|
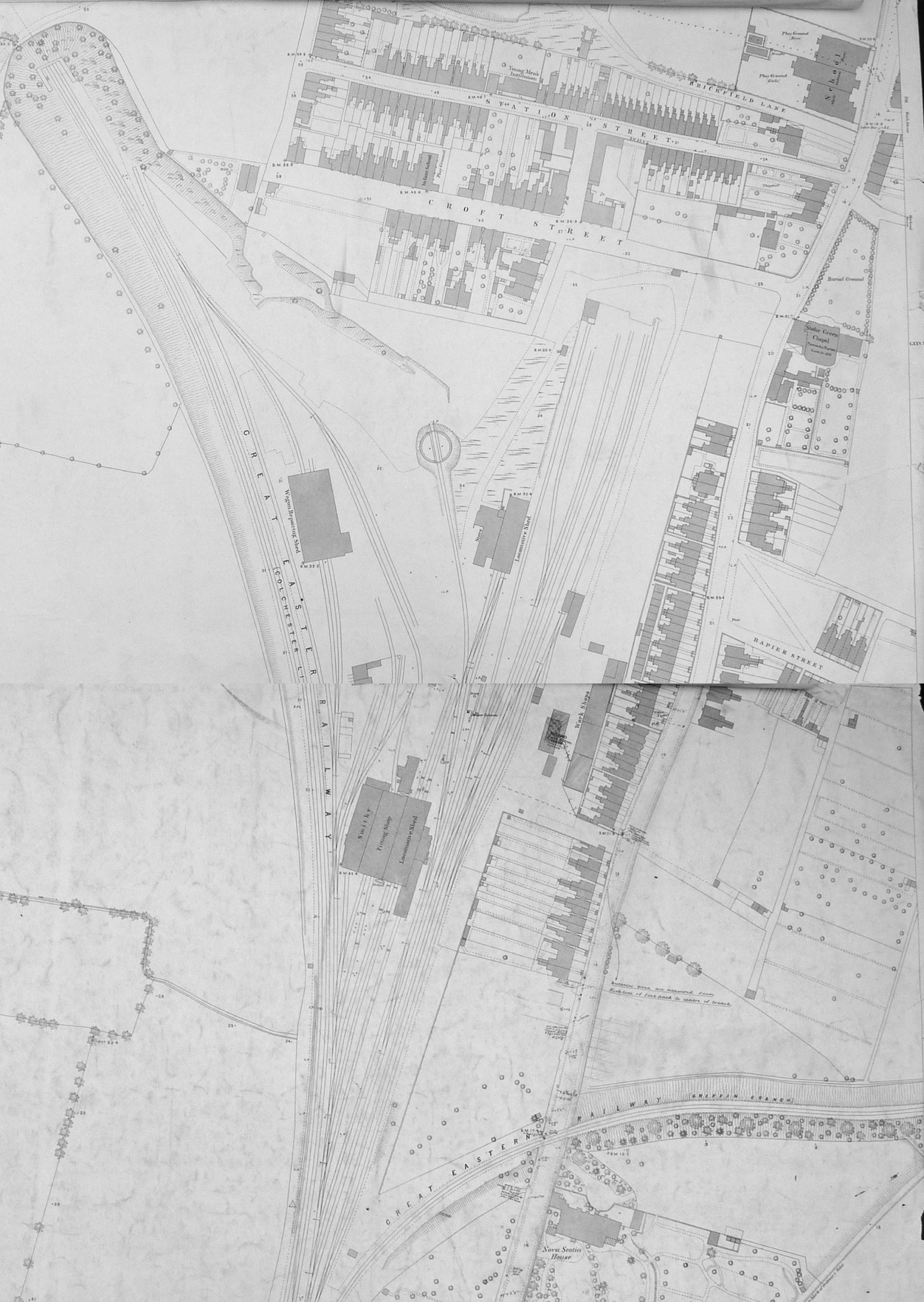
Ipswich Stoke Hill Railway Station
Ipswich Stoke Hill railway station was the northern terminus of the Eastern Union Railway line from Colchester to Ipswich from its opening in June 1846 until 1860 when the present Ipswich station opened at the other end of the Stoke tunnel. It was located in Croft Street, Stoke. Trains from London terminated at the station but from November 1846 when a new line was built by the Ipswich and Bury Railway to Bury St Edmunds trains from Bury used to pass the station, stop at Halifax Junction a short distance to the south and propel back into the terminus usually using the western platform. Trains for Bury would reverse out as far as Halifax Junction before travelling north. The station was designed by Frederick Barnes who also designed a number of other early railway stations and bridges in East Anglia. The EUR and I&BR (who shared many directors, same engineer and secretary) worked as one organisation from January 1847. For more than one hundred and twenty years after the station ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Brett Russell
Frederick Brett Russell (25 June 1813, Walworth – 1 November 1869, Ipswich) was an English architect and artist based in Ipswich, Suffolk. Russell was based at a studio in Berners Street, Ipswich. He is buried in Old Ipswich Cemetery Old Ipswich Cemetery is a cemetery in Ipswich, Suffolk, which was opened in 1855. It is one of a group of cemeteries run by Ipswich Borough Council. History Following the passage of the Burial Act 1854 (17 & 18 Vict c 87), Municipal Borough of .... Architectural career Fredrick was apprenticed to Henry William Inwood. Artistic career Frederick spelt his surname with one "l" for his artistic works. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Russell, Frederick Brett 1813 births 1869 deaths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Bruff
Peter Schuyler Bruff (23 July 1812 – 24 February 1900) was an English civil engineer'Obituary. Peter Schuyler Bruff, 1812-1900', ''Minutes of the Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers'', Volume 141 Part 3, 1900, (January 1900)pp. 339-341(Institution of Civil Engineers, Virtual Library pdf, free access). remembered primarily for his part in establishing the East Anglian railway networks between the 1840s and 1860s. His contribution to the region's infrastructure and development extended far beyond the railways, however, and included the renovation of the Colchester water supply (1851-1880) and the Ipswich sewerage system (completed 1881), the development of the town of Harwich and the Essex resorts of Walton-on-the-Naze and Clacton on Sea (which he built up from an empty piece of farmland into a flourishing seaside town),E.A. Labrum, ''Civil Engineering Heritage'' (T. Telford 1994), p. 282. and (not least) the late Victorian revival of the Coalport porcelain facto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1846 Establishments In England
Events January–March * January 5 – The United States House of Representatives votes to stop sharing the Oregon Country with the United Kingdom. * January 13 – The Milan–Venice railway's bridge, over the Venetian Lagoon between Mestre and Venice in Italy, opens, the world's longest since 1151. * February 4 – Many Mormons begin their migration west from Nauvoo, Illinois, to the Great Salt Lake, led by Brigham Young. * February 10 – First Anglo-Sikh War: Battle of Sobraon – British forces defeat the Sikhs. * February 18 – The Galician slaughter, a peasant revolt, begins. * February 19 – United States president James K. Polk's annexation of the Republic of Texas is finalized by Texas president Anson Jones in a formal ceremony of transfer of sovereignty. The newly formed Texas state government is officially installed in Austin. * February 20– 29 – Kraków uprising: Galician slaughter – Polish nationalists stage an uprising in the Free City of Kraków; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Great Britain Closed In 1860
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer faciliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Great Britain Opened In 1846
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer facilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Great Eastern Railway Stations
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bentley (Suffolk) Railway Station
Bentley railway station, also known as Bentley Junction between 1849 and 1878, was located in Bentley, Suffolk on the Great Eastern Main Line. It opened in 1846 and became a junction in 1847 when the Hadleigh Railway opened. The station was closed in 1966. Description When built the station was half a mile from the village itself although a few buildings, including a pub called the Railway Tavern (opened c1850 closed 1970), grew up around it. The station building was of wooden construction and shared a roof with the goods shed. It was located on the up side of the line and a small waiting room was provided on the downside. The station had two through mainline platforms and an end bay at the country end of the downside platform to handle services on the Hadleigh branch. North of the station there were three tracks for about half a mile as far as the junction where the branch to Hadleigh diverged. The bay platform could accommodate five coaches. When built the junction was a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ipswich Engine Shed
Ipswich engine shed was an engine shed located in Ipswich, Suffolk on the Great Eastern Main Line. It was located just south of Stoke tunnel and the current Ipswich railway station. Locomotives accessed the site from Halifax Junction which was also the junction for the Griffin Wharf branch of Ipswich docks. The depot opened in 1846 and closed in 1968 although the site remained in railway use for a further thirty years. In British Railways days it was allocated the code 32B. History Opening and early years Locomotive activity started on the depot site with the opening of the original Ipswich station located at Croft Street and (presumably the newly named) Station St in June 1846 by the Eastern Union Railway. Locomotives belonging to sister company the Ipswich and Bury Railway would also have used the facilities when their line opened in November 1846 although the two railway companies were worked as one from January the following year. In June 1851 the EUR had 31 locomotive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ipswich
Ipswich () is a port town and borough in Suffolk, England, of which it is the county town. The town is located in East Anglia about away from the mouth of the River Orwell and the North Sea. Ipswich is both on the Great Eastern Main Line railway and the A12 road; it is north-east of London, east-southeast of Cambridge and south of Norwich. Ipswich is surrounded by two Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB): Suffolk Coast and Heaths and Dedham Vale. Ipswich's modern name is derived from the medieval name ''Gippeswic'', probably taken either from an Anglo-Saxon personal name or from an earlier name given to the Orwell Estuary (although possibly unrelated to the name of the River Gipping). It has also been known as ''Gyppewicus'' and ''Yppswyche''. The town has been continuously occupied since the Saxon period, and is contested to be one of the oldest towns in the United Kingdom.Hills, Catherine"England's Oldest Town" Retrieved 2 August 2015. Ipswich was a settleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Barnes (architect)
Frederick Barnes (1814–1898) was a British architect who is best remembered for his work on railway stations in East Anglia. Early life Frederick (sometimes Frederic) Barnes was born in the London Borough of Hackney in 1814, although the exact date is uncertain. Barnes attended Christ's Hospital which was located at Hertford at the time and his father was a teacher at the school. After leaving school he worked in London and was articled to a prominent London architect Sydney Smirke. After that Barnes worked in Liverpool for several years. Career Barnes moved to Ipswich in 1843 to assist his friend, locally-based architect John Medland Clark (1813–1849) on the construction of new Custom House building located in the Ipswich Docks. Medland Clark had won a competition for the design of the building which today is the finest building on Ipswich Waterfront. During the 1840s Barnes was working with two of the nascent East Anglian Railways – the Eastern Union Railway and the I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bury St Edmunds
Bury St Edmunds (), commonly referred to locally as Bury, is a historic market town, market, cathedral town and civil parish in Suffolk, England.OS Explorer map 211: Bury St.Edmunds and Stowmarket Scale: 1:25 000. Publisher:Ordnance Survey – Southampton A2 edition. Publishing Date:2008. Bury St Edmunds Abbey is near the town centre. Bury is the seat of the Diocese of St Edmundsbury and Ipswich of the Church of England, with the episcopal see at St Edmundsbury Cathedral. The town, originally called Beodericsworth, was built on a grid pattern by Abbot Baldwin around 1080. It is known for brewing and malting (Greene King brewery) and for a British Sugar processing factory, where Silver Spoon sugar is produced. The town is the cultural and retail centre for West Suffolk and tourism is a major part of the economy. Etymology The name ''Bury'' is etymologically connected with ''borough'', which has cognates in other Germanic languages such as the German meaning "fortress, castle"; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |