|
Peroxidase
Peroxidases or peroxide reductases ( EC numberbr>1.11.1.x are a large group of enzymes which play a role in various biological processes. They are named after the fact that they commonly break up peroxides. Functionality Peroxidases typically catalyze a reaction of the form: :ROOR' + \overset + 2H+ -> ce + R'OH Optimal substrates For many of these enzymes the optimal substrate is hydrogen peroxide, but others are more active with organic hydroperoxides such as lipid peroxides. Peroxidases can contain a heme cofactor in their active sites, or alternately redox-active cysteine or selenocysteine residues. The nature of the electron donor is very dependent on the structure of the enzyme. * For example, horseradish peroxidase can use a variety of organic compounds as electron donors and acceptors. Horseradish peroxidase has an accessible active site, and many compounds can reach the site of the reaction. * On the other hand, for an enzyme such as cytochrome c peroxidase, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutathione Peroxidase
Glutathione peroxidase (GPx) () is the general name of an enzyme family with peroxidase activity whose main biological role is to protect the organism from oxidative damage. The biochemical function of glutathione peroxidase is to reduce lipid hydroperoxides to their corresponding alcohols and to reduce free hydrogen peroxide to water. Isozymes Several isozymes are encoded by different genes, which vary in cellular location and substrate specificity. Glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPx1) is the most abundant version, found in the cytoplasm of nearly all mammalian tissues, whose preferred substrate is hydrogen peroxide. Glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPx4) has a high preference for lipid hydroperoxides; it is expressed in nearly every mammalian cell, though at much lower levels. Glutathione peroxidase 2 is an intestinal and extracellular enzyme, while glutathione peroxidase 3 is extracellular, especially abundant in plasma. So far, eight different isoforms of glutathione peroxidase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPX1
Glutathione peroxidase 1, also known as GPx1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''GPX1'' gene on chromosome 3. This gene encodes a member of the glutathione peroxidase family. Glutathione peroxidase functions in the detoxification of hydrogen peroxide, and is one of the most important antioxidant enzymes in humans. Structure This gene encodes a member of the glutathione peroxidase family, consisting of eight known glutathione peroxidases (GPx1-8) in humans. Mammalian Gpx1 (this gene), Gpx2, Gpx3, and Gpx4 have been shown to be selenium-containing enzymes, whereas Gpx6 is a selenoprotein in humans with cysteine-containing homologues in rodents. In selenoproteins, the 21st amino acid selenocysteine is inserted in the nascent polypeptide chain during the process of translational recoding of the UGA stop codon. In addition to the UGA-codon, a cis-acting element in the mRNA, called SECIS, binds SBP2 to recruit other proteins, such as eukaryotic elongation factor seleno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NADH Peroxidase
In enzymology, a NADH peroxidase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :NADH + H+ + H2O2 \rightleftharpoons NAD+ + 2 H2O The presumed function of NADH peroxidase is to inactivate H2O2 generated within the cell, for example by glycerol-3-phosphate oxidase during glycerol metabolism or dismutation of superoxide, before the H2O2 causes damage to essential cellular components. The 3 substrates of this enzyme are NADH, H+, and H2O2, whereas its two products are NAD+ and H2O. It employs one cofactor, FAD, however no discrete FADH2 intermediate has been observed. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on a peroxide as acceptor (peroxidases). The systematic name of this enzyme class is NADH:hydrogen-peroxide oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include DPNH peroxidase, NAD peroxidase, diphosphopyridine nucleotide peroxidase, NADH-peroxidase, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide peroxidase, and NADH2 peroxidase. Structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome C Peroxidase
Cytochrome ''c'' peroxidase, or CCP, is a water-soluble heme-containing enzyme of the peroxidase family that takes reducing equivalents from cytochrome ''c'' and reduces hydrogen peroxide to water: :CCP + H2O2 + 2 ferrocytochrome ''c'' + 2H+ → CCP + 2H2O + 2 ferricytochrome ''c'' CCP can be derived from aerobically grown yeast strains and can be isolated in both native and recombinant forms with high yield from ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae.'' The enzyme’s primary function is to eliminate toxic radical molecules produced by the cell which are harmful to biological systems. It works to maintain low concentration levels of hydrogen peroxide, which is generated by the organism naturally through incomplete oxygen reduction. When glucose levels in fast growing yeast strains are exhausted, the cells turn to respiration which raises the concentration of mitochondrial H2O2. In addition to its peroxidase activity, it acts as a sensor and a signaling molecule to exogenous H2O2, which acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haloperoxidase
Haloperoxidases are peroxidases that are able to mediate the oxidation of halides by hydrogen peroxide. Both halides and hydrogen peroxide are widely available in the environment. The Nernst equation shows that hydrogen peroxide can oxidize chloride (E°= 1.36 V), bromide (E°= 1.09 V) and iodide (E°= 0.536 V) from a thermodynamic perspective under natural conditions, i.e., a temperature range of about 0–30 °C and a pH ranging from about 3 ( humic soil layer) to about 8 (sea water). Fluoride (E°= 2.87 V) cannot be oxidized by hydrogen peroxide. Classification The table shows the classification of haloperoxidases according to the halides whose oxidation they are able to catalyze. The classification of these enzymes by substrate-usability does not necessarily indicate enzyme substrate ''preference.'' For example, although eosinophil peroxidase is ''able'' to oxidize chloride, it preferentially oxidizes bromide. The mammalian haloperoxidases myeloperoxidase (MPO), lac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPX4
Glutathione peroxidase 4, also known as GPX4, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''GPX4'' gene. GPX4 is a phospholipid hydroperoxidase that protects cells against membrane lipid peroxidation. Function The antioxidant enzyme glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) belongs to the family of glutathione peroxidases, which consists of 8 known mammalian isoenzymes (GPX1–8). GPX4 catalyzes the reduction of hydrogen peroxide, organic hydroperoxides, and lipid peroxides at the expense of reduced glutathione and functions in the protection of cells against oxidative stress. The oxidized form of glutathione (glutathione disulfide), which is generated during the reduction of hydroperoxides by GPX4, is recycled by glutathione reductase and NADPH/H+. GPX4 differs from the other GPX family members in terms of its monomeric structure, a less restricted dependence on glutathione as reducing substrate, and the ability to reduce lipid-hydroperoxides inside biological membranes. Inactiva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
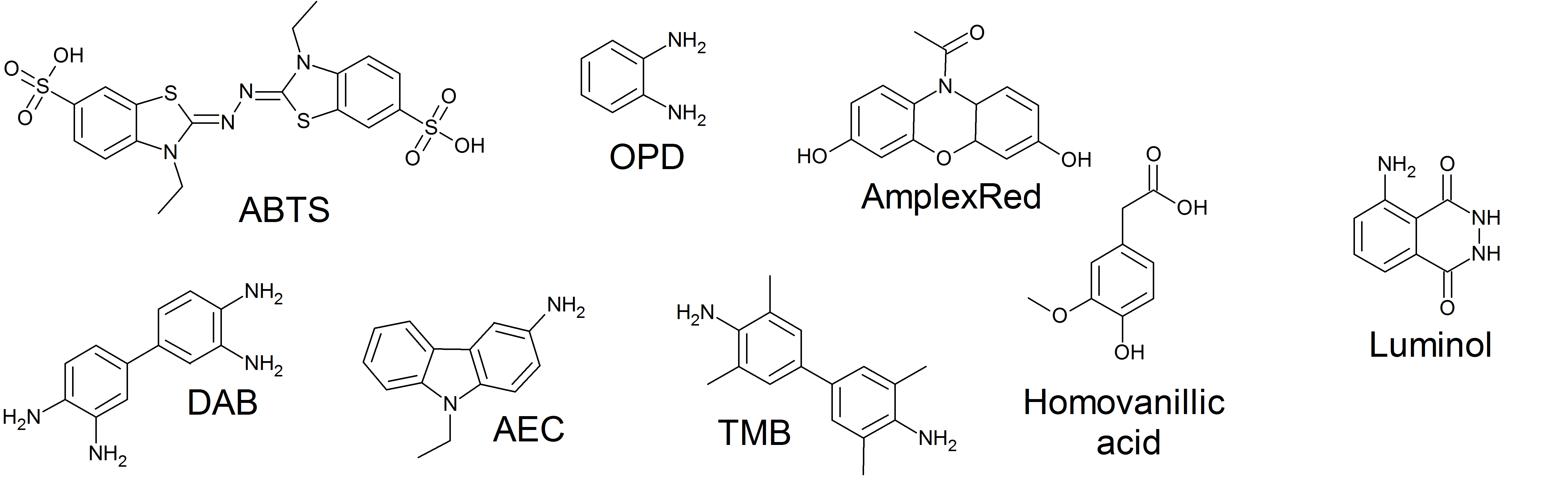
Horseradish Peroxidase
The enzyme horseradish peroxidase (HRP), found in the roots of horseradish, is used extensively in biochemistry applications. It is a metalloenzyme with many isoforms, of which the most studied type is C. It catalyzes the oxidation of various organic substrates by hydrogen peroxide. Structure The structure of the enzyme was first solved by X-ray crystallography in 1997; and has since been solved several times with various substrates. It is a large alpha-helical glycoprotein which binds heme as a redox cofactor. Substrates Alone, the HRP enzyme, or conjugates thereof, is of little value; its presence must be made visible using a substrate that, when oxidized by HRP using hydrogen peroxide as the oxidizing agent, yields a characteristic color change that is detectable by spectrophotometric methods. Numerous substrates for horseradish peroxidase have been described and commercialized to exploit the desirable features of HRP. These substrates fall into several distinct ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DyP-type Peroxidase Family
In molecular biology, the DyP-type peroxidase family is a family of haem peroxidase enzymes. Haem peroxidases were originally divided into two superfamilies, namely, the animal peroxidases and the plant peroxidases (which are subdivided into class I, II and III), which include fungal (class II) and bacterial peroxidases. The DyP (for dye de-colourising peroxidase) family constitutes a novel class of haem peroxidase. Because these enzymes were derived from fungal sources, the DyP family was thought to be structurally related to the class II secretory fungal peroxidases. However, the DyP family exhibits only low sequence similarity to classical fungal peroxidases, such as LiP and MnP, and does not contain the conserved proximal and distal histidines and an essential arginine found in other plant peroxidase superfamily members. DyP proteins have several characteristics that distinguish them from all other peroxidases, including a particularly wide substrate specificity, a lack of hom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadium Bromoperoxidase
Vanadium bromoperoxidases are a kind of enzymes called haloperoxidases. Its primary function is to remove hydrogen peroxide which is produced during photosynthesis from in or around the cell. By producing hypobromous acid (HOBr) a secondary reaction with dissolved organic matter, what results is the bromination of organic compounds that are associated with the defense of the organism. These enzymes produce the bulk of natural organobromine compounds in the world. Vanadium bromoperoxidases are one of the few classes of enzymes that requires vanadium. The active site features a vanadium oxide center attached to the protein via one histidine side chain and a collection of hydrogen bonds to the oxide ligands. Occurrence and function Vanadium bromoperoxidases have been found in bacteria, fungi, marine macro algae (seaweeds), and marine microalgae (diatoms) which produce brominated organic compounds. It has not been definitively identified as the bromoperoxidase of higher eukaryotes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heme
Heme, or haem (pronounced / hi:m/ ), is a precursor to hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver. In biochemical terms, heme is a coordination complex "consisting of an iron ion coordinated to a porphyrin acting as a tetradentate ligand, and to one or two axial ligands." The definition is loose, and many depictions omit the axial ligands. Among the metalloporphyrins deployed by metalloproteins as prosthetic groups, heme is one of the most widely used and defines a family of proteins known as hemoproteins. Hemes are most commonly recognized as components of hemoglobin, the red pigment in blood, but are also found in a number of other biologically important hemoproteins such as myoglobin, cytochromes, catalases, heme peroxidase, and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. The word ''haem'' is derived from Greek ''haima'' meaning "blood". Function Hemoproteins have diverse biological f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haem Peroxidase
Heme, or haem (pronounced / hi:m/ ), is a precursor to hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver. In biochemical terms, heme is a coordination complex "consisting of an iron ion coordinated to a porphyrin acting as a tetradentate ligand, and to one or two axial ligands." The definition is loose, and many depictions omit the axial ligands. Among the metalloporphyrins deployed by metalloproteins as prosthetic groups, heme is one of the most widely used and defines a family of proteins known as hemoproteins. Hemes are most commonly recognized as components of hemoglobin, the red pigment in blood, but are also found in a number of other biologically important hemoproteins such as myoglobin, cytochromes, catalases, heme peroxidase, and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. The word ''haem'' is derived from Greek ''haima'' meaning "blood". Function Hemoproteins have diverse biological function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPX2 (gene)
Glutathione peroxidase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''GPX2'' gene. This gene is a member of the glutathione peroxidase family encoding a selenium-dependent glutathione peroxidase that is one of two isoenzymes responsible for the majority of the glutathione-dependent hydrogen peroxide-reducing activity in the epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract. Studies in knockout mice indicate that mRNA expression levels respond to luminal microflora, suggesting a role of the ileal glutathione peroxidases in preventing inflammation in the GI tract. The antioxidant enzyme glutathione peroxidase 2 (Gpx2) is one out of eight known glutathione peroxidases (Gpx1-8) in humans. Mammalian Gpx1, GPx2 (this protein), Gpx3, and Gpx4 have been shown to be selenium-containing enzymes, whereas Gpx6 is a selenoprotein in humans with cysteine-containing homologues in rodents. In selenoproteins, the 21st amino acid selenocysteine Selenocysteine (symbol Sec or U, in older publications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |