|
Inducible Plant Defenses Against Herbivory
Plants and herbivores have co-evolved together for 350 million years. Plants have evolved many defense mechanisms against insect herbivory. Such defenses can be broadly classified into two categories: (1) permanent, constitutive defenses, and (2) temporary, inducible defenses.Karban R, Baldwin IT. Induced responses to herbivory. Chicago: Chicago University Press; 1997. Both types are achieved through similar means but differ in that constitutive defenses are present before an herbivore attacks, while induced defenses are activated only when attacks occur. In addition to constitutive defenses, initiation of specific defense responses to herbivory is an important strategy for plant persistence and survival. Benefits of induced defences Inducible defenses allow plants to be phenotypically plastic. This may confer an advantage over constitutive defenses for multiple reasons. First, it may reduce the chance that attacking insects adapt to plant defenses.Karban R, Agrawal AA, Mangel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Co-evolution
In biology, coevolution occurs when two or more species reciprocally affect each other's evolution through the process of natural selection. The term sometimes is used for two traits in the same species affecting each other's evolution, as well as gene-culture coevolution. Charles Darwin mentioned evolutionary interactions between flowering plants and insects in ''On the Origin of Species'' (1859). Although he did not use the word coevolution, he suggested how plants and insects could evolve through reciprocal evolutionary changes. Naturalists in the late 1800s studied other examples of how interactions among species could result in reciprocal evolutionary change. Beginning in the 1940s, plant pathologists developed breeding programs that were examples of human-induced coevolution. Development of new crop plant varieties that were resistant to some diseases favored rapid evolution in pathogen populations to overcome those plant defenses. That, in turn, required the development o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
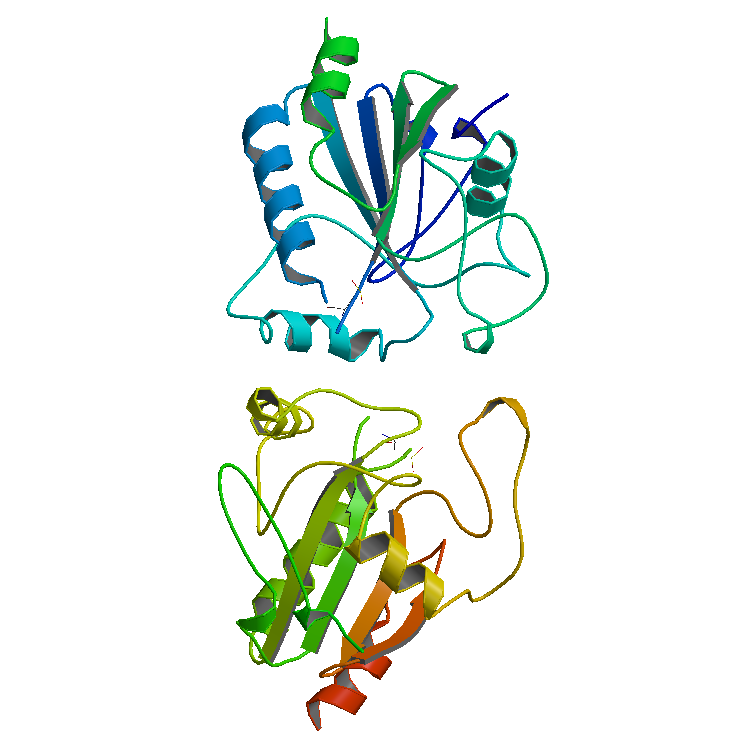
Rubisco
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase, commonly known by the abbreviations RuBisCo, rubisco, RuBPCase, or RuBPco, is an enzyme () involved in the first major step of carbon fixation, a process by which atmospheric carbon dioxide is converted by plants and other photosynthetic organisms to energy-rich molecules such as glucose. In chemical terms, it catalyzes the carboxylation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (also known as RuBP). It is probably the most abundant enzyme on Earth. Alternative carbon fixation pathways RuBisCO is important biologically because it catalyzes the primary chemical reaction by which inorganic carbon enters the biosphere. While many autotrophic bacteria and archaea fix carbon via the reductive acetyl CoA pathway, the 3-hydroxypropionate cycle, or the reverse Krebs cycle, these pathways are relatively small contributors to global carbon fixation compared to that catalyzed by RuBisCO. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, unlike RuBisCO, only tempora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbivory
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthparts adapted to rasping or grinding. Horses and other herbivores have wide flat teeth that are adapted to grinding grass, tree bark, and other tough plant material. A large percentage of herbivores have mutualistic gut flora that help them digest plant matter, which is more difficult to digest than animal prey. This flora is made up of cellulose-digesting protozoans or bacteria. Etymology Herbivore is the anglicized form of a modern Latin coinage, ''herbivora'', cited in Charles Lyell's 1830 ''Principles of Geology''.J.A. Simpson and E.S.C. Weiner, eds. (2000) ''The Oxford English Dictionary'', vol. 8, p. 155. Richard Owen employed the anglicized term in an 1854 work on fossil teeth and skeletons. ''Herbivora'' is derived from Latin ''herba' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Defense (other)
Plant defense may refer to: * Plant defense against herbivory * Inducible plant defenses against herbivory * Plant tolerance to herbivory * Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense * Plant disease resistance * Disease resistance in fruit and vegetables * Secondary metabolite * Hypersensitive response Hypersensitive response (HR) is a mechanism used by plants to prevent the spread of infection by microbial pathogens. HR is characterized by the rapid death of cells in the local region surrounding an infection and it serves to restrict the g ... See also * Protocarnivorous plant {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Tolerance To Herbivory
Tolerance is the ability of plants to mitigate the negative fitness effects caused by herbivory. It is one of the general plant defense strategies against herbivores, the other being resistance, which is the ability of plants to prevent damage (Strauss and Agrawal 1999). Plant defense strategies play important roles in the survival of plants as they are fed upon by many different types of herbivores, especially insects, which may impose negative fitness effects (Strauss and Zangerl 2002). Damage can occur in almost any part of the plants, including the roots, stems, leaves, flowers and seeds (Strauss and Zergerl 2002). In response to herbivory, plants have evolved a wide variety of defense mechanisms and although relatively less studied than resistance strategies, tolerance traits play a major role in plant defense (Strauss and Zergerl 2002, Rosenthal and Kotanen 1995). Traits that confer tolerance are controlled genetically and therefore are heritable traits under selection (Strau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Defense Against Herbivory
Plant defense against herbivory or host-plant resistance (HPR) describes a range of adaptations evolved by plants which improve their survival and reproduction by reducing the impact of herbivores. Plants can sense being touched, and they can use several strategies to defend against damage caused by herbivores. Many plants produce secondary metabolites, known as allelochemicals, that influence the behavior, growth, or survival of herbivores. These chemical defenses can act as repellents or toxins to herbivores or reduce plant digestibility. Another defensive strategy of plants is changing their attractiveness. To prevent overconsumption by large herbivores, plants alter their appearance by changing their size or quality, overall decreasing their consumption rate. Other defensive strategies used by plants include escaping or avoiding herbivores at any time and/or in any place, for example, by growing in a location where plants are not easily found or accessed by herbivores or b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peroxidase
Peroxidases or peroxide reductases ( EC numberbr>1.11.1.x are a large group of enzymes which play a role in various biological processes. They are named after the fact that they commonly break up peroxides. Functionality Peroxidases typically catalyze a reaction of the form: :ROOR' + \overset + 2H+ -> ce + R'OH Optimal substrates For many of these enzymes the optimal substrate is hydrogen peroxide, but others are more active with organic hydroperoxides such as lipid peroxides. Peroxidases can contain a heme cofactor in their active sites, or alternately redox-active cysteine or selenocysteine residues. The nature of the electron donor is very dependent on the structure of the enzyme. * For example, horseradish peroxidase can use a variety of organic compounds as electron donors and acceptors. Horseradish peroxidase has an accessible active site, and many compounds can reach the site of the reaction. * On the other hand, for an enzyme such as cytochrome c peroxidase, the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrophysa Viridula
''Gastrophysa viridula'', known as the green dock beetle (note: the similar '' Gastrophysa cyanea'' in North America is also called the green dock beetle), green dock leaf beetle or green sorrel beetle, is a species of beetle native to Europe. Description The length of the green dock beetle varies between sexes, with the males being 4 mm and the females being 7 mm. During the mating season, females have enlarged abdomens. Both sexes are green with a metallic shimmer, which, depending on the light, can be gold green, blue, purple, violet, or red. The legs of this species also shimmer a metallic green, and are strongly built. The antennae are serrated and are medium in length. Subspecies *''Gastrophysa viridula pennina'' (Weise, 1882) *''Gastrophysa viridula viridula'' (De Geer, 1775) Distribution and habitat The green dock beetle is commonly found in central Europe, also common and widespread in Britain. Its range extends eastward into western Siberia and the Caucasus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rumex Obtusifolius
''Rumex obtusifolius'', commonly known as bitter dock, broad-leaved dock, bluntleaf dock, dock leaf, dockens or butter dock, is a perennial plant in the family Polygonaceae. It is native to Europe, but is found on all temperate continents. It is a highly invasive species in some zones, resulting from its abundant seed dispersal, adaptability to reproduce, aggressive roots, ability to tolerate extreme climates, and hardiness. Etymology The name, ''Rumex obtusifolius'', was assigned by Carl Linnaeus in the 18th century, and has remained unchanged, although there are numerous subspecies. ''Rumex'' was Pliny's name for sorrel,Gledhill, David (2008). "The Names of Plants". Cambridge University Press. (hardback), (paperback). pp 277, 335 while ''obtusifolius'' means 'obtuse-leaved' (obtuse + foliage). Description ''Rumex obtusifolius'' is a perennial herbaceous flowering plant that grows to a height of . It is easily recognizable by its very large oval leaves with cordate base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiosperm plants. Seeds are the product of the ripened ovule, after the embryo sac is fertilized by sperm from pollen, forming a zygote. The embryo within a seed develops from the zygote, and grows within the mother plant to a certain size before growth is halted. The seed coat arises from the integuments of the ovule. Seeds have been an important development in the reproduction and success of vegetable gymnosperm and angiosperm plants, relative to more primitive plants such as ferns, mosses and liverworts, which do not have seeds and use water-dependent means to propagate themselves. Seed plants now dominate biological niches on land, from forests to grasslands both in hot and cold climates Climate is the long-term weather p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaloids
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.Chemical Encyclopedia: alkaloids xumuk.ru Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms including , , [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation tends to exist within any given population as a result of genetic mutation and recombination. Evolution occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection (including sexual selection) and genetic drift act on this variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more common or more rare within a population. The evolutionary pressures that determine whether a characteristic is common or rare within a population constantly change, resulting in a change in heritable characteristics arising over successive generations. It is this process of evolution that has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms, and molecules. The theory of evolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_grazing_-_20050809.jpg)