|
Islamic Music
Islamic music may refer to religious music, as performed in Islamic public services or private devotions, or more generally to musical traditions of the Muslim world. The heartland of Islam is the Middle East, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, West Africa, Iran, Central Asia, and South Asia. Due to Islam being a multi-ethnic religion, the musical expression of its adherents is vastly diverse. Indigenous traditions of various part have influenced the musical styles popular among Muslims today. The word "music" in Arabic, the language of Islam, (''mūsīqā'' ) is defined more narrowly than in English or some other languages, and "its concept" was at least originally "reserved for secular art music; separate names and concepts belonged to folk songs and to religious chants".) At least one scholar (Jacob M. Landau) makes the generalization about Islamic music that it "is characterized by a highly subtle organization of melody and rhythm", that "the vocal component predominates ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Musical Gathering - Ottoman, 18th Century
A, or a, is the first Letter (alphabet), letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is English alphabet#Letter names, ''a'' (pronounced ), plural English alphabet#Letter names, ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Greek alphabet#History, Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The Letter case, uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the double-storey a and single-storey ɑ. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English grammar, "English articles, a", and its variant "English articles#Indefinite article, an", are Article (grammar)#Indefinite article, indefinite arti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raï
Raï (, ; ar, راي, Latn, ar, rāʾy, ), sometimes written rai, is a form of Algerian folk music that dates back to the 1920s. Singers of Raï are called ''cheb'' (Arabic: شاب) (or ''shabab,'' i.e. young) as opposed to ''sheikh'' (Arabic: شيخ) ('' shaykh'', i.e. old), the name given to Chaabi singers. The tradition arose in the city of Oran, primarily among the poor. Traditionally sung by men, by the end of the 20th century, female singers had become common. The lyrics of Raï have concerned social issues such as disease and the policing of European colonies that affected native populations.Gross, Joan, David McMurray, and Ted Swedenburg. "Arab Noise and Ramadan Nights: Raï, Rap, and Franco-Maghrebi Identities." Diaspora 3:1 (1994): 3- 39. Reprinted in The Anthropology of Globalization: A Reader, ed. by Jonathan Xavier and Renato Rosaldo, History Origins Raï is a type of Algerian popular music that arose in the 1920s in the port city of Oran, and that self-con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Egypt to the north, Eritrea to the northeast, Ethiopia to the southeast, Libya to the northwest, South Sudan to the south and the Red Sea. It has a population of 45.70 million people as of 2022 and occupies 1,886,068 square kilometres (728,215 square miles), making it Africa's List of African countries by area, third-largest country by area, and the third-largest by area in the Arab League. It was the largest country by area in Africa and the Arab League until the 2011 South Sudanese independence referendum, secession of South Sudan in 2011, since which both titles have been held by Algeria. Its Capital city, capital is Khartoum and its most populated city is Omdurman (part of the metropolitan area of Khar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the Eritrea–Ethiopia border, north, Djibouti to the Djibouti–Ethiopia border, northeast, Somalia to the Ethiopia–Somalia border, east and northeast, Kenya to the Ethiopia–Kenya border, south, South Sudan to the Ethiopia–South Sudan border, west, and Sudan to the Ethiopia–Sudan border, northwest. Ethiopia has a total area of . As of 2022, it is home to around 113.5 million inhabitants, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, 13th-most populous country in the world and the List of African countries by population, 2nd-most populous in Africa after Nigeria. The national capital and largest city, Addis Ababa, lies several kilometres west of the East African Rift that splits the country into the African Plate, Africa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
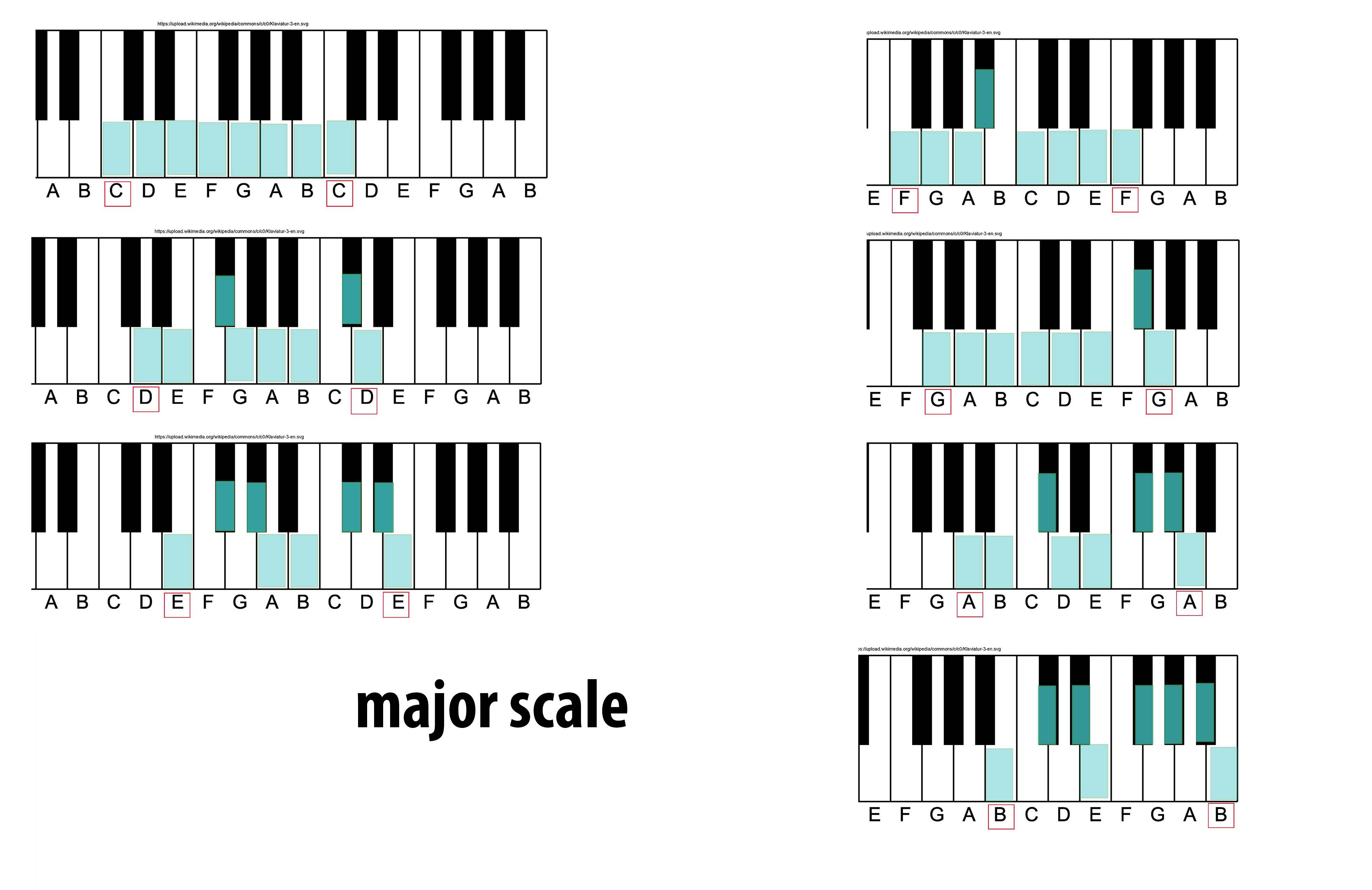
Major Scale
The major scale (or Ionian mode) is one of the most commonly used musical scales, especially in Western music. It is one of the diatonic scales. Like many musical scales, it is made up of seven notes: the eighth duplicates the first at double its frequency so that it is called a higher octave of the same note (from Latin "octavus", the eighth). The simplest major scale to write is C major, the only major scale not requiring sharps or flats: The major scale had a central importance in Western music, particularly in the common practice period and in popular music. In Carnatic music, it is known as ''Sankarabharanam''. In Hindustani classical music, it is known as ''Bilaval''. Structure A major scale is a diatonic scale. The sequence of intervals between the notes of a major scale is: : whole, whole, half, whole, whole, whole, half where "whole" stands for a whole tone (a red u-shaped curve in the figure), and "half" stands for a semitone (a red angled lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heptatonic Scale
A heptatonic scale is a musical scale that has seven pitches, or tones, per octave. Examples include the major scale or minor scale; e.g., in C major: C D E F G A B C—and in the relative minor, A minor, natural minor: A B C D E F G A; the melodic minor scale, A B C D E FGA ascending, A G F E D C B A descending; the harmonic minor scale, A B C D E F GA; and a scale variously known as the Byzantine, and Hungarian,''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', second edition, edited by Stanley Sadie and John Tyrrell (London, 2001) scale, C D E F G A B C. Indian classical theory postulates seventy-two seven-tone scale types, collectively called '' thaat'', whereas others postulate twelve or ten (depending on the theorist) seven-tone scale types. Several heptatonic scales in Western, Roman, Spanish, Hungarian, and Greek music can be analyzed as juxtapositions of tetrachords.Dupré, Marcel (1962). ''Cours Complet d'Improvisation a l'Orgue'', v.2, p. 35, trans. John Fenste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octave
In music, an octave ( la, octavus: eighth) or perfect octave (sometimes called the diapason) is the interval between one musical pitch and another with double its frequency. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referred to as the "basic miracle of music," the use of which is "common in most musical systems." The interval between the first and second harmonics of the harmonic series is an octave. In Western music notation, notes separated by an octave (or multiple octaves) have the same name and are of the same pitch class. To emphasize that it is one of the perfect intervals (including unison, perfect fourth, and perfect fifth), the octave is designated P8. Other interval qualities are also possible, though rare. The octave above or below an indicated note is sometimes abbreviated ''8a'' or ''8va'' ( it, all'ottava), ''8va bassa'' ( it, all'ottava bassa, sometimes also ''8vb''), or simply ''8'' for the octave in the direction indicated by plac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch (music)
Pitch is a perceptual property of sounds that allows their ordering on a frequency-related scale, or more commonly, pitch is the quality that makes it possible to judge sounds as "higher" and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melodies. Pitch is a major auditory attribute of musical tones, along with duration, loudness, and timbre. Pitch may be quantified as a frequency, but pitch is not a purely objective physical property; it is a subjective psychoacoustical attribute of sound. Historically, the study of pitch and pitch perception has been a central problem in psychoacoustics, and has been instrumental in forming and testing theories of sound representation, processing, and perception in the auditory system. Perception Pitch and frequency Pitch is an auditory sensation in which a listener assigns musical tones to relative positions on a musical scale based primarily on their perception of the frequency of vibration. Pitch is closely related to frequency, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentatonic Scale
A pentatonic scale is a musical scale with five notes per octave, in contrast to the heptatonic scale, which has seven notes per octave (such as the major scale and minor scale). Pentatonic scales were developed independently by many ancient civilizations and are still used in various musical styles to this day. There are two types of pentatonic scales: those with semitones (hemitonic) and those without (anhemitonic). Types Hemitonic and anhemitonic Musicology commonly classifies pentatonic scales as either ''hemitonic'' or ''anhemitonic''. Hemitonic scales contain one or more semitones and anhemitonic scales do not contain semitones. (For example, in Japanese music the anhemitonic ''yo'' scale is contrasted with the hemitonic ''in'' scale.) Hemitonic pentatonic scales are also called "ditonic scales", because the largest interval in them is the ditone (e.g., in the scale C–E–F–G–B–C, the interval found between C–E and G–B). (This should not be co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Of Somalia
The Music of the Somali people () is music following the musical styles, techniques and sounds of the Somali people. Overview Traditional Somali music Somali people have a rich musical heritage centered on traditional Somali folklore. Somali songs are pentatonic. That is, they only use five pitches per octave in contrast to a heptatonic (seven note) scale such as the major scale. At first listen, Somali music might be mistaken for the sounds of nearby regions such as Oromo in Ethiopia, Sudan or the Arabian peninsula, but it is ultimately recognizable by its own unique tunes and styles. Somali songs are usually the product of collaboration between lyricists (''lahamiste''), songwriters (''abwaan''), and vocalists (''odka'' or "voice").Abdullahi, pp.170-171 The Somali word for dance is ''ciyaar''. Traditional instruments prominently featured in the music of Somaliland include the oud lute (''kaban''). It is often accompanied by small drums and a reed flute in the bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Of Morocco
Moroccan music varies greatly between geographic regions and social groups. It is influenced by musical styles including Arab, Berber, Andalusi, Mediterranean, Saharan, West African, and others. Musical styles vary by geography. Andalusi music and ''malhun'' are associated with urban centers in the north, ''chaabi'' and ''aita'' are associated with the Atlantic coastal plains, '' reggada'' is associated with the Beni-Znassen region ( Oujda, Berkane..), gnawa with Essaouira and Marrakesh, '' ahidus'' with the Middle Atlas, '' ahwash'' with the Sous region, and '' guedra'' in the Sahara. Particularly since the 20th century, musicians have been synthesizing Moroccan musical traditions with influences from around the world, such as blues, rock, metal, reggae, rap, etc. Each genre and musical style is made up of regional subgroups, and is further divided between 'modern' and 'traditional' music. Traditional music styles ''Aita'' Aita ( "call, cry or lament") is a popul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |