|
Institut De Recherche D'Hydro-Québec
L'Institut de recherche d'Hydro-Québec ''(Hydro-Québec Research Institute)'', known by its acronym IREQ ("Institut de recherche en électricité du Québec", ''Quebec Electricity Research Institute'') is a research institute established in 1967 by government-owned utility Hydro-Québec. IREQ operates from Varennes, a town on the south shore of Montreal, Quebec, Canada. IREQ operates on an annual research budget of approximately $100 million and specializes in the areas of high voltage, mechanics and thermomechanics, network simulations and calibration. In the last 20 years, the institute has also conducted research and development work towards the electrification of ground transportation. Current projects include battery advanced materials, including work on molten salts, lithium iron phosphate and nanotitanate, improved electric drive trains and the impacts of the large scale deployment of electric vehicles on the power grid. Projects focus on technologies to increase ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Institute
A research institute, research centre, research center or research organization, is an establishment founded for doing research. Research institutes may specialize in basic research or may be oriented to applied research. Although the term often implies natural science research, there are also many research institutes in the social science as well, especially for sociological and historical research purposes. Famous research institutes In the early medieval period, several astronomical observatories were built in the Islamic world. The first of these was the 9th-century Baghdad observatory built during the time of the Abbasid caliph al-Ma'mun, though the most famous were the 13th-century Maragheh observatory, and the 15th-century Ulugh Beg Observatory. The Kerala School of Astronomy and Mathematics was a school of mathematics and astronomy founded by Madhava of Sangamagrama in Kerala, India. The school flourished between the 14th and 16th centuries and the original discoverie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Presse (Canadian Newspaper)
, founded in 1884, is a French-language digital newspaper published daily in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. It is owned by an independent nonprofit trust. ' was formerly a broadsheet daily, considered a newspaper of record in Canada. Its Sunday edition was discontinued in 2009, and the weekday edition in 2016. The weekend Saturday printed edition was discontinued on 31 December 2017, turning ' into an entirely digital newspaper. Audience and sections ' is published on its website, .ca, and its mobile app, . The newspaper targets an educated, middle-class readership. Its main competitors are two Montreal print dailies, the tabloid-format ', which aims at a more populist audience, and the more left-leaning broadsheet . ' comprises several sections, dealing individually with arts, sports, business and economy and other themes. Its Saturday print edition (now discontinued) contained over 10 sections. The newspaper's archives from 2000 to 2019 are available on its website. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Materials Science Institutes
Material is a substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical and chemical properties, or on their geological origin or biological function. Materials science is the study of materials, their properties and their applications. Raw materials can be processed in different ways to influence their properties, by purification, shaping or the introduction of other materials. New materials can be produced from raw materials by synthesis. In industry, materials are inputs to manufacturing processes to produce products or more complex materials. Historical elements Materials chart the history of humanity. The system of the three prehistoric ages (Stone Age, Bronze Age, Iron Age) were succeeded by historical ages: steel age in the 19th century, polymer age in the middle of the following century (plastic age) and silicon age in the second half of the 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineering Research Institutes
Engineering is the use of scientific method, scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more specialized List of engineering branches, fields of engineering, each with a more specific emphasis on particular areas of applied mathematics, applied science, and types of application. See glossary of engineering. The term ''engineering'' is derived from the Latin ''ingenium'', meaning "cleverness" and ''ingeniare'', meaning "to contrive, devise". Definition The American Engineers' Council for Professional Development (ECPD, the predecessor of Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology, ABET) has defined "engineering" as: The creative application of scientific principles to design or develop structures, machines, apparatus, or manufacturing processes, or works utilizing them singly or in combination; or to construct o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Research Institutes
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Institutes In Canada
Research is " creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion on past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, discovery, interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. There are several forms of research: scientific, humanities, artistic, econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokamak
A tokamak (; russian: токамáк; otk, 𐱃𐰸𐰢𐰴, Toḳamaḳ) is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field to confine plasma in the shape of a torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement devices being developed to produce controlled thermonuclear fusion power. , it was the leading candidate for a practical fusion reactor. Tokamaks were initially conceptualized in the 1950s by Soviet physicists Igor Tamm and Andrei Sakharov, inspired by a letter by Oleg Lavrentiev. The first working tokamak was attributed to the work of Natan Yavlinsky on the T-1 in 1958. It had been demonstrated that a stable plasma equilibrium requires magnetic field lines that wind around the torus in a helix. Devices like the z-pinch and stellarator had attempted this, but demonstrated serious instabilities. It was the development of the concept now known as the safety factor (labelled ''q'' in mathematical notation) that guided tokamak development; by arranging the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TM4 Electrodynamic Systems
Dana TM4, previously known as TM4 Inc., is a joint-venture between Dana Incorporated, Dana Corporation and government-owned public utility Hydro-Québec. Established in 1998, it is active in the development of electric vehicle motors and related power systems. After spinning-off from Hydro-Québec's research center to commercialize their electric powertrain technologies, TM4 encountered some success in the 2000s, participating in many short-lived OEM demonstration programs. Commercially, things began to take-off in the 2010s, especially after they diversified their product ranges to serve the commercial vehicle (bus and truck) market. As of 2018, thousands of electric and hybrid vehicles were equipped with TM4 systems. To help TM4 become a global player in the supply of electric drivetrain components, Hydro-Québec, who had been its sole shareholder for most of TM4's existence, announced that it planned to set up a joint-venture with a world-scale auto parts manufacturer to faci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
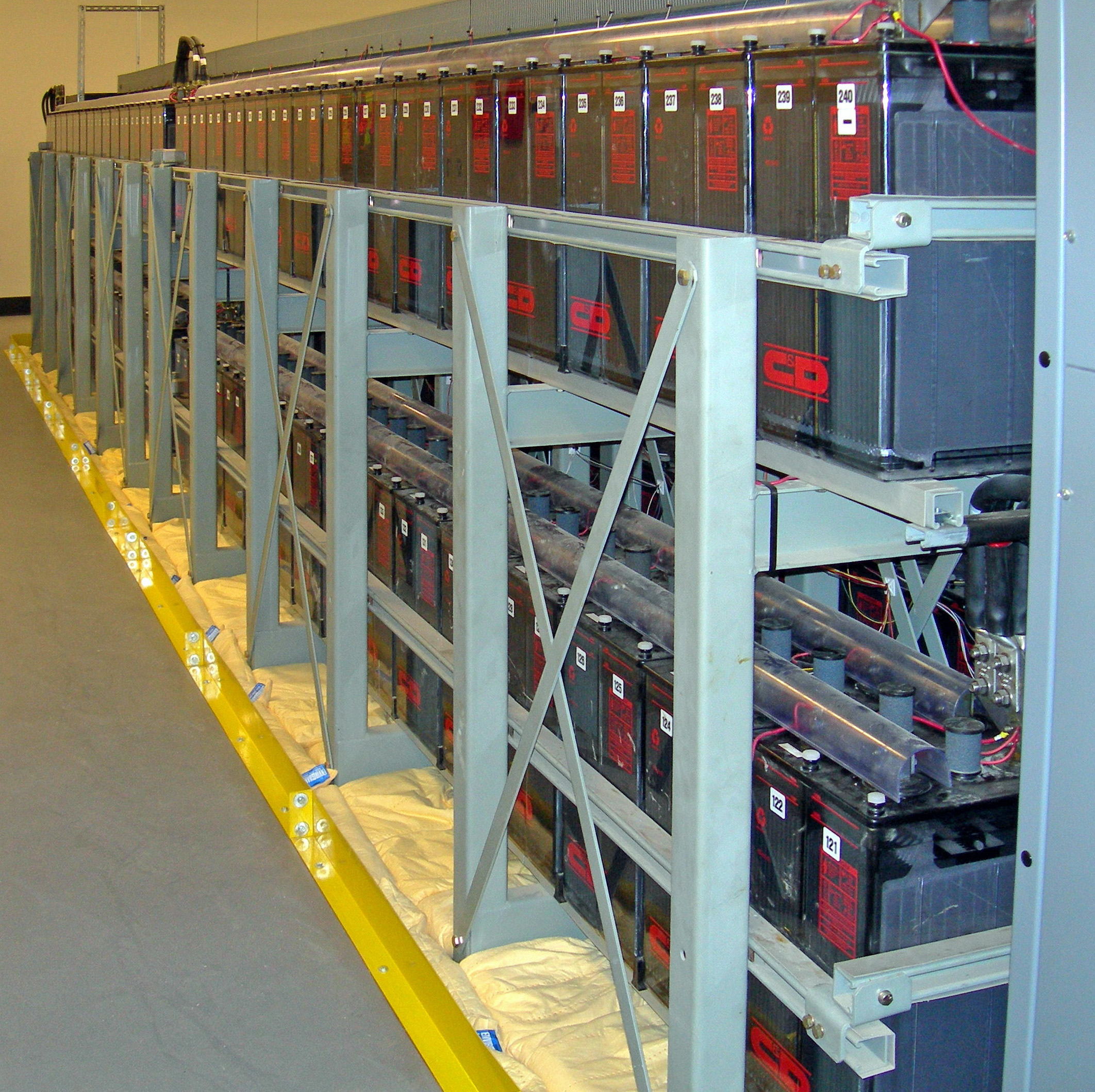
Rechargeable Battery
A rechargeable battery, storage battery, or secondary cell (formally a type of Accumulator (energy), energy accumulator), is a type of electrical battery which can be charged, discharged into a load, and recharged many times, as opposed to a disposable or primary battery, which is supplied fully charged and discarded after use. It is composed of one or more electrochemical cells. The term "accumulator" is used as it accumulator (energy), accumulates and energy storage, stores energy through a reversible electrochemical Chemical reaction, reaction. Rechargeable batteries are produced in many different shapes and sizes, ranging from Button cell#Rechargeable variants, button cells to megawatt systems connected to grid energy storage, stabilize an electrical distribution network. Several different combinations of electrode materials and electrolytes are used, including lead–acid battery, lead–acid, zinc–air battery, zinc–air, nickel–cadmium battery, nickel–cadmium (Ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Range (vehicle)
The maximal total range is the maximum distance an aircraft can fly between takeoff and landing. Powered aircraft range is limited by the aviation fuel energy storage capacity (chemical or electrical) considering both weight and volume limits. Unpowered aircraft range depends on factors such as cross-country speed and environmental conditions. The range can be seen as the cross-country ground speed multiplied by the maximum time in the air. The fuel time limit for powered aircraft is fixed by the available fuel (considering reserve fuel requirements) and rate of consumption. Some aircraft can gain energy while airborne through the environment (e.g. collecting solar energy or through rising air currents from mechanical or thermal lifting) or from in-flight refueling. These aircraft could theoretically have an infinite range. Ferry range means the maximum range that an aircraft engaged in ferry flying can achieve. This usually means maximum fuel load, optionally with extra fuel tan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Grid
An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. It consists of:Kaplan, S. M. (2009). Smart Grid. Electrical Power Transmission: Background and Policy Issues. The Capital.Net, Government Series. Pp. 1-42. * power stations: often located near energy and away from heavily populated areas * electrical substations to step voltage up or down * electric power transmission to carry power long distances * electric power distribution to individual customers, where voltage is stepped down again to the required service voltage(s). Grids are nearly always synchronous, meaning all distribution areas operate with three phase alternating current (AC) frequencies synchronized (so that voltage swings occur at almost the same time). This allows transmission of AC power throughout the area, connecting a large number of electricity generators and consumers and potenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powertrain
A drivetrain (also frequently spelled as drive train or sometimes drive-train) is the group of components that deliver mechanical power from the prime mover to the driven components. In automotive engineering, the drivetrain is the components of a motor vehicle that deliver power to the drive wheels. This excludes the engine or motor that generates the power. In marine applications, the drive shaft will drive a propeller, thruster, or waterjet rather than a drive axle, while the actual engine might be similar to an automotive engine. Other machinery, equipment and vehicles may also use a drivetrain to deliver power from the engine(s) to the driven components. In contrast, the powertrain is considered to include both the engine and/or motor(s) as well as the drivetrain. Function The function of the drivetrain is to couple the engine that produces the power to the driving wheels that use this mechanical power to rotate the axle. This connection involves physically linking the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |