|
Ivor Broom
Air Marshal Sir Ivor Gordon Broom, (2 June 1920 – 24 January 2003) was a senior Royal Air Force commander, and a decorated bomber pilot of the Second World War. Ivor Gordon Broom was born on 2 June 1920 in Cardiff, Wales, to parents Albert and Janet Broom. He had 2 siblings: an older sister, Eva Cameron Broom, who died aged 16 of Tuberculosis, and an older brother, Godfrey Kitchener Broom. They all grew up together in Cardiff. Ivor joined the Royal Air Force as a trainee pilot in early 1940 at the age of 19. Eleven months later, he was a sergeant pilot on 114 Squadron undertaking low-level daylight bombing raids in Blenheim aircraft. He flew similar operations from Malta in 1941 with Nos 105 and 107 Squadrons and while there was commissioned after No.107 Squadron had lost all their officers. In July 1942, Broom returned home to marry Jessie Cooper. Together they had a son, David Broom, born on the 18th of March 1944, and a daughter Diane Broom, born on the 8th of July 1945 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiff
Cardiff (; cy, Caerdydd ) is the capital and largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Cardiff ( cy, Dinas a Sir Caerdydd, links=no), and the city is the eleventh-largest in the United Kingdom. Located in the south-east of Wales and in the Cardiff Capital Region, Cardiff is the county town of the historic county of Glamorgan and in 1974–1996 of South Glamorgan. It belongs to the Eurocities network of the largest European cities. A small town until the early 19th century, its prominence as a port for coal when mining began in the region helped its expansion. In 1905, it was ranked as a city and in 1955 proclaimed capital of Wales. Cardiff Built-up Area covers a larger area outside the county boundary, including the towns of Dinas Powys and Penarth. Cardiff is the main commercial centre of Wales as well as the base for the Senedd. At the 2021 census, the unitary authority area population was put at 362,400. The popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
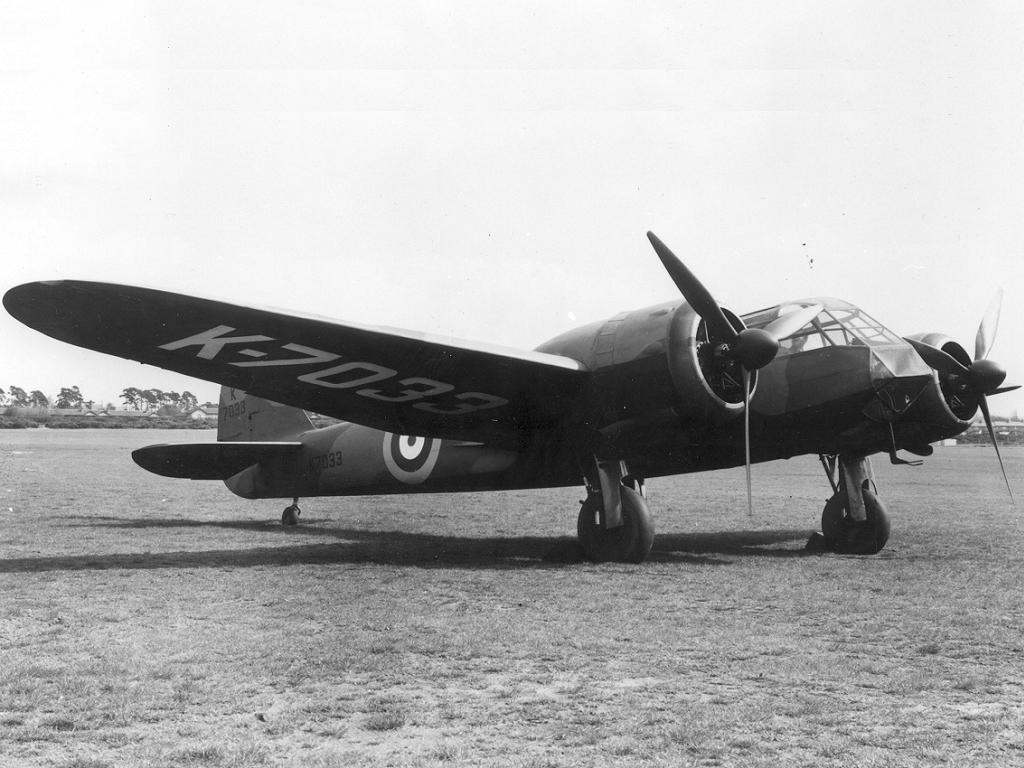
Bristol Blenheim
The Bristol Blenheim is a British light bomber aircraft designed and built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company (Bristol) which was used extensively in the first two years of the Second World War, with examples still being used as trainers until the end of the war. Development began with the ''Type 142'', a civil airliner, in response to a challenge from Lord Rothermere to produce the fastest commercial aircraft in Europe. The ''Type 142'' first flew in April 1935, and the Air Ministry, impressed by its performance, ordered a modified design as the ''Type 142M'' for the Royal Air Force (RAF) as a bomber. Deliveries of the newly named Blenheim to RAF squadrons commenced on 10 March 1937. In service the Type 142M became the Blenheim Mk.I which would be developed into the longer Type 149, designated the Blenheim Mk.IV, except in Canada where Fairchild Canada built the Type 149 under licence as the Bolingbroke. The Type 160 Bisley was also developed from the Blenheim, but was already o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
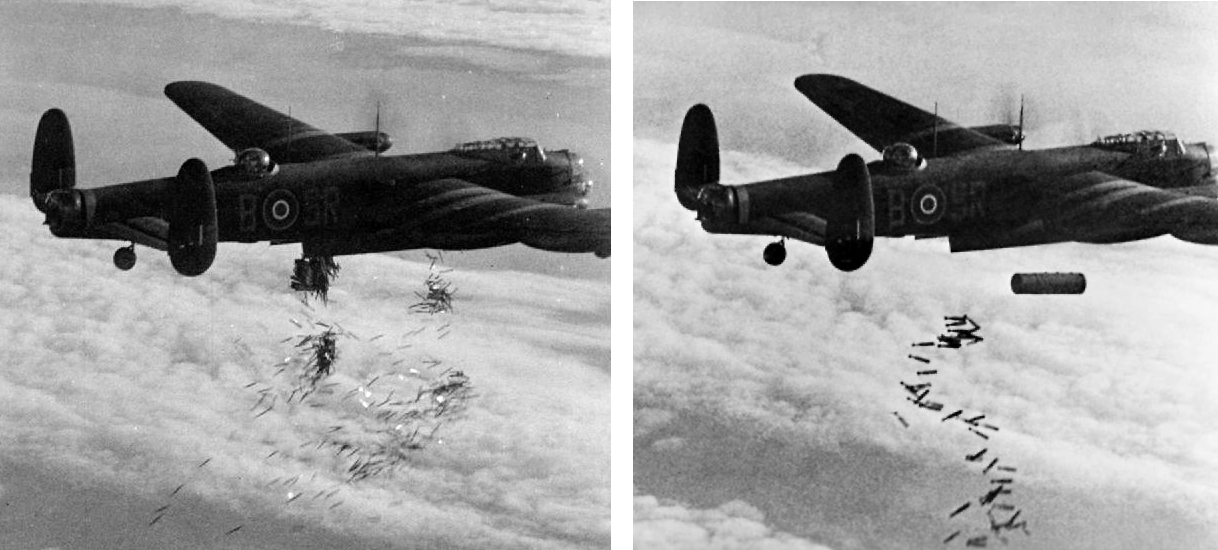
Blockbuster Bomb
A blockbuster bomb or cookie was one of several of the largest conventional bombs used in World War II by the Royal Air Force (RAF). The term ''blockbuster'' was originally a name coined by the press and referred to a bomb which had enough explosive power to destroy an entire street or large building through the effects of blast in conjunction with incendiary bombs. Design The bombs then called ''Blockbusters'' were the RAF's HC (high capacity) bombs. These bombs had especially thin casings that allowed them to contain approximately three-quarters of their weight in explosive, with a 4000 lb bomb (nominal weight) containing about of explosive (Amatol, RDX or Torpex). Most general-purpose bombs, termed "medium capacity'" (MC) by the RAF, contained 50% explosive by weight, the rest being made up of the fragmentation casing. Larger Blockbusters were made later in the war, from the original version, up to . The 4000 lb High Capacity Mark I bomb – actual weight around – was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tommy Broom
Squadron Leader Thomas John Broom, (22 January 1914 – 18 May 2010) was a Royal Air Force officer who was awarded the Distinguished Flying Cross three times for bomber operations during the Second World War. Early life Broom was born in Portishead, Somerset, on 22 January 1914 and educated at Slade Road School. After leaving school Broom got a job in a local garage. e soon grew bored and, in 1932, joined the Royal Air Force (RAF) where he trained to be a navigator. RAF career Broom was mobilised to France at the outbreak of the Second World War, assigned to No. 105 Squadron operating Fairey Battle light bombers. After the German Blitzkrieg through France in 1940, Broom returned home and transferred to No. 13 Operational Training Unit at Bicester, where he taught navigators the skills required for combat. He returned to No. 105 Squadron in 1942 and completed another tour, after which he was posted to 1655 Mosquito Training Unit where he remained until May 1944. Subsequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight Lieutenant
Flight lieutenant is a junior commissioned rank in air forces that use the Royal Air Force (RAF) system of ranks, especially in Commonwealth countries. It has a NATO rank code of OF-2. Flight lieutenant is abbreviated as Flt Lt in the Indian Air Force (IAF) and RAF, and as FLTLT in the Pakistan Air Force (PAF), Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) and Royal New Zealand Air Force (RNZAF) and has sometimes also been abbreviated as F/L in many services; it has never been correctly abbreviated as "lieutenant". A flight lieutenant ranks above flying officer and below a squadron leader and is sometimes used as an English language translation of a similar rank in non-English-speaking countries. The rank originated in the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS) in 1914. It fell into abeyance when the RNAS merged with the Royal Flying Corps during the First World War but was revived in 1919 in the post-war RAF. An RAF flight lieutenant is the equivalent of a lieutenant in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathfinder (RAF)
The Pathfinders were target-marking squadrons in RAF Bomber Command during World War II. They located and marked targets with flares, which a main bomber force could aim at, increasing the accuracy of their bombing. The Pathfinders were normally the first to receive new blind-bombing aids like Gee, Oboe and the H2S radar. The early Pathfinder Force (PFF) squadrons was expanded to become a group, No. 8 (Pathfinder Force) Group in January 1943. The initial Pathfinder Force was five squadrons, while No. 8 Group ultimately grew to a strength of 19 squadrons. While the majority of Pathfinder squadrons and personnel were from the Royal Air Force, the group also included many from the air forces of other Commonwealth countries. History Background At the start of the war in September 1939, RAF Bomber Command's doctrine was based on tight formations of heavily armed bombers attacking during daylight and fending off attacks by fighters with their defensive guns. In early missions ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Havilland Mosquito
The de Havilland DH.98 Mosquito is a British twin-engined, shoulder-winged, multirole combat aircraft, introduced during the Second World War. Unusual in that its frame was constructed mostly of wood, it was nicknamed the "Wooden Wonder", or "Mossie". Lord Beaverbrook, Minister of Aircraft Production, nicknamed it "Freeman's Folly", alluding to Air Chief Marshal Sir Wilfrid Freeman, who defended Geoffrey de Havilland and his design concept against orders to scrap the project. In 1941, it was one of the fastest operational aircraft in the world.Bowman 2005, p. 21. Originally conceived as an unarmed fast bomber, the Mosquito's use evolved during the war into many roles, including low- to medium-altitude daytime tactical bomber, high-altitude night bomber, pathfinder, day or night fighter, fighter-bomber, intruder, maritime strike, and photo-reconnaissance aircraft. It was also used by the British Overseas Airways Corporation as a fast transport to carry small, high-value c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Royal Air Force Operational Training Units
Royal Air Force Operational Training Units (OTUs) were training units that prepared aircrew for operations on a particular type or types of aircraft or roles. OTUs ; No. 1 (Coastal) Operational Training Unit RAF (1 OTU): The Unit was formed in 1940 as part of RAF Coastal Command at RAF Silloth for training aircrew on coastal command patrol aircraft types until it was disbanded on 19 October 1943.Sturtivant 2007, pp. 198-206 ;No. 2 (Coastal) Operational Training Unit RAF (2 OTU): 2 OTU was formed in 1940 as part of Coastal Command at RAF Catfoss for training aircrew on coastal command twin-engined fighter and strike aircraft types until it was disbanded 15 February 1944. ;No. 3 (Coastal) Operational Training Unit RAF (3 OTU): 3 OTU was formed in 1940 as part of Coastal Command at RAF Catfoss for training aircrew on coastal command aircraft types including the Avro Anson and Bristol Beaufighter, until it was disbanded 4 January 1944. ; No. 4 (Coastal) Operational Training Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
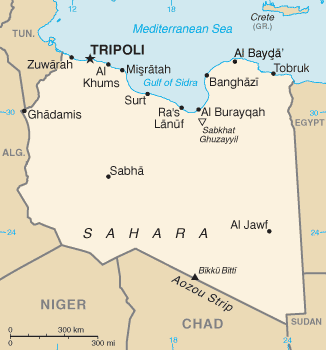
Gulf Of Sidra
The Gulf of Sidra ( ar, خليج السدرة, Khalij as-Sidra, also known as the Gulf of Sirte ( ar, خليج سرت, Khalij Surt, is a body of water in the Mediterranean Sea on the northern coast of Libya, named after the oil port of Sidra or the city of Sirte. It was also historically known as the Great Sirte or Greater Syrtis ( la, Syrtis Major; grc, Σύρτις μεγάλη; contrasting with Syrtis Minor on the coast of Tunisia). Geography The Gulf of Sidra or Sirte has been a major center for tuna fishing in the Mediterranean for centuries. It gives its name to the city of Sirte situated on its western side. The gulf measures from the promontory of Boreum (now Ras Teyonas) on the East side to the promontory of Cephalae (Ras Kasr Hamet) on the West. The greatest extension of the gulf inland is land inward and occupies an area of 57,000 square kilometres. History Ancient history Syrtis is referred to in the New Testament of the Bible, where Luke relates the Apostl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilot Officer
Pilot officer (Plt Off officially in the RAF; in the RAAF and RNZAF; formerly P/O in all services, and still often used in the RAF) is the lowest commissioned rank in the Royal Air Force and the air forces of many other Commonwealth countries. It ranks immediately below flying officer. It has a NATO ranking code of OF-1 and is equivalent to a second lieutenant in the British Army or the Royal Marines. The Royal Navy has no exact equivalent rank, and a pilot officer is senior to a Royal Navy midshipman and junior to a Royal Navy sub-lieutenant. In the Australian Armed Forces, the rank of pilot officer is equivalent to acting sub lieutenant in the Royal Australian Navy. The equivalent rank in the Women's Auxiliary Air Force (WAAF) was "assistant section officer". Origins In the Royal Flying Corps, officers were designated pilot officers at the end of pilot training. As they retained their commissions in their customary ranks (usually second lieutenant or lieutenant), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh Pughe Lloyd
Air Chief Marshal Sir Hugh Pughe Lloyd, (12 December 1894 – 14 July 1981) was a senior Royal Air Force commander. RAF career Lloyd joined the Royal Engineers as a sapper in 1915 during the First World War: he was wounded in action three times before enlisting as a cadet in the Royal Flying Corps in 1917 and joining No. 52 Squadron RAF, No. 52 Squadron, flying the Royal Aircraft Factory R.E.8, RE.8 on army co-operation missions. After the war, he remained with the recently formed Royal Air Force on a permanent commissioned officer, commission. In January 1939 Lloyd became Officer Commanding No. 9 Squadron RAF, No. 9 Squadron, equipped with Vickers Wellington, Wellingtons. Later in 1939, with the Second World War under way, he was promoted to group captain and given command of RAF Marham. His stay at RAF Marham was brief and in November he was appointed to the staff of No. 3 Group RAF, No. 3 Group and, in May 1940, he became Senior Air Staff Officer at No. 2 Group RAF, No. 2 Grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Malta (World War II)
The siege of Malta in World War II was a military campaign in the Mediterranean Theatre. From June 1940 to November 1942, the fight for the control of the strategically important island of the British Crown Colony of Malta pitted the air and naval forces of Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany against the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the Royal Navy. The opening of a new front in North Africa in June 1940 increased Malta's already considerable value. British air and sea forces based on the island could attack Axis ships transporting vital supplies and reinforcements from Europe; Churchill called the island an " unsinkable aircraft carrier". General Erwin Rommel, de facto field command of Axis forces in North Africa, recognised its importance quickly. In May 1941, he warned that "Without Malta the Axis will end by losing control of North Africa". The Axis resolved to bomb or starve Malta into submission, to soften it up for invasion, by attacking its ports, towns, cities, and Allied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)