|
Ivar Jacobson
Ivar Hjalmar Jacobson (; born September 2, 1939) is a Swedish computer scientist and software engineer, known as a major contributor to UML, Objectory, Rational Unified Process (RUP), aspect-oriented software development, and Essence. Biography Ivar Jacobson was born in Ystad, on September 2, 1939. He received his Master of Electrical Engineering degree at Chalmers Institute of Technology in Gothenburg in 1962. After his work at Ericsson, he formalized the language and method he had been working on in his PhD at the Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm in 1985 on the thesis "Language Constructs for Large Real Time Systems". After his master's degree, Jacobson joined Ericsson and worked in R&D on computerized switching systems AKE and AXE including PLEX. In April 1987, he started Objective Systems. A majority stake of the company was acquired by Ericsson in 1991, and the company was renamed Objectory AB. Jacobson developed the software method Object-Oriented Sof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
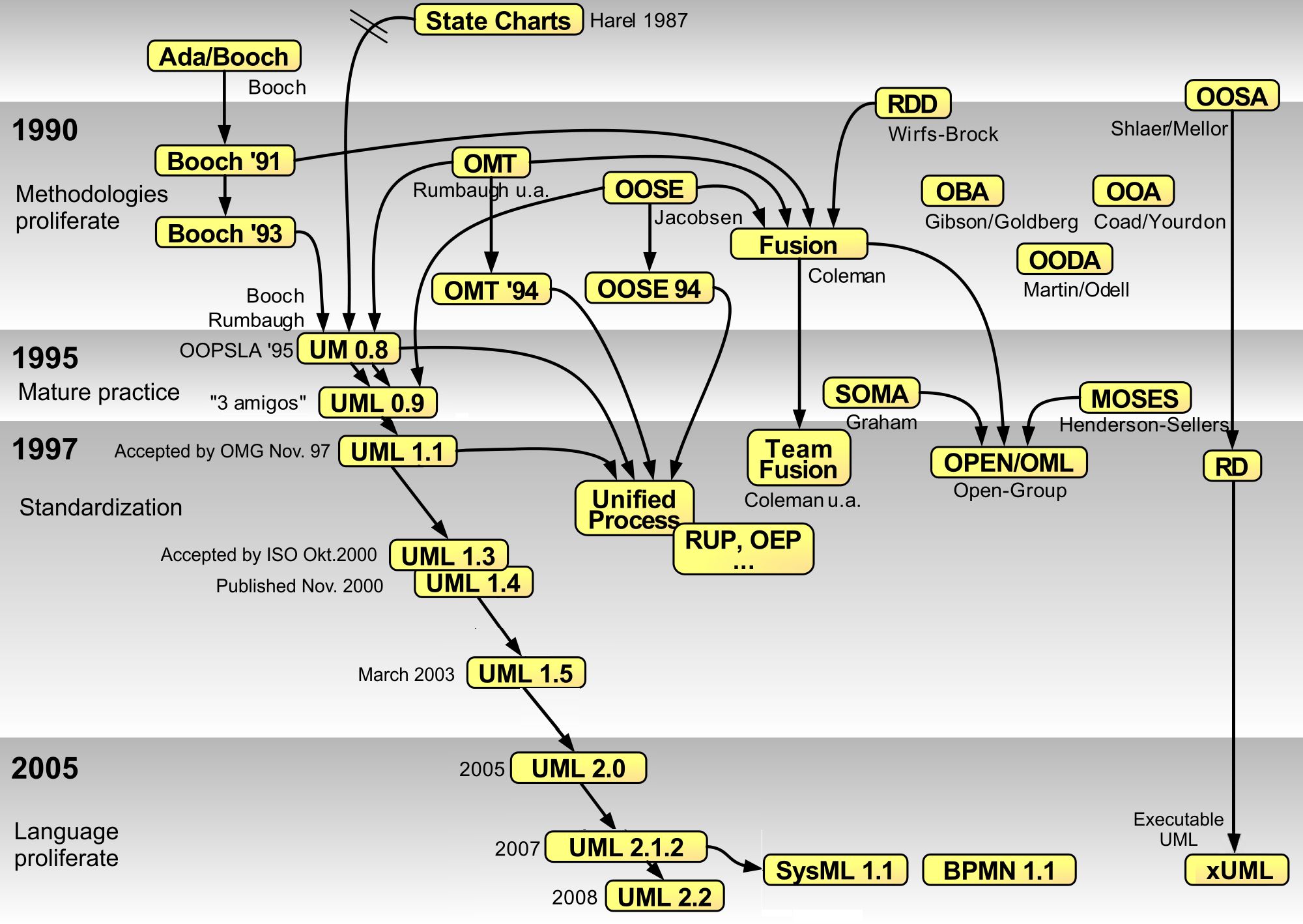
Unified Modeling Language
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose visual modeling language that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system. UML provides a standard notation for many types of diagrams which can be roughly divided into three main groups: behavior diagrams, interaction diagrams, and structure diagrams. The creation of UML was originally motivated by the desire to standardize the disparate notational systems and approaches to software design. It was developed at Rational Software in 1994–1995, with further development led by them through 1996. In 1997, UML was adopted as a standard by the Object Management Group (OMG) and has been managed by this organization ever since. In 2005, UML was also published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as the ISO/IEC 19501 standard. Since then the standard has been periodically revised to cover the latest revision of UML. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ystad
Ystad () is a town and the seat of Ystad Municipality, in Scania County, Sweden. Ystad had 18,350 inhabitants in 2010. The settlement dates from the 11th century and has become a busy ferryport, local administrative centre, and tourist attraction. Etymology In 1285, the town's name was written ''Ystath''. Its original meaning is not fully understood, but the ''y'' probably is related to an old word for the yew tree, while ''stad'' means ''town'' or ''place''. History After the time of Absalon, Bishop of Roskilde and Archbishop of Lund, peace was brought to the area in the 11th century, fishing families settled at the mouth of the river Vassa as herring fishing became the main source of trade. Ystad was not mentioned in documents until 1244, in a record of King Eric's visit to the town with his brother, Abel. A Franciscan monastery, ''Gråbrödraklostret'', was founded in 1267, and Ystad joined the Hanseatic League in the 14th century. The charter of 1599 gave the town t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Engineer
Software engineering is a branch of both computer science and engineering focused on designing, developing, testing, and maintaining software applications. It involves applying engineering principles and computer programming expertise to develop software systems that meet user needs. The terms '' programmer'' and ''coder'' overlap ''software engineer'', but they imply only the construction aspect of a typical software engineer workload. A software engineer applies a software development process, which involves defining, implementing, testing, managing, and maintaining software systems, as well as developing the software development process itself. History Beginning in the 1960s, software engineering was recognized as a separate field of engineering. The development of software engineering was seen as a struggle. Problems included software that was over budget, exceeded deadlines, required extensive debugging and maintenance, and unsuccessfully met the needs of consume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications. The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital computers in the mid-20th century. Early programs were written in the machine language specific to the hardware. The introduction of high-level programming languages in 1958 allowed for more human-readable instructions, making software development easier and more portable across different computer architectures. Software in a programming language is run through a compiler or Interpreter (computing), interpreter to execution (computing), execute on the architecture's hardware. Over time, software has become complex, owing to developments in Computer network, networking, operating systems, and databases. Software can generally be categorized into two main types: # operating systems, which manage hardware resources and provide services for applicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Component
A software component is a modular unit of software that encapsulates specific functionality. The desired characteristics of a component are reusability and maintainability. Value Components allow software development to assemble software with reliable parts rather than writing code for every aspect; allowing for implementation to be more like factory assembly than custom building. Attributes Desirable attributes of a component include but are not limited to: * Cohesive encapsulates related functionality * Reusable * Robust * ''Substitutable'' can be replaced by another component with the same interface * Documented * Tested Third-party Some components are built in-house by the same organization or team building the software system. Some are third-party, developed elsewhere and assembled into the software system. Component-based software engineering For large-scale systems, component-based development encourages a disciplined process to manage comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic country by both area and population, and is the List of European countries by area, fifth-largest country in Europe. Its capital and largest city is Stockholm. Sweden has a population of 10.6 million, and a low population density of ; 88% of Swedes reside in urban areas. They are mostly in the central and southern half of the country. Sweden's urban areas together cover 1.5% of its land area. Sweden has a diverse Climate of Sweden, climate owing to the length of the country, which ranges from 55th parallel north, 55°N to 69th parallel north, 69°N. Sweden has been inhabited since Prehistoric Sweden, prehistoric times around 12,000 BC. The inhabitants emerged as the Geats () and Swedes (tribe), Swedes (), who formed part of the sea-faring peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The UK includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and most of List of islands of the United Kingdom, the smaller islands within the British Isles, covering . Northern Ireland shares Republic of Ireland–United Kingdom border, a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the UK is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. It maintains sovereignty over the British Overseas Territories, which are located across various oceans and seas globally. The UK had an estimated population of over 68.2 million people in 2023. The capital and largest city of both England and the UK is London. The cities o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Rumbaugh
James E. Rumbaugh (born August 22, 1947) is an American computer scientist and object-oriented methodologistBiography on InformIT Accessed 22 Jan 2010. who is best known for his work in creating the Object Modeling Technique (OMT) and the Unified Modeling Language (UML). Biography Born in , Rumbaugh received a B.S. in |
Grady Booch
Grady Booch (born February 27, 1955) is an American software engineer, best known for developing the Unified Modeling Language (UML) with Ivar Jacobson and James Rumbaugh. He is recognized internationally for his innovative work in software architecture, software engineering, and collaborative development environments. Education Booch earned his bachelor's degree in 1977 from the United States Air Force Academy and a master's degree in electrical engineering in 1979 from the University of California, Santa Barbara. Career and research Booch worked at Vandenberg Air Force Base after he graduated. He started as a project engineer and later managed ground-support missions for the space shuttle and other projects. After he gained his master's degree he became an instructor at the Air Force Academy. Booch served as Chief Scientist of Rational Software Corporation from its founding in 1981 through its acquisition by IBM in 2003, where he continued to work until March 2008. After thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Objectory AB
Objectory Systems was a software company based in Sweden that was instrumental in the development of Object-oriented program design. Founded in 1987 by Ivar Jacobson, the company developed Objectory, an object-oriented development method which was an extension of what is known as the '' Ericsson Approach'', a modeling language developed at Ericsson. This language featured state charts with activity diagrams, as well as sequence diagrams. In 1991, Ericsson purchased a substantial amount of the stake in Objectory Systems. As a result, Objectory Systems became known as Objectory AB — a subsidiary of Ericsson. In 1995, Rational Software Corporation acquired the subsidiary. See also * Rational Software *Object-oriented software engineering External linksWhat You Didn’t Know About RUPa Jacobson presentation about RUP — Rational Unified Process The rational unified process (RUP) is an iterative software development process framework created by the Rational Software ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PLEX (programming Language)
PLEX (Programming Language for EXchanges) is a special-purpose, concurrent, real-time programming language. The proprietary PLEX language is closely tied to the architecture of Ericsson's AXE telephone exchanges which it was designed to control. PLEX was developed by Göran Hemdahl at Ericsson in the 1970s, and it has been continuously evolving since then. PLEX was described in 2008 as "a cross between Fortran and a macro assembler." The language has two variants: ''Plex-C'' used for the AXE Central Processor (CP) and ''Plex-M'' used for Extension Module Regional Processors (EMRP). Ericsson started a project in the mid-1980s to create a successor language, which resulted in Erlang. According to co-creator Joe Armstrong, "Erlang was heavily influenced by PLEX and the AXE design." Erlang did not replace PLEX, but was used alongside it. Execution model A system is divided into separately compiled and loaded units of code called "blocks." A block waits for one or more signal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AXE Telephone Exchange
The AXE telephone exchange is a product line of circuit switched digital telephone exchanges manufactured by Ericsson, a Swedish telecom company. It was developed in 1974 by Ellemtel, a research and development subsidiary of Ericsson and Televerket. The first system was deployed in 1976. AXE is not an acronym, but an Ericsson product code. The AXE is the digital successor to the AKE analogue telephone exchange and ARF/ARM family of crossbar switches. The design is modular with an APZ dual processor running in sync mode, an APT switching part and an APG I/O part. It is used for connecting local landline A landline is a physical telephone connection that uses metal wires or optical fiber from the subscriber's premises to the network, allowing multiple phones to operate simultaneously on the same phone number. It is also referred to as plain old ...s, operating mobile networks (Digital AMPS, TDMA, GSM, Code division multiple access, CDMA, W-CDMA, Personal Digital Cellular, PDC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |