|
Impact Of The COVID-19 Pandemic
As of 2022, the COVID‑19 pandemic is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‑19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS CoV‑2). Its impact has been broad, affecting general society, the global economy, culture, ecology, politics, and other areas. These aspects are discussed across many articles: Economic impact * 2020 Russia–Saudi Arabia oil price war * 2020 stock market crash * Charitable activities related to the COVID-19 pandemic ** Moldovan–Romanian collaboration during the COVID-19 pandemic * COVID-19 recession * Financial market impact of the COVID-19 pandemic ** Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on mink farming By country * Economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada * Economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in India ** Indian migrant workers during the COVID-19 pandemic * Economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in the Republic of Ireland ** COVID-19 Pandemic Unemployment Payment ** July Jobs Stim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identified in an outbreak in the Chinese city of Wuhan in December 2019. Attempts to contain it there failed, allowing the virus to spread to other areas of Asia and later worldwide. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the outbreak a public health emergency of international concern on 30 January 2020, and a pandemic on 11 March 2020. As of , the pandemic had caused more than cases and confirmed deaths, making it one of the deadliest in history. COVID-19 symptoms range from undetectable to deadly, but most commonly include fever, dry cough, and fatigue. Severe illness is more likely in elderly patients and those with certain underlying medical conditions. COVID-19 transmits when people breathe in air contaminated by droplets and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Impact Of The COVID-19 Pandemic In Malaysia
The COVID-19 pandemic in Malaysia has had a significant impact on the Malaysian economy, leading to the devaluation of the Malaysian ringgit (MYR) and the decline in the country's gross domestic product. The pandemic also adversely affected several key sectors including entertainment, markets, retail, hospitality, and tourism. Besides shortages in goods and services, many businesses had to cope with social distancing and lockdown restrictions, which affected their operations and revenue.The pandemic also drew attention to workplace safety and the exploitation of migrant workers working in Malaysian industries. Economy Stocks on Malaysia's stock exchange of Bursa Malaysia tumbled during the outbreak as investors sold securities due to the expected economic impact caused by the virus, which along with other emerging stock markets are predicted to remain until June 2020. With China as Malaysia's largest trading partner, the country's economy was directly impacted and economic exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Of The COVID-19 Pandemic On The Restaurant Industry In The United States
The COVID-19 pandemic impacted the United States restaurant industry via government closures, resulting in layoffs of workers and loss of income for restaurants and owners and threatening the survival of independent restaurants as a category. Within a week after the first closures, industry groups representing independent restaurateurs were asking for immediate relief measures from local, state, and federal governments, saying that as many as 75 percent of independent restaurants could not survive closures of more than a few weeks. By late July, nearly 16,000 restaurants had permanently closed. Restaurant closures started March 15 when Ohio Governor Mike DeWine ordered all bars and restaurants in the state to close their dining rooms and bars; within a week most other states followed suit. By March 23, industry experts were estimating nearly half of the industry's 15 million workers had been laid off. Insurers refused to cover the restaurants' financial losses via business interru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Of The COVID-19 Pandemic On The Restaurant Industry
The COVID-19 pandemic affects the global food industry as governments close down restaurants and bars to slow the spread of the virus. Across the world, restaurants' daily traffic dropped precipitously compared to the same period in 2019. Closures of restaurants caused a ripple effect among related industries such as food production, liquor, wine, and beer production, food and beverage shipping, fishing, and farming. The issues were particularly disruptive in industrialized areas where large proportions of entire categories of food are typically imported using just-in-time logistics. In June 2020, the United Nations warned that the world was facing the worst food crisis in half a century due to the recession caused by the pandemic. Global impact Global food security expert Peter Alexander of the University of Edinburgh said that the free-market, just-in-time logistical systems common in industrialized areas are very good at dealing with disruptions in one place or sudden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Of The COVID-19 Pandemic On The Meat Industry In The United States
The meat industry has been severely affected by the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States. Outbreaks of the virus have taken place in factories operated by the meat packing industry and the poultry processing industry. These outbreaks affected dozens of plants, leading to closures of some factories and disruption of others, and posed a significant threat to the meat supply in the United States. By April 27, 2020, there were at least 115 facilities with cases across 23 states, and at least 4,913 workers diagnosed positive with COVID-19, or approximately 3percent of the workforce, with 20 deaths reported. By May 5, 2020, over 10,000 meatpacking plant workers in 29 states and working at 170 plants had tested positive for the coronavirus. At least 45 of those meat industry workers had died. As of May 20, at least 15,300 workers were infected with COVID-19 at 192 different meatpacking plants in the United States, based on ongoing reporting by the Midwest Center for Investigative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Of The COVID-19 Pandemic On The Meat Industry In Canada
During the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada, outbreaks of the virus took place in factories operated by the meat packing industry and the poultry processing industry. These outbreaks affected multiple plants, leading to closures of some factories and disruption of others, and posing a threat to the food supply in Canada. The Cargill beef processing plant in High River, Alberta is the largest workplace outbreak in Canada, and having over 1000 cases linked to the site, it is considered the single largest infection cause in North America. Early response Sometime in late March 2020 several industry groups, among them the Canadian Meat Council which included as regular members Cargill, JBS Foods International and the Alberta Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry, distributed a flyer entitled "Safeguarding the Canadian Meat Supply". The flyer, which stressed the industry's adherence to CFIA regulations, detailed measures which would be taken to do just that: * Symptom monitoring - 4 points ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Of The COVID-19 Pandemic On The Food Industry
The COVID-19 pandemic affects the global food industry as governments close down restaurants and bars to slow the spread of the virus. Across the world, restaurants' daily traffic dropped precipitously compared to the same period in 2019. Closures of restaurants caused a ripple effect among related industries such as food production, liquor, wine, and beer production, food and beverage shipping, fishing, and farming. The issues were particularly disruptive in industrialized areas where large proportions of entire categories of food are typically imported using just-in-time logistics. In June 2020, the United Nations warned that the world was facing the worst food crisis in half a century due to the recession caused by the pandemic. Global impact Global food security expert Peter Alexander of the University of Edinburgh said that the free-market, just-in-time logistical systems common in industrialized areas are very good at dealing with disruptions in one place or sudden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Of The COVID-19 Pandemic On The Cannabis Industry
The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on the cannabis industry. ''Investor's Business Daily'' said the industry was affected as "customers stock up on prescriptions and recreational customers load up on something to make the lockdown a little more mellow or a little less boring". Europe The Netherlands' coffeeshops were initially closed, but later deemed essential businesses. In North Macedonia, construction of Pharmacon's 178,000-square-foot cannabis grow house slowed because of social distancing requirements. In Barcelona, Cannabis Social Clubs – private, non-profit organizations in which cannabis is collectively grown and distributed to registered members – shut their doors following the government's declaration of a state of alarm across the country. According to ''El País'', the price of hashish and cannabis rose to double or triple its usual price on the Spanish black market. Patricia Amiguet, president of the Catalan Federation of Cannabis Associations, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
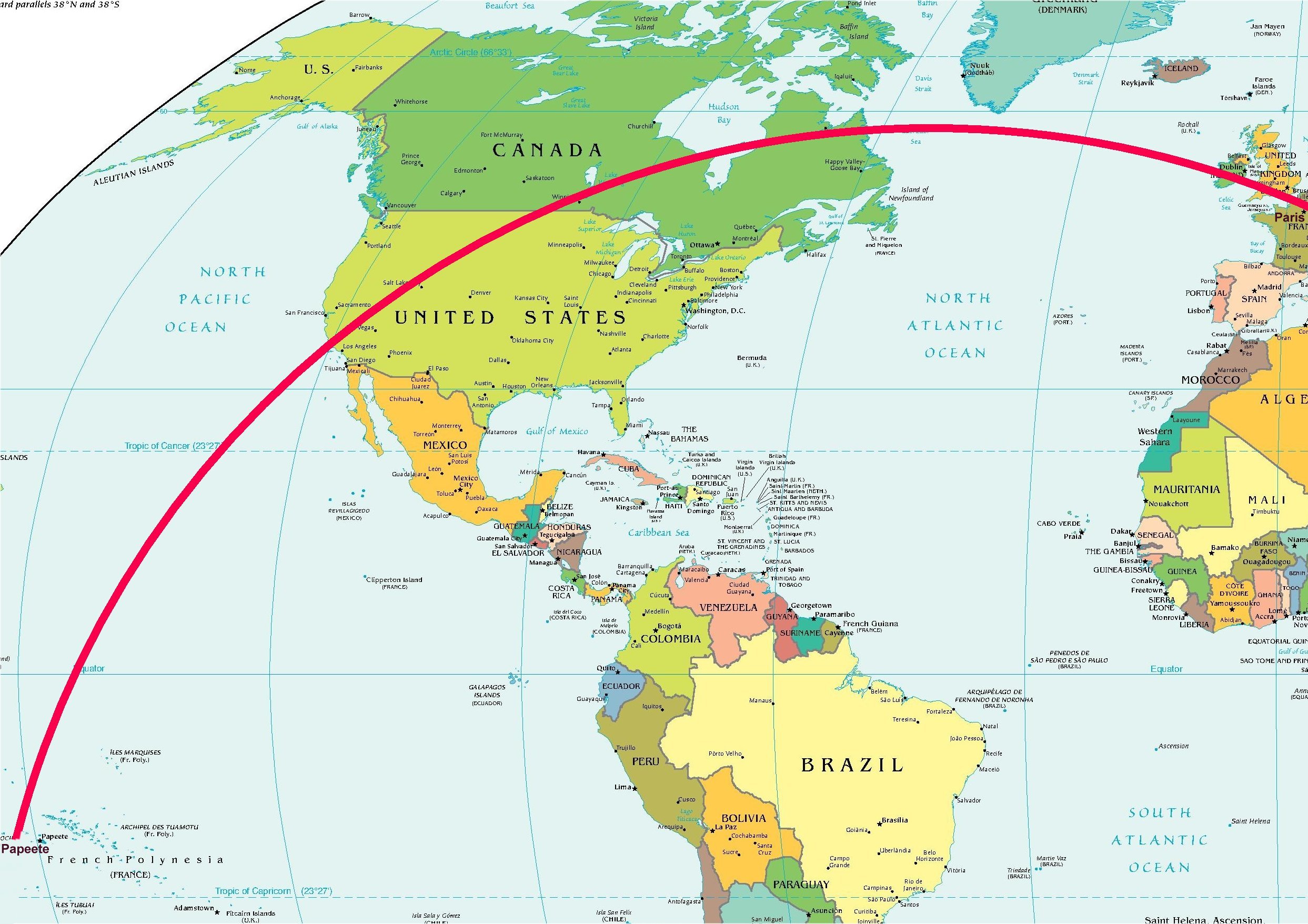
World's Longest Domestic Flight
Air Tahiti Nui Flight 64 (TN64/THT64) was the world's longest domestic flight ever. It was created due to restrictions imposed by the United States over international flights in a context of COVID-19 pandemic. The flight, operated by Air Tahiti Nui, was between Papeete in French Polynesia and Paris in metropolitan France, traversing a distance of and taking 16 hours, 20 minutes. It is considered a domestic flight as French Polynesia forms an integral part of the French Republic. Historical records Longest domestic flight The world's longest commercial domestic flight was flight TN64 operated by Air Tahiti Nui, a French airline based in French Polynesia. The flight operated between Tahiti's Faa'a International Airport near Papeete to Charles de Gaulle Airport near Paris, France. It covered a great-circle distance of taking approximately 16 hours and 20 minutes. With its great-circle distance, it set the record both for world's longest domestic flight as well as the world's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Of The COVID-19 Pandemic On Airlines
Mirroring its impact on aviation, the COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on airline companies due to travel restrictions and a slump in demand among travelers. Several airlines have declared bankruptcy, with some ceasing operations, while other airlines reported historic reductions in flights, as well as accelerating retirements of certain aircraft types, such as the Airbus A340, Airbus A380, or the Boeing 747. By 8 October 2020, 43 commercial airlines had gone bankrupt, and many more were expected to follow. In late October 2020, ACI Europe stated that 193 (mostly regional) of the 740 airports in Europe were also risking bankruptcy. Bankruptcies * On 11 February 2020, Air Italy ceased operating. This decision was made following the shareholders' meeting of Air Italy (Alisarda and Qatar Airways through AQA Holdings spa). According to the airline, its flights were operated by other carriers according to the original schedule between 11 and 25 February. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Of The COVID-19 Pandemic On Aviation
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the airline industry due to travel restrictions and a decimation in demand among travelers. Significant reductions in passenger numbers have resulted in flights being cancelled or planes flying empty between airports, which in turn massively reduced revenues for airlines and forced many airlines to lay off employees or declare bankruptcy. Some have attempted to avoid refunding cancelled trips to diminish their losses. Airliner manufacturers and airport operators have also laid off employees. Only several months into the pandemic, the crisis was already the worst in the aviation industry's history, according to statements made in early 2020 by Airbus' Guillaume Faury, EasyJet's Johan Lundgren, United Airlines' Oscar Munoz, Qantas' Alan Joyce, and media outlets: the ''Financial Times'', ''The New York Times'', and ''The Independent''. Flight cancellations Government regulations in Europe and the United States mandated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
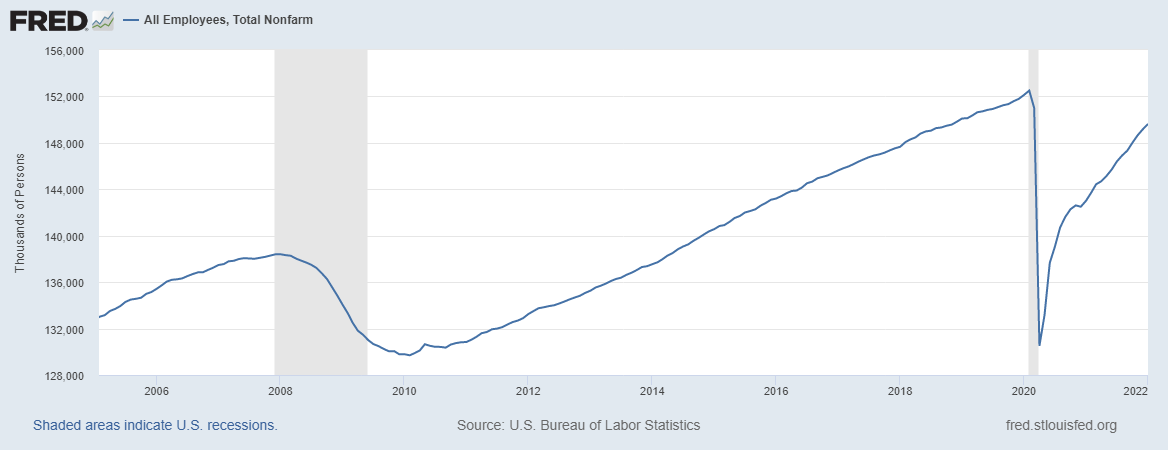
Economic Impact Of The COVID-19 Pandemic In The United States
The economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States has been widely disruptive, adversely affecting travel, financial markets, employment, shipping, and other industries. The impacts can be attributed not just to government intervention to contain the virus (including at the Federal and State level), but also to consumer and business behavior to reduce exposure to and spread of the virus. Real GDP contracted in 2020 by 3.5%, the first contraction since the 2008 Financial Crisis. Millions of workers were dislocated from their jobs, leading to multiple weeks of record shattering numbers of unemployment insurance applications. Consumer and retail activity contracted, with many businesses (especially restaurants) closing. Many businesses and offices transitioned to remote work to avoid the spread of COVID-19 at the office. Congress passed several pieces of legislation, such as the American Rescue Plan Act of 2021 to provide stimulus to mitigate the effect of workplace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)