|
IEEE 1076
The VHSIC Hardware Description Language (VHDL) is a hardware description language (HDL) that can model the behavior and structure of digital systems at multiple levels of abstraction, ranging from the system level down to that of logic gates, for design entry, documentation, and verification purposes. Since 1987, VHDL has been standardized by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) as IEEE Std 1076; the latest version of which is IEEE Std 1076-2019. To model analog and mixed-signal systems, an IEEE-standardized HDL based on VHDL called VHDL-AMS (officially IEEE 1076.1) has been developed. VHDL is named after the United States Department of Defense program that created it, the Very High-Speed Integrated Circuits Program (VHSIC). In the early 1980s, the VHSIC Program sought a new HDL for use in the design of the integrated circuits it aimed to develop. The product of this effort was VHDL Version 7.2, released in 1985. The eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concurrent Computing
Concurrent computing is a form of computing in which several computations are executed '' concurrently''—during overlapping time periods—instead of ''sequentially—''with one completing before the next starts. This is a property of a system—whether a program, computer, or a network—where there is a separate execution point or "thread of control" for each process. A ''concurrent system'' is one where a computation can advance without waiting for all other computations to complete. Concurrent computing is a form of modular programming. In its paradigm an overall computation is factored into subcomputations that may be executed concurrently. Pioneers in the field of concurrent computing include Edsger Dijkstra, Per Brinch Hansen, and C.A.R. Hoare. Introduction The concept of concurrent computing is frequently confused with the related but distinct concept of parallel computing, Pike, Rob (2012-01-11). "Concurrency is not Parallelism". ''Waza conference'', 11 January ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuits
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) integrate into a small chip. This results in circuits that are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete electronic components. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design has ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discrete transistors. ICs are now used in virtually all electronic equipment and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones and other home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the small size and low cost of ICs such as modern compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drive Strength
Drive or The Drive may refer to: Motoring * Driving, the act of controlling a vehicle * Road trip, a journey on roads Roadways Roadways called "drives" may include: * Driveway, a private road for local access to structures, abbreviated "drive" * Road, an identifiable thoroughfare, route, way, or path between two places Science * Drive theory, a diverse set of motivational theories in psychology * Drive reduction theory (learning theory), a theory of learning and motivation * Prey drive, in the study of animal behavior, the predictable tendency of a carnivore to pursue and capture prey * Gene drive, in genetics, a type of bias in the inheritance of a gene Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Drive'' (1997 film), an action film starring Mark Dacascos * ''Drive'' (2002 film), a Japanese film starring Ren Osugi * ''Drive'' (2011 film), an American crime drama film starring Ryan Gosling * ''Drive'' (2019 film), an Indian romantic drama film Literature * '' Drive: The Story ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
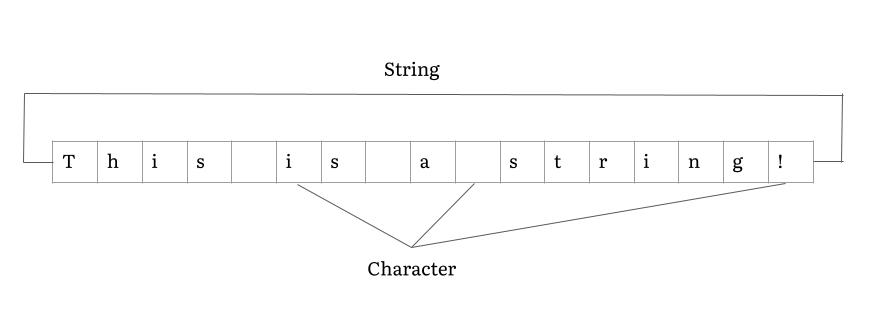
String (computer Science)
In computer programming, a string is traditionally a sequence of characters, either as a literal constant or as some kind of variable. The latter may allow its elements to be mutated and the length changed, or it may be fixed (after creation). A string is generally considered as a data type and is often implemented as an array data structure of bytes (or words) that stores a sequence of elements, typically characters, using some character encoding. ''String'' may also denote more general arrays or other sequence (or list) data types and structures. Depending on the programming language and precise data type used, a variable declared to be a string may either cause storage in memory to be statically allocated for a predetermined maximum length or employ dynamic allocation to allow it to hold a variable number of elements. When a string appears literally in source code, it is known as a string literal or an anonymous string. In formal languages, which are used in mathematical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Array Data Type
In computer science, array is a data type that represents a collection of ''elements'' (value (computer science), values or variable (computer science), variables), each selected by one or more indices (identifying keys) that can be computed at Run time (program lifecycle phase), run time during program execution. Such a collection is usually called an array variable or array value.Robert W. Sebesta (2001) ''Concepts of Programming Languages''. Addison-Wesley. 4th edition (1998), 5th edition (2001), By analogy with the mathematical concepts vector (mathematics), vector and matrix (mathematics), matrix, array types with one and two indices are often called vector type and matrix type, respectively. More generally, a multidimensional array type can be called a tensor type, by anology with the physical concept, tensor. Language support for array types may include certain built-in type, built-in array data types, some syntactic constructions (''array type constructors'') that the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, to compare the duration of events or the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change of quantities in material reality or in the conscious experience. Time is often referred to as a fourth dimension, along with three spatial dimensions. Time has long been an important subject of study in religion, philosophy, and science, but defining it in a manner applicable to all fields without circularity has consistently eluded scholars. Nevertheless, diverse fields such as business, industry, sports, the sciences, and the performing arts all incorporate some notion of time into their respective measuring systems. 108 pages. Time in physics is operationally defined as "what a clock reads". The physical nature of time is addre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Character (computing)
In computer and machine-based telecommunications terminology, a character is a unit of information that roughly corresponds to a grapheme, grapheme-like unit, or symbol, such as in an alphabet or syllabary in the written form of a natural language. Examples of characters include letters, numerical digits, common punctuation marks (such as "." or "-"), and whitespace. The concept also includes control characters, which do not correspond to visible symbols but rather to instructions to format or process the text. Examples of control characters include carriage return and tab as well as other instructions to printers or other devices that display or otherwise process text. Characters are typically combined into strings. Historically, the term ''character'' was used to denote a specific number of contiguous bits. While a character is most commonly assumed to refer to 8 bits (one byte) today, other options like the 6-bit character code were once popular, and the 5-bit Baudot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boolean Datatype
In computer science, the Boolean (sometimes shortened to Bool) is a data type that has one of two possible values (usually denoted ''true'' and ''false'') which is intended to represent the two truth values of logic and Boolean algebra. It is named after George Boole, who first defined an algebraic system of logic in the mid 19th century. The Boolean data type is primarily associated with conditional statements, which allow different actions by changing control flow depending on whether a programmer-specified Boolean ''condition'' evaluates to true or false. It is a special case of a more general ''logical data type—''logic does not always need to be Boolean (see probabilistic logic). Generalities In programming languages with a built-in Boolean data type, such as Pascal and Java, the comparison operators such as > and ≠ are usually defined to return a Boolean value. Conditional and iterative commands may be defined to test Boolean-valued expressions. Languages with no exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Data Type
A real data type is a data type used in a computer program to represent an approximation of a real number. Because the real numbers are not Countable set, countable, computers cannot represent them exactly using a finite amount of information. Most often, a computer will use a rational number, rational approximation to a real number. Rational numbers The most general data type for a rational number stores the numerator and denominator as Integer (computer science), integers. Fixed-point numbers A fixed-point data type uses the same denominator for all numbers. The denominator is usually a power of two. For example, in a fixed-point system that uses the denominator 65,536 (216), the hexadecimal number 0x12345678 means 0x12345678/65536 or 305419896/65536 or 4660 + 22136/65536 or about 4660.33777. Floating-point numbers A floating-point data type is a compromise between the flexibility of a general rational number data type and the speed of fixed-point arithmetic. It uses some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integer
An integer is the number zero (), a positive natural number (, , , etc.) or a negative integer with a minus sign (−1, −2, −3, etc.). The negative numbers are the additive inverses of the corresponding positive numbers. In the language of mathematics, the set of integers is often denoted by the boldface or blackboard bold \mathbb. The set of natural numbers \mathbb is a subset of \mathbb, which in turn is a subset of the set of all rational numbers \mathbb, itself a subset of the real numbers \mathbb. Like the natural numbers, \mathbb is countably infinite. An integer may be regarded as a real number that can be written without a fractional component. For example, 21, 4, 0, and −2048 are integers, while 9.75, , and are not. The integers form the smallest group and the smallest ring containing the natural numbers. In algebraic number theory, the integers are sometimes qualified as rational integers to distinguish them from the more general algebraic integers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The mission of the IEEE is ''advancing technology for the benefit of humanity''. The IEEE was formed from the amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers in 1963. Due to its expansion of scope into so many related fields, it is simply referred to by the letters I-E-E-E (pronounced I-triple-E), except on legal business documents. , it is the world's largest association of technical professionals with more than 423,000 members in over 160 countries around the world. Its objectives are the educational and technical advancement of electrical and electronic engineering, telecommunications, computer engineering and similar disciplines. History Origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntax
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). There are numerous approaches to syntax that differ in their central assumptions and goals. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from Ancient Greek roots: "coordination", which consists of ''syn'', "together", and ''táxis'', "ordering". Topics The field of syntax contains a number of various topics that a syntactic theory is often designed to handle. The relation between the topics is treated differently in different theories, and some of them may not be considered to be distinct but instead to be derived from one another (i.e. word order can be seen as the result of movement rules derived from grammatical relations). Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)