Gulf of Sidra on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
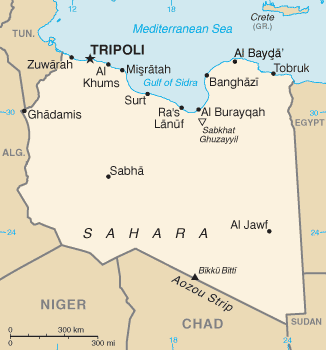 The Gulf of Sidra ( ar, خليج السدرة, Khalij as-Sidra, also known as the Gulf of Sirte ( ar, خليج سرت, Khalij Surt, is a body of water in the
The Gulf of Sidra ( ar, خليج السدرة, Khalij as-Sidra, also known as the Gulf of Sirte ( ar, خليج سرت, Khalij Surt, is a body of water in the
/ref> and occupies an area of 57,000 square kilometres.
 Two naval battles were fought in the Gulf of Sidra in World War II:
*
Two naval battles were fought in the Gulf of Sidra in World War II:
*
(10 April 2002). Foreign Press Centers, U.S. Department of State. Retrieved 18 October 2010. The RC-135 was not hit and the United States took no retaliatory action after the incident.
 * First Battle of Brega, 2 March 2011
*
* First Battle of Brega, 2 March 2011
*
 The Gulf of Sidra ( ar, خليج السدرة, Khalij as-Sidra, also known as the Gulf of Sirte ( ar, خليج سرت, Khalij Surt, is a body of water in the
The Gulf of Sidra ( ar, خليج السدرة, Khalij as-Sidra, also known as the Gulf of Sirte ( ar, خليج سرت, Khalij Surt, is a body of water in the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
on the northern coast of Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya bo ...
, named after the oil port of Sidra Sidra may refer to:
*Sidra (name)
Places
*Gulf of Sidra, a body of water in the Mediterranean Sea on the northern coast of Libya
*Sidra, Libya, a Libyan port
*Sidra, Sokółka County, a village in Poland
*Gmina Sidra, a Polish administrative dis ...
or the city of Sirte
Sirte (; ar, سِرْت, ), also spelled Sirt, Surt, Sert or Syrte, is a city in Libya. It is located south of the Gulf of Sirte, between Tripoli and Benghazi. It is famously known for its battles, ethnic groups, and loyalty to Muammar G ...
. It was also historically known as the Great Sirte or Greater Syrtis ( la, Syrtis Major; grc, Σύρτις μεγάλη; contrasting with Syrtis Minor
Syrtis ( grc, Σύρτις) may refer to: Places North African coast
* Syrtis Major (or the Great rSyrtis) is the Latin name for the Gulf of Sirte, a body of water in the Mediterranean Sea on the northern coast of Libya
* Syrtis Minor (or the Lesse ...
on the coast of Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
).
Geography
The Gulf of Sidra or Sirte has been a major center fortuna fishing
''Tuna Fishing (Homage to Meissonier)'' was painted by Salvador Dalí in 1966–1967 and is seen by many as one of Dalí's last masterpieces. Filled chaotically with the violent struggle of the men in the picture and the big fish. A golden knife s ...
in the Mediterranean for centuries. It gives its name to the city of Sirte
Sirte (; ar, سِرْت, ), also spelled Sirt, Surt, Sert or Syrte, is a city in Libya. It is located south of the Gulf of Sirte, between Tripoli and Benghazi. It is famously known for its battles, ethnic groups, and loyalty to Muammar G ...
situated on its western side.
The gulf measures from the promontory of Boreum (now Ras Teyonas) on the East side to the promontory of Cephalae (Ras Kasr Hamet) on the West. The greatest extension of the gulf inland is land inwardSyrtis Major And Syrtis Minor/ref> and occupies an area of 57,000 square kilometres.
History
Ancient history
Syrtis is referred to in theNew Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christ ...
of the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
, where Luke relates the Apostle Paul
Paul; grc, Παῦλος, translit=Paulos; cop, ⲡⲁⲩⲗⲟⲥ; hbo, פאולוס השליח (previously called Saul of Tarsus;; ar, بولس الطرسوسي; grc, Σαῦλος Ταρσεύς, Saũlos Tarseús; tr, Tarsuslu Pavlus; ...
being sent in chains to Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
to stand trial before the Roman emperor, Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68), was the fifth Roman emperor and final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 un ...
. The crew of his ship was worried about being driven by a storm into Syrtis, and they took precautions to prevent it, but the ship was shipwrecked on the island of Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
, in the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
.
In ancient literature, the Syrtes (the Greater, or , in the eastern and the Lesser, or , in the western part of the Gulf) were notorious sandbanks, which sailors always took pains to avoid. The local climate features frequent calms and a relatively powerful north wind. The shoreline between Cyrene in the east and Carthage in the west featured few ports.
Ancient writers frequently mention the sandbanks and their vicinity as dangerous for shipping. The Syrtes maiores are unusually tidal and feature a strong (3 knots) clockwise current, at the rising tide, which then switches when the tide ebbs. That feature may explain the curious corkscrew shape in the area on the Peutinger Table
' (Latin for "The Peutinger Map"), also referred to as Peutinger's Tabula or Peutinger Table, is an illustrated ' (ancient Roman road map) showing the layout of the ''cursus publicus'', the road network of the Roman Empire.
The map is a 13th-cen ...
. The landward side was a featureless plain which contrasted with the fertility of the rest of Tripolitania, to the west.
Ancient writers mention sandstorms and serpents in this area. Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
describes a march by the Roman general, Cato the Younger in 47 BC which took thirty days "through deep and scorching sand". Strabo also gives a full account of the dangers for shipping: "the difficulty with both the Greater and the Lesser Syrtes is that in many places the water is shallow, and at the rise and fall of the tides ships sometimes fall into the shallows and settle there, and it is rare for them to be saved" (17.3.20). Pomponius Mela gives a very melodramatic description:
"The Syrtes inores... have no ports and are alarming because of the frequent shallows and even more dangerous because of the reversing movements of the sea as it flows in and out ... then here is
Here is an adverb that means "in, on, or at this place". It may also refer to:
Software
* Here Technologies, a mapping company
* Here WeGo (formerly Here Maps), a mobile app and map website by Here
Television
* Here TV (formerly "here!"), a TV ...
a second Syrtes, equal in name and nature to the first, but about twice the size" (1.35–37).
These sources should not however be taken at face value: Mela goes on to say that there were no ports in the Greater Syrtes either, but his reliability on this point – and therefore presumably others – is highly questionable: Pseudo-Scylax, writing in the early 4th century BC, records a port in the larger gulf (109), and Strabo places a "very large emporium" in the smaller one before Mela's time (17.3.17). Furthermore, the ancient textual evidence is not unambiguous in its condemnation of the Syrtes. Plutarch gives a much less melodramatic account of Cato's march than Strabo's, saying (admittedly implausibly) that it took only seven days, and that locals were engaged to protect his troops from serpents (Cato Minor 56; see also the uneventful late 5th-century journey along the coast from Euesperides to Neapolis reported at Thucydides 7.50.2). And while Strabo pointed out the dangers of the sandbanks, he continues: "On this account sailors travel along the coast at a distance, taking care lest they are caught off their guard and driven into these gulfs by winds." As in Cato, they do not avoid the area, but merely take precautions against its relative dangers. Similarly, Pliny's warning that the gulf was "formidable because of the shallow and tidal water of the two Syrtes" at ''Natural History'' 5.26 should be seen in the context of his broader claim in that work that all the coastlines of the Mediterranean were welcoming (''NH'' 2.118).
Their infamous reputation is, however, found in Roman poetry, from Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; traditional dates 15 October 7021 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: t ...
(Aeneid IV, 41) on.
The information in this section is largely taken from ''The Syrtes between East and West'' by Josephine Crawley Quinn.
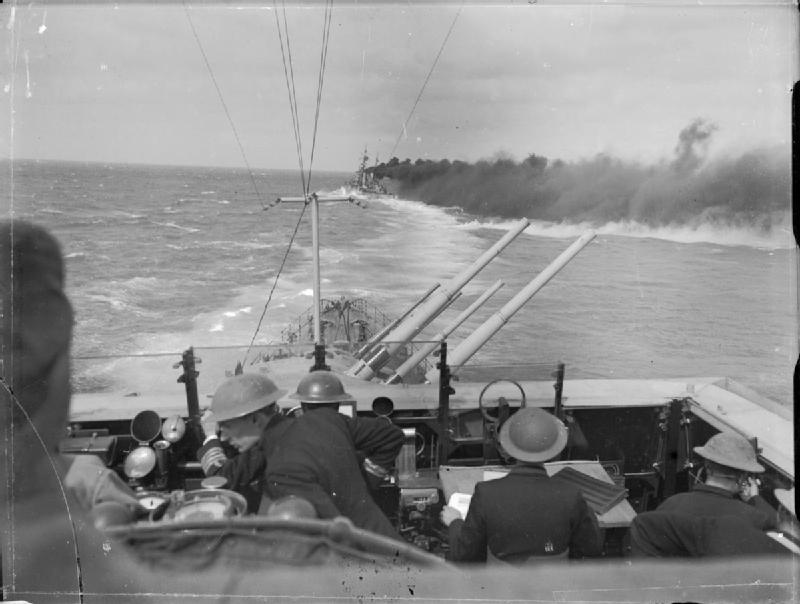
World War II
 Two naval battles were fought in the Gulf of Sidra in World War II:
*
Two naval battles were fought in the Gulf of Sidra in World War II:
* First Battle of Sirte
The First Battle of Sirte was fought between the British Royal Navy and the ''Regia Marina'' (Italian Royal Navy) during the Mediterranean campaign of the Second World War. The engagement took place on 17 December 1941, south-east of Malta, ...
, between Regia Marina
The ''Regia Marina'' (; ) was the navy of the Kingdom of Italy (''Regno d'Italia'') from 1861 to 1946. In 1946, with the Italian constitutional referendum, 1946, birth of the Italian Republic (''Repubblica Italiana''), the ''Regia Marina'' ch ...
and the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
in December 1941.
* Second Battle of Sirte
The Second Battle of Sirte (on 22 March 1942) was a naval engagement in the Mediterranean Sea, north of the Gulf of Sidra and southeast of Malta, during the Second World War. The escorting warships of a British convoy to Malta held off a much ...
, between Regia Marina
The ''Regia Marina'' (; ) was the navy of the Kingdom of Italy (''Regno d'Italia'') from 1861 to 1946. In 1946, with the Italian constitutional referendum, 1946, birth of the Italian Republic (''Repubblica Italiana''), the ''Regia Marina'' ch ...
and the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
in March 1942.
Cold War
After the coup d'état which broughtMuammar Gaddafi
Muammar Muhammad Abu Minyar al-Gaddafi, . Due to the lack of standardization of transcribing written and regionally pronounced Arabic, Gaddafi's name has been romanized in various ways. A 1986 column by ''The Straight Dope'' lists 32 spellin ...
to power in 1969, there were a number of international incidents concerning territorial claims of the Gaddafi regime
Muammar Gaddafi became the ''de facto'' leader of Libya on 1 September 1969 after leading a group of young Libyan Army officers against King Idris I in a bloodless coup d'état. After the king had fled the country, the Revolutionary Comma ...
over the waters of the Gulf of Sidra. The gulf was generally referred to by the US military in those times as "Gulf of Sidra", after the increasingly important oil port of Sidra Sidra may refer to:
*Sidra (name)
Places
*Gulf of Sidra, a body of water in the Mediterranean Sea on the northern coast of Libya
*Sidra, Libya, a Libyan port
*Sidra, Sokółka County, a village in Poland
*Gmina Sidra, a Polish administrative dis ...
on its shores.
1973
In 1973, Gaddafi claimed much of the Gulf of Sidra to be within Libyan internal waters by drawing a straight line at 32 degrees, 30 minutes north between a point near Benghazi and the western headland of the gulf at Misrata with an exclusive fishing zone. Gaddafi declared it the Line of Death, the crossing of which would invite a military response. The US claimed its rights to conduct naval operations in international waters, using the modern international standard of territorial limit from a country's shore as defined by the 1982United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty, is an international agreement that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities. , 167 c ...
. Gaddafi claimed it to be a territorial sea, not just a coastal area. In response the United States authorized Naval exercises in the Gulf of Sidra to conduct Freedom of Navigation (FON) operations.
On 21 March 1973, Libyan fighter planes intercepted and fired on a U.S. Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Sign ...
C-130
The Lockheed C-130 Hercules is an American four-engine turboprop military transport aircraft designed and built by Lockheed (now Lockheed Martin). Capable of using unprepared runways for takeoffs and landings, the C-130 was originally desig ...
conducting signals intelligence
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is intelligence-gathering by interception of ''signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly used in communication ( ...
off the Libyan coast. During the encounter, two Libyan Mirage
A mirage is a naturally-occurring optical phenomenon in which light rays bend via refraction to produce a displaced image of distant objects or the sky. The word comes to English via the French ''(se) mirer'', from the Latin ''mirari'', meanin ...
fighters signaled the C-130 to follow them toward Libya and land, prompting the American plane to take evasive action. The C-130 received cannon fire from the Libyan fighters as it fled, but was able to escape by using cloud cover. According to US officials, the American plane was never closer than 120 kilometres to the Libyan coast.
1980
While operating over the Mediterranean Sea on 16 September 1980, a USBoeing RC-135
The Boeing RC-135 is a family of large reconnaissance aircraft built by Boeing and modified by a number of companies, including General Dynamics, Lockheed, LTV, E-Systems, and L3 Technologies, and used by the United States Air Force and Royal ...
V/W reconnaissance plane was fired on by a Libyan fighter."Congressional Research Service Issue Brief for Congress: Libya"(10 April 2002). Foreign Press Centers, U.S. Department of State. Retrieved 18 October 2010. The RC-135 was not hit and the United States took no retaliatory action after the incident.
1981
In August 1981, during the United States Sixth FleetFreedom of Navigation
Freedom of navigation (FON) is a principle of law of the sea that ships flying the flag of any sovereign state shall not suffer interference from other states, apart from the exceptions provided for in international law. In the realm of internat ...
exercises, Libyan fighter planes were assembled from elsewhere in the country to fly patrols near the American ships. On 19 August, two Libyan Su-22 Fitter fighter-bombers were intercepted by two F-14 Tomcat
The Grumman F-14 Tomcat is an American carrier-capable supersonic aircraft, supersonic, twinjet, twin-engine, two-seat, twin-tail, variable-sweep wing fighter aircraft. The Tomcat was developed for the United States Navy's Naval Fighter Experi ...
fighters from the aircraft carrier . During the engagement, one of the American planes was targeted by an air-to-air Atoll missile. After evading the missile, the Tomcats shot down both Libyan planes with Sidewinder missiles. According to some reports, the two Libyan pilots managed to eject and were rescued from the sea. According to other reports, the parachute of one of the Libyan pilots failed to open.
1986
In the spring of 1986, theU.S. Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage o ...
deployed three aircraft carrier task force groups, USS ''America'', USS ''Coral Sea'' and USS ''Saratoga'' from the Sixth Fleet with 225 aircraft and some 30 warships across the "Line of Death" and into the disputed Gulf of Sidra. After a day of armed conflict, the operation was terminated after an unknown number of human and materiel losses to the Libyan side and no losses to the American side.
Two weeks later on 5 April 1986, a bomb exploded in a West Berlin
West Berlin (german: Berlin (West) or , ) was a political enclave which comprised the western part of Berlin during the years of the Cold War. Although West Berlin was de jure not part of West Germany, lacked any sovereignty, and was under mi ...
disco, La Belle, killing two American servicemen, a Turkish woman and wounding 200 others. The United States claimed to have obtained cable transcripts from Libyan agents in East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
involved in the attack. After several days of diplomatic talks with European and Arab partners, President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
ordered eighteen F-111F strike aircraft of the 48th Tactical Fighter Wing, flying from RAF Lakenheath
Royal Air Force Lakenheath or RAF Lakenheath is a Royal Air Force station near the village of Lakenheath in Suffolk, England, UK, north-east of Mildenhall and west of Thetford. The base also sits close to Brandon.
Despite being an RAF sta ...
supported by four EF-111A Ravens of the 20th Tactical Fighter Wing, from RAF Upper Heyford
RAF Upper Heyford was a Royal Air Force station located north-west of Bicester near the village of Upper Heyford, Oxfordshire, England. In the Second World War the airfield was used by Bomber Command. During the Cold War, Upper Heyford was one ...
in England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
to strike targets in Libya in conjunction with fifteen A-6, A-7, F/A-18
The McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet is an all-weather, twin-engine, supersonic, carrier-capable, multirole combat aircraft, designed as both a fighter and attack aircraft (hence the F/A designation). Designed by McDonnell Douglas (now part ...
attack aircraft and EA-6B Prowler
The Northrop Grumman (formerly Grumman) EA-6B Prowler is a twin-engine, four-seat, mid-wing electronic-warfare aircraft derived from the A-6 Intruder airframe. The EA-6A was the initial electronic warfare version of the A-6 used by the United ...
Electronic Warfare Aircraft from the aircraft carriers USS ''Saratoga'', USS ''America'' and USS ''Coral Sea'' on station in the Gulf of Sidra. The planes flying from Britain had to fly over the Atlantic, down the coast of Spain, and then turn east into the Mediterranean because the French and Spanish governments refused permission to use their airspace for the attack. This necessitated use of mid-air refueling. The attack lasted about ten minutes, hitting several targets early on 15 April. Two American airmenCaptain Paul F. Lorence, Major Fernando L. Ribas-Dominicci
Major Fernando Luis Ribas-Dominicci (June 24, 1952 – April 15, 1986), was an F-111F pilot in the United States Air Force. He was killed in action during Operation El Dorado Canyon, the April 15, 1986, U.S. air raid on Libya.
Early years ...
were killed when their plane was shot down over the Gulf of Sidra. Forty-five Libyan soldiers and government officials and fifteen civilians were also killed.
1989
In 1989, in another Gulf of Sidra incident, two LibyanMiG-23
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-23 (russian: Микоян и Гуревич МиГ-23; NATO reporting name: Flogger) is a variable-geometry fighter aircraft, designed by the Mikoyan-Gurevich design bureau in the Soviet Union. It is a third-generatio ...
Flogger aircraft were shot down when it was believed they were about to attack the U.S. fighters that were in the area. In this instance, the Flogger pilots were reportedly lost when they were fired on and successfully shot down after a series of missile launches, although they were seen to eject and parachute into the sea.
2011 Libyan Civil War
Battle of Ra's Lanuf
The Battle of Ras Lanuf was a two-phase battle in 2011 during the Libyan Civil War between forces loyal to Libyan leader Muammar Gaddafi and those loyal to the National Transitional Council. Both forces sought control of the town of Ras Lanuf. T ...
, 4–12 March 2011
*Battle of Bin Jawad
The Battle of Bin Jawad was a battle in the Libyan Civil War between forces loyal to Libyan leader Muammar Gaddafi and anti-Gaddafi forces for control of the town of Bin Jawad.
Battle
On 5 March 2011, following the Battle of Ra's Lanuf, rebel ...
, 6 March 2011
* Second Battle of Brega, 13–15 March 2011
*First Gulf of Sidra offensive
The First Gulf of Sidra offensive was the second major rebel offensive of the Libyan Civil War. It was mounted by anti-Gaddafi forces immediately after their victory in the Battle of Ajdabiya. The offensive was meant to have the rebel forces quic ...
, 26–30 March 2011
* Third Battle of Brega, 31 March – 6 April 2011
* Second Gulf of Sidra offensive, 22 August – 20 October 2011
* Battle of Sirte, 15 September – 20 October 2011
See also
*Libyan Sea
The Libyan Sea (Greek , Latin ''Libycum Mare'', Arabic البحر الليبي) is the portion of the Mediterranean Sea north of the African coast of ancient ''Libya'', i.e. Cyrenaica, and Marmarica
(the coast of what is now eastern Libya and ...
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Sidra Gulfs of the Mediterranean Gulfs of Libya Baladiyat of Libya