islands, as part of Operation Ivy. It was the first full test of the Teller–Ulam design, a staged fusion device. Due to its physical size and fusion fuel type ( cryogenic liquid deuterium), the "Mike" device was not suitable for use as a deliverable weapon. It was intended as a "technically conservative" proof of concept experiment to validate the concepts used for multi-megaton detonations. As a result of the collection of samples from the explosion by U.S. Air Force pilots, scientists found traces of the isotopes plutonium-246 and plutonium-244, and confirmed the existence of the predicted but undiscovered elements einsteinium and fermium. Schedule Beginning w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mushroom Cloud
A mushroom cloud is a distinctive mushroom-shaped flammagenitus cloud of debris, smoke and usually condensed water vapor resulting from a large explosion. The effect is most commonly associated with a nuclear explosion, but any sufficiently energetic detonation or deflagration will produce the same effect. They can be caused by powerful conventional weapons, like thermobaric weapons, including the ATBIP and GBU-43/B Massive Ordnance Air Blast. Some volcanic eruptions and impact events can produce natural mushroom clouds. Mushroom clouds result from the sudden formation of a large volume of lower-density gases at any altitude, causing a Rayleigh–Taylor instability. The buoyant mass of gas rises rapidly, resulting in turbulent vortices curling downward around its edges, forming a temporary vortex ring that draws up a central column, possibly with smoke, debris, condensed water vapor, or a combination of these, to form the "mushroom stem". The mass of gas plus entrained moist ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Weapon Design
Nuclear weapon designs are physical, chemical, and engineering arrangements that cause the physics package of a nuclear weapon to detonate. There are three existing basic design types: * pure fission weapons, the simplest and least technically demanding, were the first nuclear weapons built and have so far been the only type ever used in warfare (by the United States on Empire of Japan, Japan during World War II, WWII). * boosted fission weapons increase yield beyond that of the implosion design by using small quantities of fusion fuel to enhance the fission chain reaction. Boosting can more than double the weapon's fission energy yield. * thermonuclear weapon, staged thermonuclear weapons are essentially arrangements of two or more "stages", most usually two. The first stage is normally a boosted fission weapon as above (except for the earliest thermonuclear weapons, which used a pure fission weapon instead). Its detonation causes it to shine intensely with x-radiation, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry S
Harry may refer to: TV shows * ''Harry'' (American TV series), a 1987 American comedy series starring Alan Arkin * ''Harry'' (British TV series), a 1993 BBC drama that ran for two seasons * ''Harry'' (talk show), a 2016 American daytime talk show hosted by Harry Connick Jr. People and fictional characters * Harry (given name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name * Harry (surname), a list of people with the surname * Dirty Harry (musician) (born 1982), British rock singer who has also used the stage name Harry * Harry Potter (character), the main protagonist in a Harry Potter fictional series by J. K. Rowling Other uses * Harry (derogatory term), derogatory term used in Norway * ''Harry'' (album), a 1969 album by Harry Nilsson *The tunnel used in the Stalag Luft III escape ("The Great Escape") of World War II * ''Harry'' (newspaper), an underground newspaper in Baltimore, Maryland See also *Harrying (laying waste), may refer to the following historical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordon Dean (lawyer)
Gordon Evans Dean (December 28, 1905 – August 15, 1958) was a Seattle-born"A friendly favor" ''Time'' magazine, Jul. 24, 1950. Retrieved 2-7-09. American lawyer and prosecutor who served as chairman of the (AEC) from 1950 to 1953. Early years Dean received his J.D. from the in 1930 and an LL.M. from |
United States Atomic Energy Commission
The United States Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) was an agency of the United States government established after World War II by U.S. Congress to foster and control the peacetime development of atomic science and technology. President Harry S. Truman signed the McMahon/Atomic Energy Act on August 1, 1946, transferring the control of atomic energy from military to civilian hands, effective on January 1, 1947. This shift gave the members of the AEC complete control of the plants, laboratories, equipment, and personnel assembled during the war to produce the atomic bomb. An increasing number of critics during the 1960s charged that the AEC's regulations were insufficiently rigorous in several important areas, including radiation protection standards, nuclear reactor safety, plant siting, and environmental protection. By 1974, the AEC's regulatory programs had come under such strong attack that the U.S. Congress decided to abolish the AEC. The AEC was abolished by the Ener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marshall Holloway
Marshall Glecker Holloway (November 23, 1912 – June 18, 1991) was an American physicist who worked at the Los Alamos Laboratory during and after World War II. He was its representative, and the deputy scientific director, at the Operation Crossroads nuclear tests at Bikini Atoll in the Pacific in July 1946. Holloway became the head of the Laboratory's W Division, responsible for new weapons development. In September 1952 he was charged with designing, building and testing a thermonuclear weapon, popularly known as a hydrogen bomb. This culminated in the Ivy Mike test in November of that year. Early life Marshall Glecker Holloway was born in Oklahoma, on November 23, 1912, but his family moved to Florida when he was young. He graduated from Haines City High School, and entered the University of Florida, which awarded him a Bachelor of Science in Education in 1933, and a Master of Science degree in physics in 1935. He went on to Cornell University, where he wrote his Doctor of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Teller
Edward Teller ( hu, Teller Ede; January 15, 1908 – September 9, 2003) was a Hungarian-American theoretical physicist who is known colloquially as "the father of the hydrogen bomb" (see the Teller–Ulam design), although he did not care for the title, considering it to be in poor taste. Throughout his life, Teller was known both for his scientific ability and for his difficult interpersonal relations and volatile personality. Born in Hungary in 1908, Teller emigrated to the United States in the 1930s, one of the many so-called "Martians", a group of prominent Hungarian scientist émigrés. He made numerous contributions to nuclear and molecular physics, spectroscopy (in particular the Jahn–Teller and Renner–Teller effects), and surface physics. His extension of Enrico Fermi's theory of beta decay, in the form of Gamow–Teller transitions, provided an important stepping stone in its application, while the Jahn–Teller effect and the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermium
Fermium is a synthetic element with the symbol Fm and atomic number 100. It is an actinide and the heaviest element that can be formed by neutron bombardment of lighter elements, and hence the last element that can be prepared in macroscopic quantities, although pure fermium metal has not yet been prepared. A total of 19 isotopes are known, with 257Fm being the longest-lived with a half-life of 100.5 days. It was discovered in the debris of the first hydrogen bomb explosion in 1952, and named after Enrico Fermi, one of the pioneers of nuclear physics. Its chemistry is typical for the late actinides, with a preponderance of the +3 oxidation state but also an accessible +2 oxidation state. Owing to the small amounts of produced fermium and all of its isotopes having relatively short half-lives, there are currently no uses for it outside basic scientific research. Discovery Fermium was first discovered in the fallout from the 'Ivy Mike' nuclear test (1 November 1952), the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Einsteinium
Einsteinium is a synthetic element with the symbol Es and atomic number 99. Einsteinium is a member of the actinide series and it is the seventh transuranium element. It was named in honor of Albert Einstein. Einsteinium was discovered as a component of the debris of the first hydrogen bomb explosion in 1952. Its most common isotope, einsteinium-253 (half-life 20.47 days), is produced artificially from decay of californium-253 in a few dedicated high-power nuclear reactors with a total yield on the order of one milligram per year. The reactor synthesis is followed by a complex process of separating einsteinium-253 from other actinides and products of their decay. Other isotopes are synthesized in various laboratories, but in much smaller amounts, by bombarding heavy actinide elements with light ions. Owing to the small amounts of produced einsteinium and the short half-life of its most easily produced isotope, there are currently almost no practical applications for it outside bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
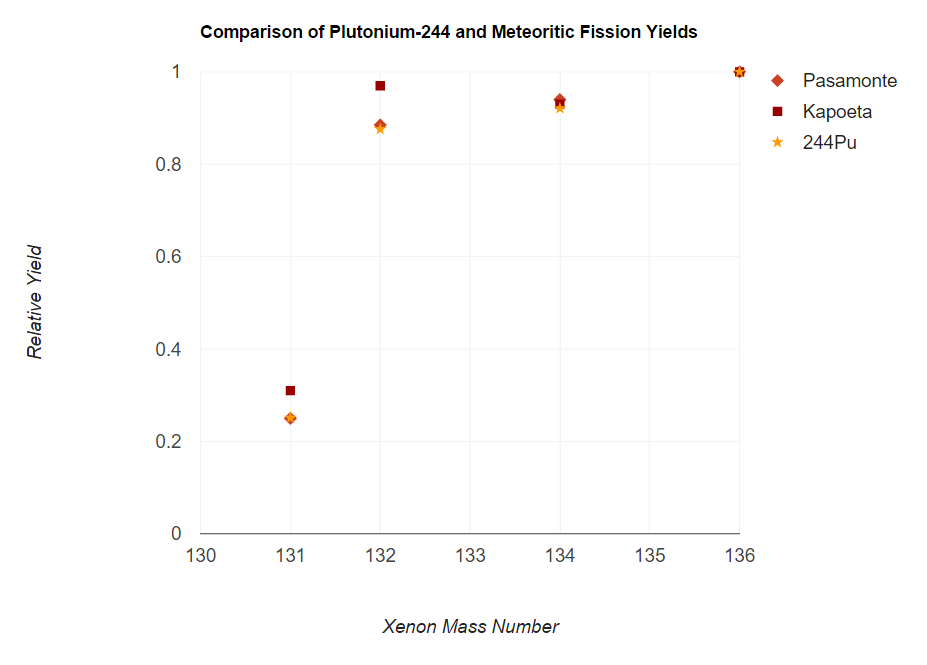
Plutonium-244
Plutonium-244 (244Pu) is an isotope of plutonium that has a half-life of 80 million years. This is longer than any of the other isotopes of plutonium and longer than any other actinide isotope except for the three naturally abundant ones: uranium-235 (704 million years), uranium-238 (4.468 billion years), and thorium-232 (14.05 billion years). Although studies are in conflict, given the mathematics of the decay of plutonium-244, an exceedingly small amount should still be present in the Earth's composition, making plutonium a likely although unproven candidate as the shortest lived primordial element. Natural occurrence Accurate measurements, beginning in the early 1970s, have detected primordial plutonium-244, making it the shortest-lived primordial nuclide. The amount of 244Pu in the pre-Solar nebula (4.57×109 years ago) was estimated as 0.8% the amount of 238U. As the age of the Earth is about 57 half-lives of 244Pu, the amount of plutonium-244 left should be very small; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutonium-246
Plutonium (94Pu) is an artificial element, except for trace quantities resulting from neutron capture by uranium, and thus a standard atomic weight cannot be given. Like all artificial elements, it has no stable isotopes. It was synthesized long before being found in nature, the first isotope synthesized being 238Pu in 1940. Twenty plutonium radioisotopes have been characterized. The most stable are plutonium-244 with a half-life of 80.8 million years, plutonium-242 with a half-life of 373,300 years, and plutonium-239 with a half-life of 24,110 years. All of the remaining radioactive isotopes have half-lives that are less than 7,000 years. This element also has eight meta states; all have half-lives of less than one second. The isotopes of plutonium range in atomic weight from 228.0387 u (228Pu) to 247.074 u (247Pu). The primary decay modes before the most stable isotope, 244Pu, are spontaneous fission and alpha emission; the primary mode after is beta emission. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Signal Corps, the USAF was established as a separate branch of the United States Armed Forces in 1947 with the enactment of the National Security Act of 1947. It is the second youngest branch of the United States Armed Forces and the fourth in order of precedence. The United States Air Force articulates its core missions as air supremacy, global integrated intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance, rapid global mobility, global strike, and command and control. The United States Air Force is a military service branch organized within the Department of the Air Force, one of the three military departments of the Department of Defense. The Air Force through the Department of the Air Force is headed by the civilian Secretary of the Air Force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)