|
ISCOM
Immune stimulating complexes (ISCOMs) are spherical open cage-like structures (typically 40 nm in diameter) that are spontaneously formed when mixing together cholesterol, phospholipids and Quillaja saponins under a specific stoichiometry. The complex displays immune stimulating properties and is thus mainly used as a vaccine adjuvant in order to induce a stronger immune response and longer protection. History ISCOM technology was invented in 1982 by Professor Bror Morein at the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences in Uppsala. The key components of ISCOMs are the Quillaja saponins, which are derived from the bark of the Chilean soap-bark tree Quillaja saponaria Molina. Quillaja saponins are well known for their ability to activate the immune system. It is also known that saponins in general can have toxic side-effects, including the induction of haemolysis. However, when Quillaia saponins, cholesterol and phospholipids are mixed under the specific stoichiometry that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or Antigen, killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins. The agent stimulates the body's immune system to recognize the agent as a threat, destroy it, and to further recognize and destroy any of the microorganisms associated with that agent that it may encounter in the future. Vaccines can be prophylaxis, prophylactic (to prevent or ameliorate the effects of a future infection by a natural or "wild" pathogen), or therapeutic vaccines, therapeutic (to fight a disease that has already occurred, such as cancer vaccine, cancer). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix-M
Matrix-M adjuvant is a saponin-based adjuvant, which stimulates humoral and cellular immune responses to vaccines. It was patented in 2020 by Novavax. It is composed of nanoparticles from saponins extracted from ''Quillaja saponaria'' (soapbark) trees, cholesterol, and phospholipids. It is an immune stimulating complex (ISCOM), which are nanospheres formed when saponin is mixed with two types of fats. Adjuvants increase the body's immune response to a vaccine by creating higher levels of antibodies. They can either enhance, modulate, and/or prolong the body's immune response, reducing the number of vaccinations needed for immunization. The Matrix-M adjuvant is used in a number of vaccine candidates, including the malaria vaccine R21/Matrix-M, influenza vaccines, and in the approved Novavax COVID-19 vaccine. In 2021, the R21/Matrix-M vaccine candidate showed a 77% efficacy over a 12-month period. In influenza vaccine candidates, Matrix-M was shown to offer cross-protection against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
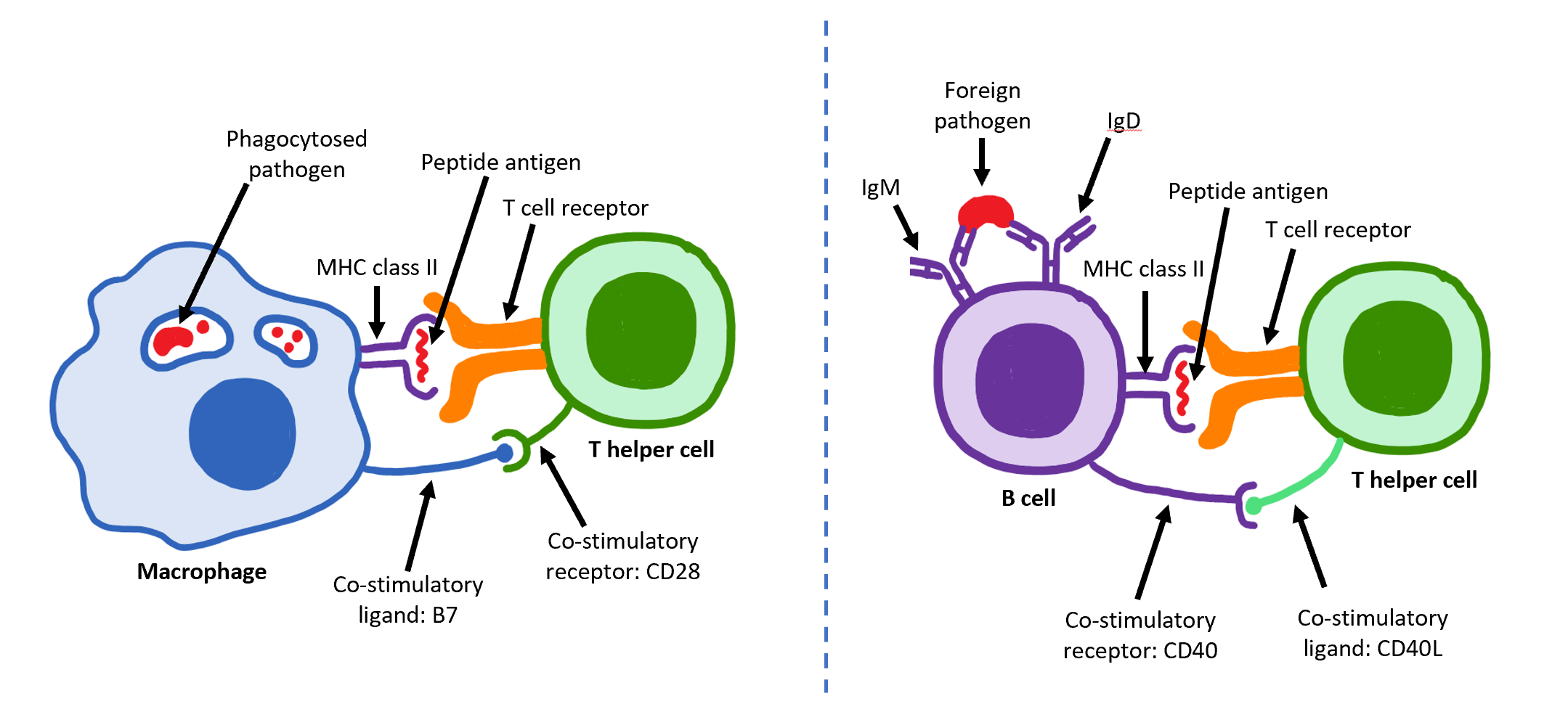
T Helper Cell
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considered essential in B cell antibody class switching, breaking cross-tolerance in dendritic cells, in the activation and growth of cytotoxic T cells, and in maximizing bactericidal activity of phagocytes such as macrophages and neutrophils. CD4+ cells are mature Th cells that express the surface protein CD4. Genetic variation in regulatory elements expressed by CD4+ cells determines susceptibility to a broad class of autoimmune diseases. Structure and function Th cells contain and release cytokines to aid other immune cells. Cytokines are small protein mediators that alter the behavior of target cells that express receptors for those cytokines. These cells help polarize the immune response depending on the nature of the immunological insult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating the body's adaptive immunity, they help prevent sickness from an infectious disease. When a sufficiently large percentage of a population has been vaccinated, herd immunity results. Herd immunity protects those who may be immunocompromised and cannot get a vaccine because even a weakened version would harm them. The effectiveness of vaccination has been widely studied and verified. Vaccination is the most effective method of preventing infectious diseases; widespread immunity due to vaccination is largely responsible for the worldwide eradication of smallpox and the elimination of diseases such as polio and tetanus from much of the world. However, some diseases, such as measles outbreaks in America, have seen rising cases due to relative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virosomes
A virosome is a drug or vaccine delivery mechanism consisting of unilamellar phospholipid membrane (either a mono- or bi-layer) vesicle incorporating virus derived proteins to allow the virosomes to fuse with target cells. Viruses are infectious agents that can replicate in their host organism, however virosomes do not replicate. The properties that virosomes share with viruses are based on their structure; virosomes are essentially safely modified viral envelopes that contain the phospholipid membrane and surface glycoproteins. As a drug or vaccine delivery mechanism they are biologically compatible with many host organisms and are also biodegradable. The use of reconstituted virally derived proteins in the formation of the virosome allows for the utilization of what would otherwise be the immunogenic properties of a live-attenuated virus, but is instead a safely killed virus. A safely killed virus can serve as a promising vector because it won't cause infection and the viral str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inoculation
Inoculation is the act of implanting a pathogen or other microorganism. It may refer to methods of artificially inducing immunity against various infectious diseases, or it may be used to describe the spreading of disease, as in "self-inoculation," the spreading of disease from one part of the body to another, or even to the spreading of bacteria in a Petri dish for culturing purposes. The terms "inoculation", "vaccination", and "immunization" are often used synonymously, but there are some important differences among them. Inoculation is the act of implanting a disease inside a person or animal, vaccination is the act of implanting or giving someone a vaccine specifically, and immunization is what happens to the immune system as a result. Terminology Until the early 1800s inoculation referred only to variolation (from the Latin word ''variola'' = smallpox), the predecessor to the smallpox vaccine. The smallpox vaccine, introduced by Edward Jenner in 1796, was called cowpox inoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunization
Immunization, or immunisation, is the process by which an individual's immune system becomes fortified against an infectious agent (known as the immunogen). When this system is exposed to molecules that are foreign to the body, called ''non-self'', it will orchestrate an immune response, and it will also develop the ability to quickly respond to a subsequent encounter because of immunological memory. This is a function of the adaptive immune system. Therefore, by exposing a human, or an animal, to an immunogen in a controlled way, its body can learn to protect itself: this is called active immunization. The most important elements of the immune system that are improved by immunization are the T cells, B cells, and the antibodies B cells produce. Memory B cells and memory T cells are responsible for a swift response to a second encounter with a foreign molecule. Passive immunization is direct introduction of these elements into the body, instead of production of these elements b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunology
Immunology is a branch of medicineImmunology for Medical Students, Roderick Nairn, Matthew Helbert, Mosby, 2007 and biology that covers the medical study of immune systems in humans, animals, plants and sapient species. In such we can see there is a difference of human immunology and comparative immunology in veterinary medicine and animal biosciences. Immunology measures, uses charts and differentiate in context in medicine the studies of immunity on cell and molecular level, and the immune system as part of the physiological level as its functioning is of major importance. In the different states of both health, occurring symptoms and diseases; the functioning of the immune system and immunological responses such as autoimmune diseases, allergic hypersensitivities, or in some cases malfunctioning of immune system as for example in immunological disorders or in immune deficiency, and the specific transplant rejection) Immunology has applications in numerous disciplines of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune System
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use molecules and cells to perform their functions. Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of enzymes that protect against virus infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient plants and animals and remain in their modern descendants. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunologic Adjuvant
In immunology, an adjuvant is a substance that increases or modulates the immune response to a vaccine. The word "adjuvant" comes from the Latin word ''adiuvare'', meaning to help or aid. "An immunologic adjuvant is defined as any substance that acts to accelerate, prolong, or enhance antigen-specific immune responses when used in combination with specific vaccine antigens." In the early days of vaccine manufacture, significant variations in the efficacy of different batches of the same vaccine were correctly assumed to be caused by contamination of the reaction vessels. However, it was soon found that more scrupulous cleaning actually seemed to ''reduce'' the effectiveness of the vaccines, and some contaminants actually enhanced the immune response. There are many known adjuvants in widespread use, including aluminium salts, oils and virosomes. Overview Adjuvants in immunology are often used to modify or augment the effects of a vaccine by stimulating the immune system to re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Stability
In chemistry, chemical stability is the thermodynamic stability of a chemical system. Thermodynamic stability occurs when a system is in its lowest energy state, or in chemical equilibrium with its environment. This may be a dynamic equilibrium in which individual atoms or molecules change form, but their overall number in a particular form is conserved. This type of chemical thermodynamic equilibrium will persist indefinitely unless the system is changed. Chemical systems might undergo changes in the phase of matter or a set of chemical reactions. State A is said to be more thermodynamically stable than state B if the Gibbs free energy of the change from A to B is positive. Versus reactivity Thermodynamic stability applies to a particular system. The reactivity of a chemical substance is a description of how it might react across a variety of potential chemical systems and, for a given system, how fast such a reaction could proceed. Chemical substances or states can persis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |