|
Index Of Economics Articles
This aims to be a complete article list of economics topics: A * Absence rate – Accountancy – Accounting reform – Actuary – Adaptive expectations – Adverse selection – Agent (economics) – Agent-based computational economics – Aggregate demand – Aggregate supply – Agricultural policy – Appropriate technology – Arbitrage – Arrow's impossibility theorem – Asymmetric information – Auction – Austrian School – Autarky – Awards B * Backward induction – Balance of payments – Balance of trade – Bank – Bank reserves – Bankruptcy – Barter – Behavioral economics – Bellman equation – Bequest motive – Big Mac Index – Big Push Model – Bioeconomics (biophysical) – Black market – Black–Scholes – Bretton Woods System – Bullionism – Business cycle – Bertrand–Edgeworth model C *Capital (economics) – Capital asset – Capital intensity – Capitalism – Cartel – Cash crop – Catch-up effect – Celti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absence Rate
In economics, the absence rate is the ratio of workers with absences to total full-time wage and salary employment. In the United States, absences are defined as instances when persons who usually work 35 or more hours per week worked less than 35 hours during the reference week for one of the following reasons: own illness, injury, or medical problems; childcare problems; other family or personal obligations; civic or military duty; and maternity or paternity leave. Statistics In 2005, workers in the education and health services sector had the highest absence rate in the private sector at 4.0 percent, while workers in natural resources, construction, and maintenance occupations and in management, professional, and related occupations had the lowest absence rates. See also * Bureau of Labor Statistics * Current Population Survey References External links Absence rate in glossary U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics Division of Information Services The Bureau of Labor Statisti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autarky
Autarky is the characteristic of self-sufficiency, usually applied to societies, communities, states, and their economic systems. Autarky as an ideal or method has been embraced by a wide range of political ideologies and movements, especially left-wing ideologies like African socialism, mutualism, war communism, communalism, swadeshi, syndicalism (especially anarcho-syndicalism), and left-wing populism, generally in an effort to build alternative economic structures or to control resources against structures a particular movement views as hostile. Conservative, centrist and nationalist movements have also adopted autarky in an attempt to preserve part of an existing social order or to develop a particular industry. Proponents of autarky have argued for national self-sufficiency to reduce foreign economic, political and cultural influences, as well as to promote international peace. Economists are generally supportive of free trade. There is a broad consensus among economist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Mac Index
The Big Mac Index is a price index published since 1986 by ''The Economist'' as an informal way of measuring the purchasing power parity (PPP) between two currencies and providing a test of the extent to which market exchange rates result in goods costing the same in different countries. It "seeks to make exchange-rate theory a bit more digestible." The index compares the relative price worldwide to purchase the Big Mac, a hamburger sold at McDonald's restaurants. Overview The Big Mac index was introduced in ''The Economist'' in September 1986 by Pam Woodall as a semi-humorous illustration of PPP and has been published by that paper annually since then. Although the Big Mac Index was not intended to be a legitimate tool for exchange rate evaluation, it is now globally recognised and featured in many academic textbooks and reports. The index also gave rise to the word ''burgernomics.'' The theory underpinning the Big Mac index stems from the concept of PPP, which states th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bequest Motive
{{Short description, Justification for leaving money to others A bequest motive seeks to provide an economic justification for the phenomenon of intergenerational transfers of wealth. In other words, to explain why people leave money behind when they die. Which bequest motive theory most realistically represents the intentions of estate planners is unclear. Attempts to test the theories empirically are mired by poor availability of data about wealth holdings. *The most common explanation for this is altruism, in which it is held that the disponer gains some form of satisfaction from knowing that his/her heirs will enjoy their inherited wealth. An example might be a parent leaving a child the family home. *Another common explanation is accidental bequest, developed by economists Yaari (1965) and Davies (1980). Here it is not assumed that the disponer (testator) gains any specific benefit from leaving a bequest, but rather that lifetime is uncertain, and so she/he holds precautionar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
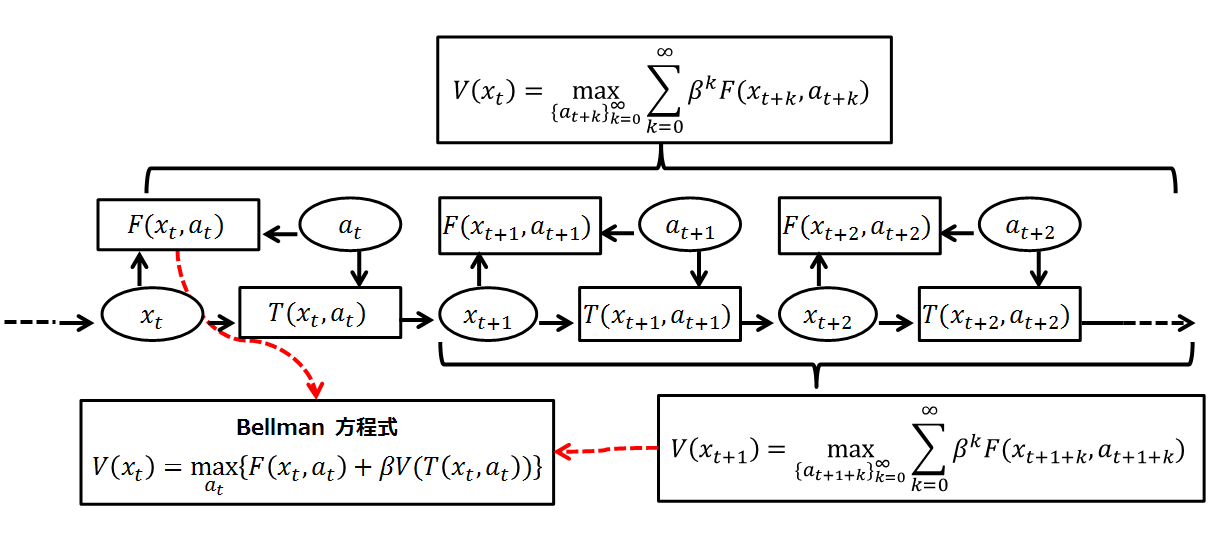
Bellman Equation
A Bellman equation, named after Richard E. Bellman, is a necessary condition for optimality associated with the mathematical optimization method known as dynamic programming. It writes the "value" of a decision problem at a certain point in time in terms of the payoff from some initial choices and the "value" of the remaining decision problem that results from those initial choices. This breaks a dynamic optimization problem into a sequence of simpler subproblems, as Bellman's “principle of optimality" prescribes. The equation applies to algebraic structures with a total ordering; for algebraic structures with a partial ordering, the generic Bellman's equation can be used. The Bellman equation was first applied to engineering control theory and to other topics in applied mathematics, and subsequently became an important tool in economic theory; though the basic concepts of dynamic programming are prefigured in John von Neumann and Oskar Morgenstern's '' Theory of Games and Econ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behavioral Economics
Behavioral economics studies the effects of psychological, cognitive, emotional, cultural and social factors on the decisions of individuals or institutions, such as how those decisions vary from those implied by classical economic theory. Behavioral economics is primarily concerned with the bounds of rationality of economic agents. Behavioral models typically integrate insights from psychology, neuroscience and microeconomic theory. The study of behavioral economics includes how market decisions are made and the mechanisms that drive public opinion. The concepts used in behavioral economics today can be traced back to 18th-century economists, such as Adam Smith, who deliberated how the economic behavior of individuals could be influenced by their desires. The status of behavioral economics as a subfield of economics is a fairly recent development; the breakthroughs that laid the foundation for it were published through the last three decades of the 20th century. Behavio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barter
In trade, barter (derived from ''baretor'') is a system of exchange in which participants in a transaction directly exchange goods or services for other goods or services without using a medium of exchange, such as money. Economists distinguish barter from gift economies in many ways; barter, for example, features immediate reciprocal exchange, not one delayed in time. Barter usually takes place on a bilateral basis, but may be multilateral (if it is mediated through a trade exchange). In most developed countries, barter usually exists parallel to monetary systems only to a very limited extent. Market actors use barter as a replacement for money as the method of exchange in times of monetary crisis, such as when currency becomes unstable (such as hyperinflation or a deflationary spiral) or simply unavailable for conducting commerce. No ethnographic studies have shown that any present or past society has used barter without any other medium of exchange or measurement, and an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bankruptcy
Bankruptcy is a legal process through which people or other entities who cannot repay debts to creditors may seek relief from some or all of their debts. In most jurisdictions, bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the debtor. Bankrupt is not the only legal status that an insolvent person may have, and the term ''bankruptcy'' is therefore not a synonym for insolvency. Etymology The word ''bankruptcy'' is derived from Italian ''banca rotta'', literally meaning "broken bank". The term is often described as having originated in renaissance Italy, where there allegedly existed the tradition of smashing a banker's bench if he defaulted on payment so that the public could see that the banker, the owner of the bench, was no longer in a condition to continue his business, although some dismiss this as a false etymology. History In Ancient Greece, bankruptcy did not exist. If a man owed and he could not pay, he and his wife, children or servants were forced into " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bank Reserves
Bank reserves are a commercial bank's cash holdings physically held by the bank, and deposits held in the bank's account with the central bank. Under the fractional-reserve banking system used in most countries, central banks typically set minimum reserve requirements that require commercial banks under its purview to hold cash or deposits at the central bank equivalent to at least a prescribed percentage of their liabilities, such as customer deposits. Such sums are usually termed required reserves, and any funds above the required amount are called excess reserves. These reserves are prescribed to ensure that, in the normal events, there is sufficient liquidity in the banking system to provide funds to bank customers wishing to withdraw cash. Even when there are no reserve requirements, banks often as a matter of prudent management hold reserves in case of unexpected events, such as unusually large net withdrawals by customers (such as before Christmas) or bank runs. In general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bank
A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital markets. Because banks play an important role in financial stability and the economy of a country, most jurisdictions exercise a high degree of regulation over banks. Most countries have institutionalized a system known as fractional reserve banking, under which banks hold liquid assets equal to only a portion of their current liabilities. In addition to other regulations intended to ensure liquidity, banks are generally subject to minimum capital requirements based on an international set of capital standards, the Basel Accords. Banking in its modern sense evolved in the fourteenth century in the prosperous cities of Renaissance Italy but in many ways functioned as a continuation of ideas and concepts of credit and lending that had their roots in the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balance Of Trade
The balance of trade, commercial balance, or net exports (sometimes symbolized as NX), is the difference between the monetary value of a nation's exports and imports over a certain time period. Sometimes a distinction is made between a balance of trade for goods versus one for services. The balance of trade measures a flow of exports and imports over a given period of time. The notion of the balance of trade does not mean that exports and imports are "in balance" with each other. If a country exports a greater value than it imports, it has a trade surplus or positive trade balance, and conversely, if a country imports a greater value than it exports, it has a trade deficit or negative trade balance. As of 2016, about 60 out of 200 countries have a trade surplus. The notion that bilateral trade deficits are bad in and of themselves is overwhelmingly rejected by trade experts and economists. Explanation The balance of trade forms part of the current account, which includes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)

