|
Ingo Wegener
Ingo Wegener (December 4, 1950 in Bremen – November 26, 2008 in Bielefeld) was an influential German computer scientist working in the field of theoretical computer science. Education and career Wegener was educated at the Bielefeld University. He earned a diploma in mathematics there in 1976, a doctorate in 1978, and a habilitation in 1981. His doctoral dissertation, ''Boolesche Funktionen, deren monotone Komplexität fast quadratisch ist'', was jointly supervised by and Rudolf Ahlswede. He was a computer science professor at Goethe University Frankfurt from 1980 until 1987, when he moved to the Technical University of Dortmund. He remained at Dortmund until his death. Contributions Wegener's dissertation research concerned circuit complexity, and he was known for his research on Boolean functions and binary decision diagrams. He wrote two books on related topics, ''The Complexity of Boolean Functions'' (Wiley, 1987, also called "the blue book") and ''Branching Programs and Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
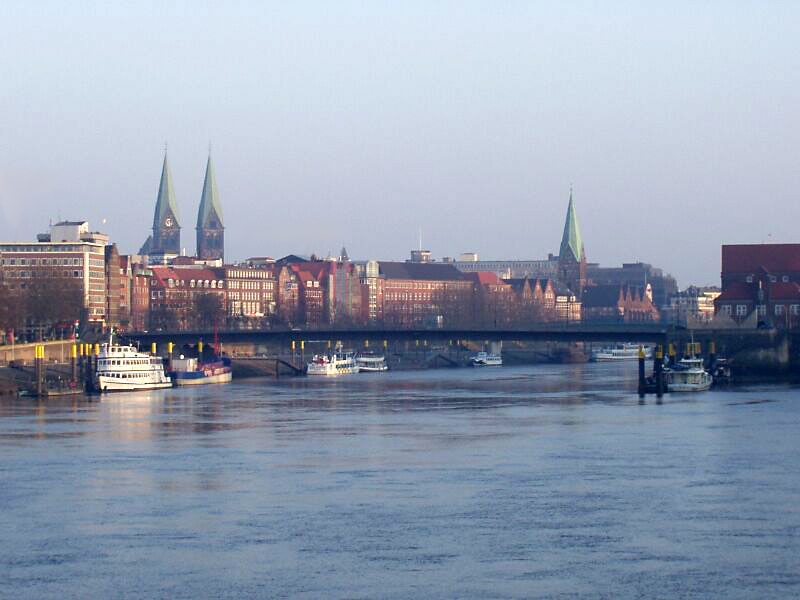
Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the German state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state consisting of the cities of Bremen and Bremerhaven. With about 570,000 inhabitants, the Hanseatic city is the 11th largest city of Germany and the second largest city in Northern Germany after Hamburg. Bremen is the largest city on the River Weser, the longest river flowing entirely in Germany, lying some upstream from its mouth into the North Sea, and is surrounded by the state of Lower Saxony. A commercial and industrial city, Bremen is, together with Oldenburg and Bremerhaven, part of the Bremen/Oldenburg Metropolitan Region, with 2.5 million people. Bremen is contiguous with the Lower Saxon towns of Delmenhorst, Stuhr, Achim, Weyhe, Schwanewede and Lilienthal. There is an exclave of Bremen in Bremerhaven, the "Citybremian Overseas Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaheuristic
In computer science and mathematical optimization, a metaheuristic is a higher-level procedure or heuristic designed to find, generate, or select a heuristic (partial search algorithm) that may provide a sufficiently good solution to an optimization problem, especially with incomplete or imperfect information or limited computation capacity. Metaheuristics sample a subset of solutions which is otherwise too large to be completely enumerated or otherwise explored. Metaheuristics may make relatively few assumptions about the optimization problem being solved and so may be usable for a variety of problems. Compared to optimization algorithms and iterative methods, metaheuristics do not guarantee that a globally optimal solution can be found on some class of problems. Many metaheuristics implement some form of stochastic optimization, so that the solution found is dependent on the set of random variables generated. In combinatorial optimization, by searching over a large set of feas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bielefeld University Alumni
Bielefeld () is a city in the Ostwestfalen-Lippe Region in the north-east of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population of 341,755, it is also the most populous city in the administrative region (''Regierungsbezirk'') of Detmold and the 18th largest city in Germany. The historical centre of the city is situated north of the Teutoburg Forest line of hills, but modern Bielefeld also incorporates boroughs on the opposite side and on the hills. The city is situated on the ', a hiking trail which runs for 156 km along the length of the Teutoburg Forest. Bielefeld is home to a significant number of internationally operating companies, including Dr. Oetker, Gildemeister and Schüco. It has a university and several technical colleges ('' Fachhochschulen''). Bielefeld is also famous for the Bethel Institution, and for the Bielefeld conspiracy, which satirises conspiracy theories by claiming that Bielefeld does not exist. This concept has been used in the town's marketing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2008 Deaths
This is a list of deaths of notable people, organised by year. New deaths articles are added to their respective month (e.g., Deaths in ) and then linked here. 2022 2021 2020 2019 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 1990 1989 1988 1987 See also * Lists of deaths by day The following pages, corresponding to the Gregorian calendar, list the historical events, births, deaths, and holidays and observances of the specified day of the year: Footnotes See also * Leap year * List of calendars * List of non-standard ... * Deaths by year {{DEFAULTSORT:deaths by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Computer Scientists
German(s) may refer to: * Germany (of or related to) **Germania (historical use) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law **Germanic peoples (Roman times) * German language **any of the Germanic languages * German cuisine, traditional foods of Germany People * German (given name) * German (surname) * Germán, a Spanish name Places * German (parish), Isle of Man * German, Albania, or Gërmej * German, Bulgaria * German, Iran * German, North Macedonia * German, New York, U.S. * Agios Germanos, Greece Other uses * German (mythology), a South Slavic mythological being * Germans (band), a Canadian rock band * "German" (song), a 2019 song by No Money Enterprise * ''The German'', a 2008 short film * "The Germans", an episode of ''Fawlty Towers'' * ''The German'', a nickname for Congolese rebel André Kisase Ngandu See also * Germanic (other) * Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1950 Births
Year 195 ( CXCV) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Scrapula and Clemens (or, less frequently, year 948 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 195 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Septimius Severus has the Roman Senate deify the previous emperor Commodus, in an attempt to gain favor with the family of Marcus Aurelius. * King Vologases V and other eastern princes support the claims of Pescennius Niger. The Roman province of Mesopotamia rises in revolt with Parthian support. Severus marches to Mesopotamia to battle the Parthians. * The Roman province of Syria is divided and the role of Antioch is diminished. The Romans annexed the Syrian cities of Edessa and Nisibis. Severus re-establ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Association For Theoretical Computer Science
The European Association for Theoretical Computer Science (EATCS) is an international organization with a European focus, founded in 1972. Its aim is to facilitate the exchange of ideas and results among theoretical computer scientists as well as to stimulate cooperation between the theoretical and the practical community in computer science. The major activities of the EATCS are: * Organization of ICALP, the International Colloquium on Automata, Languages and Programming;Brauer, Ute; Brauer, WilfriedEuropean Association for Theoretical Computer Science / About the Association / Silver Jubilee of EATCS/ref> * Publication of the ''Bulletin of the EATCS''; * Publication of a series of monographs and texts on theoretical computer science; * Publication of the journal ''Theoretical Computer Science''; * Publication of the journal ''Fundamenta Informaticae''. EATCS Award Each year, the EATCS Award is awarded in recognition of a distinguished career in theoretical computer science. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konrad Zuse Medal
The Konrad Zuse Medal for Services to Computer Science is the highest award of the (German Computer Science Society), given every two years to one or sometimes two leading German computer scientists. It is named after German computer pioneer Konrad Zuse.. Note that a different medal with the same name is also given out by the Zentralverband des Deutschen Baugewerbes (Central Association of German Construction). Recipients SourceGesellschaft für Informatik*1987: Heinz Billing *1989: Nikolaus Joachim Lehmann *1989: Robert Piloty *1991: *1993: Carl Adam Petri *1995: Kurt Mehlhorn *1997: José Luis Encarnação *1999: Günter Hotz *2001: Theo Härder *2003: Thomas Lengauer *2006: Ingo Wegener *2007: Manfred Broy *2009: Reinhard Wilhelm. *2011: Fritz-Rudolf Güntsch. *2011: Volker Strassen *2013: Markus Gross *2015: Arndt Bode *2017: Johannes Buchmann *2019: Dorothea Wagner. *2021: Gerhard Weikum See also * List of computer science awards * List of prizes named after people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gesellschaft Für Informatik
The German Informatics Society (GI) (german: Gesellschaft für Informatik) is a German professional society for computer science, with around 20,000 personal and 250 corporate members. It is the biggest organized representation of its kind in the German-speaking world. History The German Informatics Society was founded in Bonn, Germany, on September 16, 1969. Initially aimed primarily at researchers, it expanded in the mid-1970s to include computer science professionals, and in 1978 it founded its journal ''Informatik Spektrum'' to reach this broader audience.. The ''Deutsche Informatik-Akademie'' in Bonn was founded in 1987 by the German Informatics Society in order to provide seminars and continuing education for computer science professionals. In 1990, the German Informatics Society contributed to the founding of the International Conference and Research Center for Computer Science (renamed since as the Leibniz Center for Informatics) at Dagstuhl; since its founding, Schloss D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Computation
In computer science, evolutionary computation is a family of algorithms for global optimization inspired by biological evolution, and the subfield of artificial intelligence and soft computing studying these algorithms. In technical terms, they are a family of population-based trial and error problem solvers with a metaheuristic or stochastic optimization character. In evolutionary computation, an initial set of candidate solutions is generated and iteratively updated. Each new generation is produced by stochastically removing less desired solutions, and introducing small random changes. In biological terminology, a population of solutions is subjected to natural selection (or artificial selection) and mutation. As a result, the population will gradually evolve to increase in fitness, in this case the chosen fitness function of the algorithm. Evolutionary computation techniques can produce highly optimized solutions in a wide range of problem settings, making them popular i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
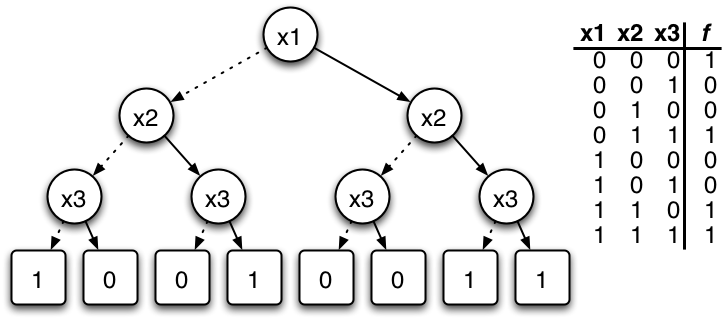
Binary Decision Diagram
In computer science, a binary decision diagram (BDD) or branching program is a data structure that is used to represent a Boolean function. On a more abstract level, BDDs can be considered as a compressed representation of sets or relations. Unlike other compressed representations, operations are performed directly on the compressed representation, i.e. without decompression. Similar data structures include negation normal form (NNF), Zhegalkin polynomials, and propositional directed acyclic graphs (PDAG). Definition A Boolean function can be represented as a rooted, directed, acyclic graph, which consists of several (decision) nodes and two terminal nodes. The two terminal nodes are labeled 0 (FALSE) and 1 (TRUE). Each (decision) node u is labeled by a Boolean variable x_i and has two child nodes called low child and high child. The edge from node u to a low (or high) child represents an assignment of the value FALSE (or TRUE, respectively) to variable x_i. Such a BDD is ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bielefeld
Bielefeld () is a city in the Ostwestfalen-Lippe Region in the north-east of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population of 341,755, it is also the most populous city in the administrative region (''Regierungsbezirk'') of Detmold and the 18th largest city in Germany. The historical centre of the city is situated north of the Teutoburg Forest line of hills, but modern Bielefeld also incorporates boroughs on the opposite side and on the hills. The city is situated on the ', a hiking trail which runs for 156 km along the length of the Teutoburg Forest. Bielefeld is home to a significant number of internationally operating companies, including Dr. Oetker, Gildemeister and Schüco. It has a university and several technical colleges ('' Fachhochschulen''). Bielefeld is also famous for the Bethel Institution, and for the Bielefeld conspiracy, which satirises conspiracy theories by claiming that Bielefeld does not exist. This concept has been used in the town's marketing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |