|
Intercalated Disc
Intercalated discs or lines of Eberth are microscopic identifying features of cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle consists of individual heart muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) connected by intercalated discs to work as a single functional syncytium. By contrast, skeletal muscle consists of multinucleated muscle fibers and exhibits no intercalated discs. Intercalated discs support synchronized contraction of cardiac tissue. They occur at the Z line of the sarcomere and can be visualized easily when observing a longitudinal section of the tissue. Structure Intercalated discs are complex structures that connect adjacent cardiac muscle cells. The three types of cell junction recognised as making up an intercalated disc are desmosomes, fascia adherens junctions, and gap junctions. * Fascia adherens are anchoring sites for actin, and connect to the closest sarcomere. * Desmosomes prevent separation during contraction by binding intermediate filaments, anchoring the cell membrane to the interm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. The cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the pericardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium), with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined by intercalated discs, and encased by collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix. Cardiac muscle contracts in a similar manner to skeletal muscle, although with some important differences. Electrical stimulation in the form of a cardiac action potential triggers the release of calcium from the cell's internal calcium store, the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The rise in calcium causes the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermediate Filament
Intermediate filaments (IFs) are cytoskeletal structural components found in the cells of vertebrates, and many invertebrates. Homologues of the IF protein have been noted in an invertebrate, the cephalochordate ''Branchiostoma''. Intermediate filaments are composed of a family of related proteins sharing common structural and sequence features. Initially designated 'intermediate' because their average diameter (10 nm) is between those of narrower microfilaments (actin) and wider myosin filaments found in muscle cells, the diameter of intermediate filaments is now commonly compared to actin microfilaments (7 nm) and microtubules (25 nm). Animal intermediate filaments are subcategorized into six types based on similarities in amino acid sequence and protein structure. Most types are cytoplasmic, but one type, Type V is a nuclear lamin. Unlike microtubules, IF distribution in cells show no good correlation with the distribution of either mitochondria or endopla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
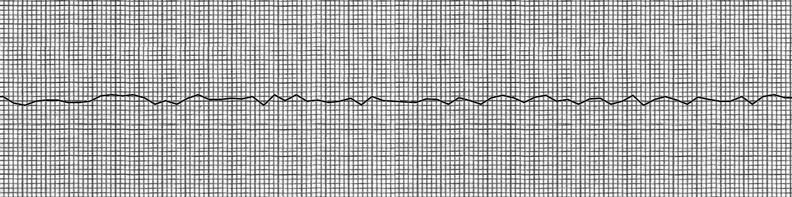
Ventricular Fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib or VF) is an abnormal heart rhythm in which the ventricles of the heart quiver. It is due to disorganized electrical activity. Ventricular fibrillation results in cardiac arrest with loss of consciousness and no pulse. This is followed by sudden cardiac death in the absence of treatment. Ventricular fibrillation is initially found in about 10% of people with cardiac arrest. Ventricular fibrillation can occur due to coronary heart disease, valvular heart disease, cardiomyopathy, Brugada syndrome, long QT syndrome, electric shock, or intracranial hemorrhage. Diagnosis is by an electrocardiogram (ECG) showing irregular unformed QRS complexes without any clear P waves. An important differential diagnosis is torsades de pointes. Treatment is with cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and defibrillation. Biphasic defibrillation may be better than monophasic. The medication epinephrine or amiodarone may be given if initial treatments are not effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Artifact
Visual artifacts (also artefacts) are artifact (error), anomalies apparent during visual representation as in digital graphics and other forms of imagery, especially photography and microscopy. In digital graphics * Image quality#Image quality factors, Image quality factors, different types of visual artifacts * Compression artifacts * Digital artifacts, visual artifacts resulting from digital image processing * Image noise, Noise * Screen-door effect, also known as fixed-pattern noise (FPN), a visual artifact of digital projection technology *Ghosting (television) *Screen burn-in * Distortion * Silk screen effect * Rainbow effect * Screen tearing * Moiré pattern * Color banding In video entertainment Many people who use their computers as a hobby experience artifacting due to a hardware or software malfunction. The cases can differ but the usual causes are: * Temperature issues, such as failure of cooling fan. * Unsuited video card (graphics card) drivers. * Drivers that have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtome
A microtome (from the Greek ''mikros'', meaning "small", and ''temnein'', meaning "to cut") is a cutting tool used to produce extremely thin slices of material known as ''sections''. Important in science, microtomes are used in microscopy, allowing for the preparation of samples for observation under transmitted light or electron radiation. Microtomes use steel, glass or diamond blades depending upon the specimen being sliced and the desired thickness of the sections being cut. Steel blades are used to prepare histological sections of animal or plant tissues for light microscopy. Glass knives are used to slice sections for light microscopy and to slice very thin sections for electron microscopy. Industrial grade diamond knives are used to slice hard materials such as bone, teeth and tough plant matter for both light microscopy and for electron microscopy. Gem-quality diamond knives are also used for slicing thin sections for electron microscopy. Microtomy is a method for the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", and -λογία '' -logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments (as "cell blocks"). Collection of tissues Histopathological examination of tissues starts with surgery, biopsy, or autopsy. The tissue is removed from the body or plant, and then, often following expert dissection in the fresh state, placed in a fixative which stabilizes the tissues to prevent decay. The most common fixative is 10% neutral buffered formalin (corresponding to 3.7% w/v formaldehyde in neutral buffered water, such as phosphate buf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histopathology Of Ruptured Intercalated Discs
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", and -λογία ''-logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments (as "cell blocks"). Collection of tissues Histopathological examination of tissues starts with surgery, biopsy, or autopsy. The tissue is removed from the body or plant, and then, often following expert dissection in the fresh state, placed in a fixative which stabilizes the tissues to prevent decay. The most common fixative is 10% neutral buffered formalin (corresponding to 3.7% w/v formaldehyde in neutral buffered water, such as phosphate buff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath may occur with exertion or while lying down, and may wake people up during the night. Chest pain, including angina, is not usually caused by heart failure, but may occur if the heart failure was caused by a heart attack. The severity of the heart failure is measured by the severity of symptoms during exercise. Other conditions that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver disease, anemia, and thyroid disease. Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excessive alcohol consumption, infection, and cardiomyopathy. These cause heart failure by altering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiomyopathies
Cardiomyopathy is a group of diseases that affect the heart muscle. Early on there may be few or no symptoms. As the disease worsens, shortness of breath, feeling tired, and swelling of the legs may occur, due to the onset of heart failure. An irregular heart beat Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults ... and Syncope (medicine), fainting may occur. Those affected are at an increased risk of sudden cardiac death. Types of cardiomyopathy include hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy, restrictive cardiomyopathy, arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia, and Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (broken heart syndrome). In hypertrophic cardiomyopathy the heart muscle enlarges and thickens. In dilated cardiomyopathy the Ventricle (heart), ventricles enlarge and weaken. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depolarization
In biology, depolarization or hypopolarization is a change within a cell, during which the cell undergoes a shift in electric charge distribution, resulting in less negative charge inside the cell compared to the outside. Depolarization is essential to the function of many cells, communication between cells, and the overall physiology of an organism. Most cells in higher organisms maintain an internal environment that is negatively charged relative to the cell's exterior. This difference in charge is called the cell's membrane potential. In the process of depolarization, the negative internal charge of the cell temporarily becomes more positive (less negative). This shift from a negative to a more positive membrane potential occurs during several processes, including an action potential. During an action potential, the depolarization is so large that the potential difference across the cell membrane briefly reverses polarity, with the inside of the cell becoming positively char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Action Potential
The cardiac action potential is a brief change in voltage ( membrane potential) across the cell membrane of heart cells. This is caused by the movement of charged atoms (called ions) between the inside and outside of the cell, through proteins called ion channels. The cardiac action potential differs from action potentials found in other types of electrically excitable cells, such as nerves. Action potentials also vary within the heart; this is due to the presence of different ion channels in different cells. Unlike the action potential in skeletal muscle cells, the cardiac action potential is not initiated by nervous activity. Instead, it arises from a group of specialized cells known as pacemaker cells, that have automatic action potential generation capability. In healthy hearts, these cells form the cardiac pacemaker and are found in the sinoatrial node in the right atrium. They produce roughly 60–100 action potentials every minute. The action potential passes along t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gap Junctions
Gap junctions are specialized intercellular connections between a multitude of animal cell-types. They directly connect the cytoplasm of two cells, which allows various molecules, ions and electrical impulses to directly pass through a regulated gate between cells. One gap junction channel is composed of two protein hexamers (or hemichannels) called connexons in vertebrates and innexons in invertebrates. The hemichannel pair connect across the intercellular space bridging the gap between two cells. Gap junctions are analogous to the plasmodesmata that join plant cells. Gap junctions occur in virtually all tissues of the body, with the exception of adult fully developed skeletal muscle and mobile cell types such as sperm or erythrocytes. Gap junctions are not found in simpler organisms such as sponges and slime molds. A gap junction may also be called a ''nexus'' or ''macula communicans''. While an ephapse has some similarities to a gap junction, by modern definition the tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |